This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Contents
- System requirements
- Getting Started
- Welcome Screen
- Basic Features
- The Menus
- Network Management
- The Network Overview Window
- Import Fixed-Format Network Files
- Import Networks from Unformatted Table Files
- Import Networks from Public Databases
- Create a New Network Manually
- Creating Nested Networks
- Visualization of Nested Networks
- SIF Format
- NNF
- GML Format
- XGMML Format
- SBML (Systems Biology Markup Language) Format
- BioPAX (Biological PAthways eXchange) Format
- PSI-MI Format
- GraphML
- Delimited Text Table and Excel Workbook
- Cytoscape.js JSON
- Import Data Table Files
- Legacy Cytoscape Attributes Format
- Import Data Table from Public Databases
- Ontology and Annotation File Format
- Default List of Ontologies
- Gene Association File
- Import Ontology and Annotation
- Column Formulas
- Introduction
- Operators
- Supported Functions
- Pitfalls
- The Formula Builder
- A Note for App Writers
- Search Bar
- Filters
- The Select Menu
- Basic Network Navigation
- Automatic Layout Algorithms
- Edge Bend and Automatic Edge Bundling
- Manual Layout
- What are Styles?
- Introduction to the Style interface
- Introduction to Style
- Images, Charts and Gradients
-
Styles Tutorials
- Tutorial 1: Creating a Basic Style and Setting Default Values
- Tutorial 2: Creating a New Style with a Discrete Mapping
- Tutorial 3: Creating a New Style with a Continuous Mapping
- Tutorial 4: Setting Automatic Values to a Discrete Mapping
- Tutorial 5: Using Images in Styles
- Tutorial 6: Creating Node Charts
- Advanced Topics
- Managing Styles
- What are apps?
- Installing Apps
- Managing your Installed Apps
- Merge Networks
- Merge Tables
- Network Analysis
- Subnetwork Creation
- Managing Properties
- Managing Bookmarks
- Managing Proxy Servers
- Managing Group View
- Adding and Removing Links
- What are Panels?
- Basic Usage
- What is Level of Detail (LOD)?
- Publish Your Visualizations
- What is Cytoscape.js?
- Data Exchange between Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js
- Build Your Own Web Application with Cytoscape.js
- Programmatic Access to Cytoscape Features
- Topics
- Background
Cytoscape @version@ User Manual
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Copyright (c) 2001-2015 The Cytoscape Consortium
Introduction
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
This manual describes the installation and use of Cytoscape. For a more thorough understanding of Cytoscape and its ecosystem, we highly recommend reading the Welcome Letter accessible on the http://cytoscape.org website.
Launching Cytoscape
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
System requirements
The system requirements for Cytoscape depend on the size of the networks you want to load, view and manipulate.
Note that as of Cytoscape v3.2, networks are loaded faster and in less memory than with previous versions. While this is good news, networks created on v3.2 on a given memory configuration (e.g., 1GB) may not be loadable by prior Cytoscape versions on the same memory configuration.
|
Small Network Visualization |
Large Network Analysis/Visualization |
Processor |
1GHz |
As fast as possible, with multiple cores |
Memory |
512MB |
2GB+ |
Graphics Card |
Integrated video |
High-end graphics Card |
Monitor |
XGA (1024X768) |
Wide or Dual Monitor |
Specific system requirements, limitations, and configuration options apply to each platform, as described in the Release Notes available on the http://cytoscape.org website.
Getting Started
Install Java
Cytoscape requires Java 8 or later.
- While Cytoscape versions prior to v3.2 run on Java 6, Oracle and other JVM suppliers have dropped Java 6 support. Consequently, Cytoscape v3.2 and later don't support Java 6 either. With v3.3, we have also dropped support for Java 7 for the same reason.
- We recommend a 64 bit Java Runtime Environment (JRE). While Cytoscape runs with 32 bit Java versions, using a 64 bit Java allows the largest networks to be loaded and enables the fastest network processing. For Windows, the default JRE download provided at java.com is 32 bits regardless of the Windows version. While Cytoscape will run with a 32 bit JRE, it will be limited to loading only small networks. We recommend downloading and installing a 64 bit JRE.
- We currently recommend only Java 8.
For additional information, select the Release Notes button on the Cytoscape web site (http://cytoscape.org).
Install Cytoscape
Downloading and installing
There are a number of options for downloading and installing Cytoscape. See the download page at the http://cytoscape.org website for all options.
- Automatic installation packages exist for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux platforms -- best for most users.
- You can install Cytoscape from a compressed archive distribution.
- You can build Cytoscape from the source code.
You can check out the latest and greatest software from our Git repository.
Cytoscape installations (regardless of platform) containing the following files and directories:
File/Directory |
Description |
p/Cytoscape_v3.3.0 |
Cytoscape program files, startup scripts, and default location for session files |
p/Cytoscape_v3.3.0/Cytoscape.vmoptions |
Cytoscape memory configuration settings |
p/Cytoscape_v3.3.0/sampleData |
Preset networks as described in the embedded README.txt file |
p/Cytoscape_v3.3.0/framework |
Cytoscape program files |
p/Cytoscape_v3.3.0/apps |
Cytoscape core app program files |
u/CytoscapeConfiguration |
Cytoscape properties and program cache files |
u/CytoscapeConfiguration/cytoscape3.props |
Cytoscape configuration settings |
The p/ directory signifies the program directory, which varies from platform to platform. For Cytoscape to work properly, all files should be left in the directory in which they were unpacked. The core Cytoscape application assumes this directory structure when looking for the various libraries needed to run the application.
The u/ directory signifies the user's home directory, which varies from user to user and from platform to platform. To change the user home directory from the default, one can set the Java environment variable user.home to the desired directory -- this is useful when Cytoscape is installed on a workstation, but the home directory is stored on a central file server. user.home can be set by adding the following option to the Cytoscape.vmoptions file or the _JAVA_OPTIONS environment variable, substituting the desired path as appropriate:
-Duser.home=/path/to/desired/home
Your operating system may have other mechanisms for setting environment variables -- see your operating system documentation for further details.
A quick note on upgrading your Cytoscape installation
If you have a previous Cytoscape installation you have two options:
Starting with a clean slate. For this you should delete your previous installation directory and the CytoscapeConfiguration directory (see below for the location of this directory).
Just keep what you have and simply pick a distinct, new directory for installation. In the unlikely event that you should encounter any problem, delete the .props files in your CytoscapeConfiguration directory. If that doesn't help try deleting the CytoscapeConfiguration directory. This latter step will cause you to lose all of the apps that you have installed via the App Store, so only do that if you are having problems or if you don't mind reinstalling your apps. The core apps will not be affected by this step.
Launch the application
As with any application, launch Cytoscape by double-clicking on the icon created by the installer, by running cytoscape.sh from the command line (Linux or Mac OS X) or by double-clickinging cytoscape.bat or the Program Launch icon (Windows).
After launching Cytoscape a window will appear that looks like this:
If your Cytoscape window does not resemble this, further configuration may be required. Consult the Release Notes available on the http://cytoscape.org website.
Note on Memory Consumption
For most regular users, Cytoscape will estimate and reserve the proper amount of memory. An incorrect estimate may result in Cytoscape hanging at startup or Cytoscape unable to load your network. Unless Cytoscape fails to start or open your network, it has likely estimated the available memory correctly, and you can continue to the Quick Tour. If Cytoscape misjudges the memory size or can't allocate enough memory, it could be that you're running with a 32 bit JRE and could get better results by installing a 64 bit JRE -- see the Install Java section above.
When Cytoscape starts, it displays the current memory usage in the lower right corner of the main interface. You can click on the Memory button at any time to access an option to Free Unused Memory. While most users won't need to use this option, it can be useful for users who have multiple large networks loaded.
Overall Memory Size for Cytoscape
By default, Cytoscape uses an estimate for initial and maximum memory allocation based on your operating system, system architecture (32 or 64 bit), and installed memory. You can change Cytoscape's initial and/or maximum memory size by editing the Cytoscape.vmoptions file, which resides in the same directory as the Cytoscape executable. The file contains one option per line, with each line terminated by a linefeed, and an extra linefeed at the end of the file. Note that for the MacOS platform, the situation is slightly different -- if you are launching Cytoscape by clicking on the Cytoscape icon, you must edit the .../Cytoscape.app/Contents/vmoptions.txt file instead. To access this in Finder, you will need to right-click the Cytoscape app icon and select "Show Package Contents", which will display the Contents subdirectory that contains vmoptions.txt.
For example, if you want Cytoscape to initially allocate 2GB of memory and use up to a maximum of 4GB, edit the Cytoscape.vmoptions file to contain the following lines (... do not forget the linefeed at the end of each line, and an extra linefeed at the end of the file!):
-Xms2GB
-Xmx4GB
Stack Size
There is one more option related to memory allocation. Some of the functions in Cytoscape use larger stack space (a temporary memory for some operations, such as layout). Since this value is set independently from the values above, sometimes layout algorithms fail due to an out of memory error. To avoid this, you can set a larger heap size for Cytoscape tasks by using the taskStackSize option in the cytoscape3.props file (located in the CytoscapeConfiguration directory). This can be edited within Cytoscape using the Preferences Editor (Edit-Preferences-Properties...) - look for taskStackSize. The value should be specified in bytes.
Command Line Arguments
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
usage: cytoscape.{sh|bat} [OPTIONS]
-h,--help Print this message.
-v,--version Print the version number.
-s,--session <file> Load a cytoscape session (.cys) file.
-N,--network <file> Load a network file (any format).
-P,--props <file> Load cytoscape properties file (Java properties
format) or individual property: -P name=value.
-V,--vizmap <file> Load vizmap properties file (Cytoscape VizMap
format).
-S,--script <file> Execute commands from script file.
-R,--rest <port> Start a rest service.Any file specified for an option may be specified as either a path or as a URL. For example you can specify a network as a file (assuming that myNet.sif exists in the current working directory): cytoscape.sh -N myNet.sif.
Note: if there are spaces in the file path, be sure to put quotes around it: cytoscape.bat -N "C:\Program Files\Cytoscape\sampleData\galFiltered.sif".
Or you can specify a network as a URL: cytoscape.sh -N http://example.com/myNet.sif.
Argument |
Description |
-h,--help |
This flag generates the help output you see above and exits. |
-v,--version |
This flag prints the version number of Cytoscape and exits. |
-s,--session <file> |
This option specifies a session file to be loaded. Since only one session file can be loaded at a given time, this option may only specified once on a given command line. The option expects a .cys Cytoscape session file. It is customary, although not necessary, for session file names to contain the .cys extension. |
-N,--network <file> |
This option is used to load all types of network files. SIF, GML, and XGMML files can all be loaded using the -N option. You can specify as many networks as desired on a single command line. |
-P,--props <file> |
This option specifies Cytoscape properties. Properties can be specified either as a properties file (in Java's standard properties format), or as individual properties. To specify individual properties, you must specify the property name followed by the property value where the name and value are separated by the '=' sign. For example to specify the defaultSpeciesName: cytoscape.sh -P defaultSpeciesName=Human. If you would like to include spaces in your property, simply enclose the name and value in quotation marks: cytoscape.sh -P "defaultSpeciesName=Homo Sapiens". The property option subsumes previous options -noCanonicalization, -species, and -bioDataServer. Now it would look like: cytoscape.sh -P defaultSpeciesName=Human -P noCanonicalization=true -P bioDataServer=myServer. |
-V,--vizmap <file> |
This option specifies a Style file. |
-S,--script <file> |
This option executes commands from a specifed Cytoscape script file. |
-R,--rest <port> |
This option starts a Cytoscape REST service on the specified port. |
All options described above (except for starting a REST service) can be accessed from the menu once Cytoscape is running.
Quick Tour of Cytoscape
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Welcome Screen
When you start Cytoscape, you can access basic functions from the Welcome Screen:
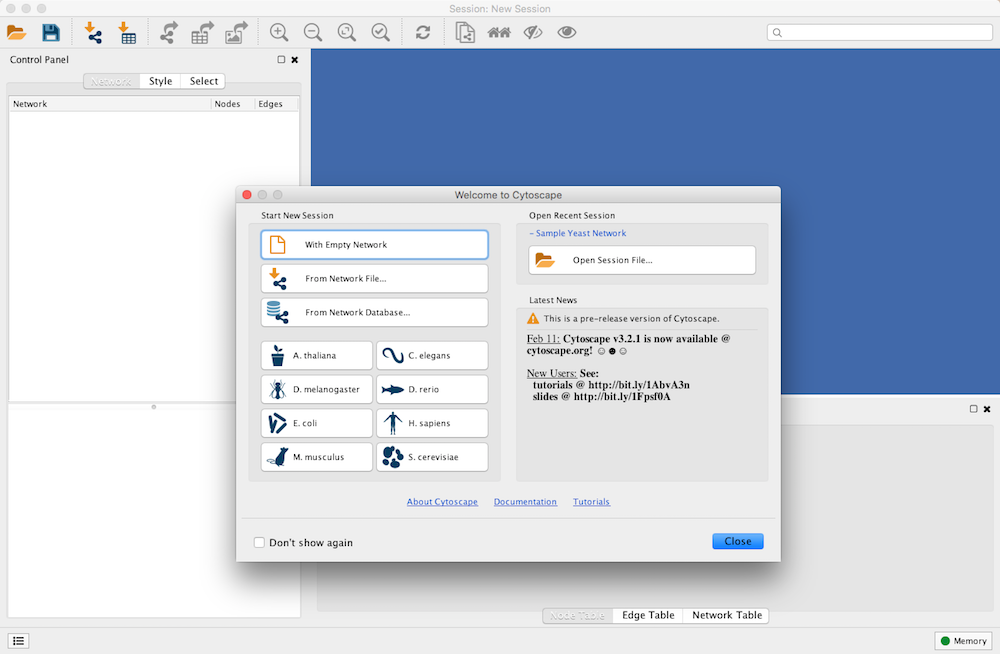
The Welcome Screen is designed to access commonly used features of Cytoscape including:
- Create new network
- Import network
- From file
- From public database
- Import interactome for model organisms
- Open recently used session file
Also, a news panel always display latest information for users. For information on user privacy, see the Cytoscape Privacy Policy.
Basic Features
When a network is loaded, Cytoscape will look similar to the image below:
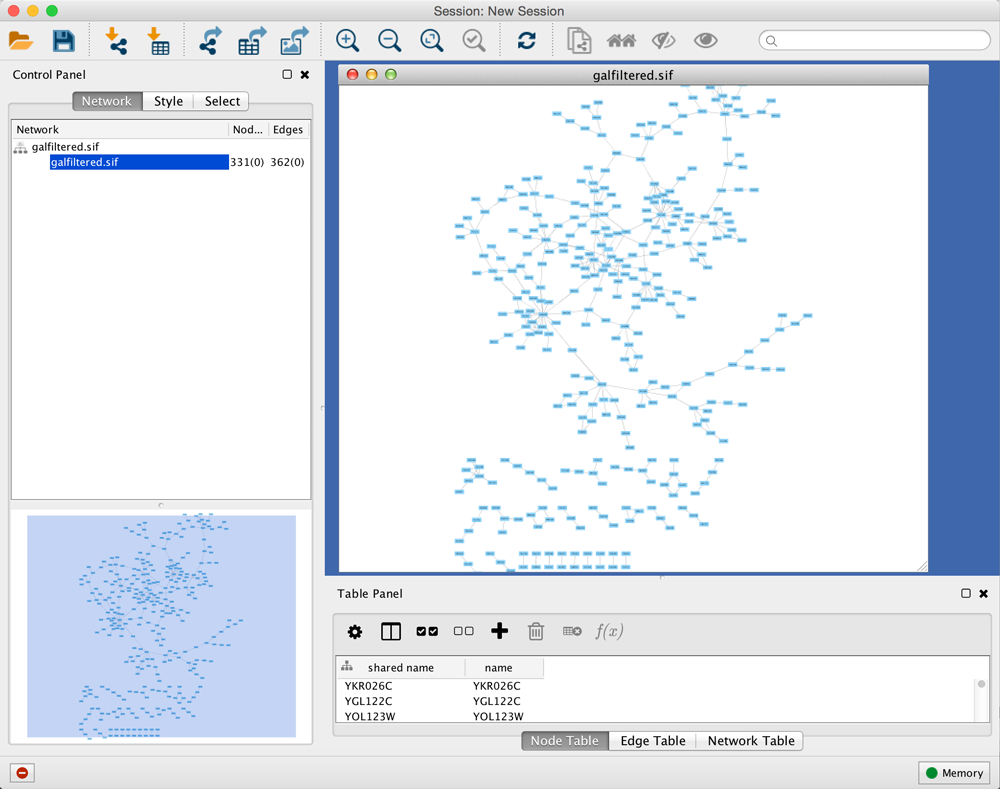
Most functionalities are self-explanatory, but we'll go through a concise explanation for clarity. The main window here has several components:
- The Menu Bar at the top (see below for more information about each menu).
- The Tool Bar, which contains icons for commonly used functions. These functions are also available via the menus. Hover the mouse pointer over an icon and wait momentarily for a description to appear as a tooltip.
- The Network Panel (Network tab of the Control Panel, top left). This contains an optional network overview pane (shown at the bottom left).
- The main Network View Window, which displays the network.
- The Table Panel (bottom right panel), which displays columns of selected nodes and edges and enables you to modify the values of column data.
The Network Panel and Table Panel are dockable tabbed Panels. You can undock any of these panels by clicking on the Float Window control  in the upper-right corner of the CytoPanel. This is useful when you want assign the network panel as much screen space as possible. To dock the window again, click the Dock Window icon
in the upper-right corner of the CytoPanel. This is useful when you want assign the network panel as much screen space as possible. To dock the window again, click the Dock Window icon  . Clicking the Hide Panel icon
. Clicking the Hide Panel icon  will hide the panel; this can be shown again by choosing View → Show and selecting the relevant panel.
will hide the panel; this can be shown again by choosing View → Show and selecting the relevant panel.
If you click this control, for example on the Table Panel, you will now have two Cytoscape windows, the main window, and a new window labeled Table Panel, similar to the one shown below. A popup will be displayed when you put the mouse pointer on a cell.
Note that Table Panel now has a Dock Window control. If you click this control, the window will dock onto the main window. For more information on the panels in Cytoscape, see the Panels section.
Network Editing
Cytoscape also has an edit functionality that enables you to build and modify networks interactively within the network canvas. To edit a network, just right-click on the open space of network window, select the menu item Add → Node, a new node will be added to the canvas. To add an edge, right click on a node, choose the menu item Edit → Add Edge. Then select the target node, a new edge will be added between the two nodes. In a similar way annotation objects can be added; pictures, shapes or textboxes; much like in MS PowerPoint or similar software. Detailed information on network editing can be found in the Editing Networks section.
The Menus
File
The File menu contains most basic file functionality: File → Open for opening a Cytoscape session file; File → New for creating a new network, either blank for editing, or from an existing network; File → Save for saving a session file; File → Import for importing data such as networks and data; and File → Export for exporting data and images. File → Export → Network View as Graphics lets you export the network in either JPEG, PDF, PNG, Post Script or SVG format.
File → Recent Session will list recently opened session files for quick access. File → Run allows you to specify a Cytoscape script file to run, and File → Print Current Network... allows printing.
Edit
The Edit menu contains Cut, Copy and Paste functions, as well as Undo and Redo functions which undo and redo edits made in the Table Panel, the Network Editor and to layout.
There are also options for creating and destroying views (graphical representations of a network) and networks (the raw network data – not yet visualized), as well as an option for deleting selected nodes and edges from the current network. All deleted nodes and edges can be restored to the network via Edit → Undo.
There are also other editing options; Remove Duplicated Edges will delete edges that are complete duplicates, keeping one edge, Remove Self-Loops removes edges that have the same source and target node, and Delete Selected Nodes and Edges... deletes a selected subset of the network. Rename Network... allows you to rename the currently selected network.
Editing preferences for properties and apps is found under Edit → Preferences → Properties.... More details on how to edit preferences can be found here.
View
The View menu allows you to display or hide the Control Panel, Table Panel, Tool Panel and the Result Panel. It also provides the control of other view-related functionality.
Select
The Select menu contains different options for selecting nodes and edges.
Layout
The Layout menu has an array of features for visually organizing the network. The features in the top portion of the network (Bundle Edges, Clear Edge Bends, Rotate, Scale, Align and Distribute) are tools for manipulating the network visualization. The bottom section of the menu lists a variety of layout algorithms which automatically lay a network out.
Apps
The Apps menu gives you access to the App Manager (Apps → App Manager) for managing (install/update/delete) your apps and may have options added by apps that have been installed. Depending on which apps are loaded, the apps that you see may be different than what appear here. The below picture shows a Cytoscape installation without installed apps.
Note: A list of available Cytoscape apps with descriptions is available online at: http://apps.cytoscape.org |
In previous versions of Cytoscape, apps were called plugins and served a similar function.
Tools
The Tools menu contains advanced features like the Command Line Dialog, Network Analyzer, Network Merge and Workflow.
Help
The Help menu allows you to launch the online help viewer and browse the table of contents for this manual (Contents).
The Citations option displays the main literature citation for Cytoscape, as well as a list of literature citations for installed apps. The list will be different depending on the set of apps you have installed.
The Help menu also allows you to connect directly to Cytoscape Help Desk and the Bug Report interface.
Network Management
Cytoscape allows multiple networks to be loaded at a time, either with or without a view. A network stores all the nodes and edges that are loaded by the user and a view displays them.
An example where a number of networks have been loaded is shown below:
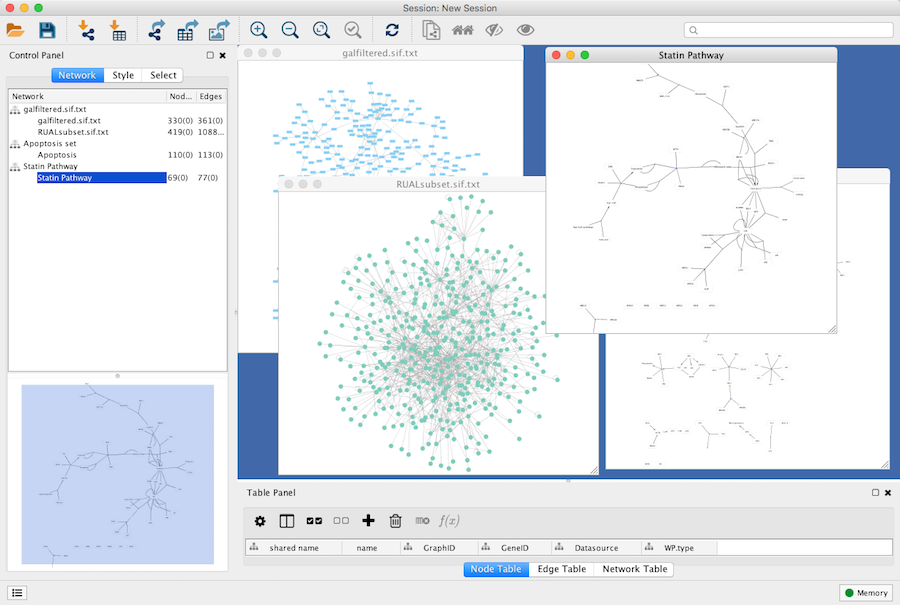
The network manager (in Control Panel) shows the networks that are loaded. Clicking on a network here will make that view active in the main window, if the view exists. Each network has a name and size (number of nodes and edges), which are shown in the network manager. If a network is loaded from a file, the network name is the name of the file.
Some networks are very large (thousands of nodes and edges) and can take a long time to display. For this reason, a network in Cytoscape may not contain a "view". Networks that have a view are in normal black font and networks that don’t have a view are highlighted in red. You can create or destroy a view for a network by right-clicking the network name in the network manager or by choosing the appropriate option in the Edit menu. You can also destroy previously loaded networks this way.
Certain operations in Cytoscape will create new networks. If a new network is created from an old network, for example by selecting a set of nodes in one network and copying these nodes to a new network (via the File → New → Network option), it will be shown immediately follows the network that it was derived from.
The available network views are also arranged as multiple overlapping windows in the network view window. You can maximize, minimize, and destroy network views by using the normal window controls for your operating system.
Arrange Network Windows
When you work on multiple networks, you can arrange the network view windows under View → Arrange Network Windows.
Vertical
Grid
The Network Overview Window
The network overview window shows an overview (or "bird’s eye view") of the network. It can be used to navigate around a large network view. The blue rectangle indicates the portion of the network currently displayed in the network view window, and it can be dragged with the mouse to view other portions of the network. Zooming in will cause the rectangle to appear smaller and vice versa.
Creating Networks
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
- Importing pre-existing, fixed-format network files.
- Importing pre-existing, unformatted text or Excel files.
- Importing data from from public databases.
- Creating an empty network and manually adding nodes and edges.
Import Fixed-Format Network Files
Network files can be specified in any of the formats described in the Supported Network Formats section. Networks are imported into Cytoscape through the File → Import → Network menu. The network file can either be located directly on the local computer, or found on a remote computer (in which case it will be referenced with a URL).
Load Networks from Local Computer
In order to load a network from a local file you can select File → Import → Network → File... or click on ![]() on the tool bar. Choose the correct file in the file chooser dialog and press Open. Some sample network files of different types have been included in the sampleData folder in Cytoscape.
on the tool bar. Choose the correct file in the file chooser dialog and press Open. Some sample network files of different types have been included in the sampleData folder in Cytoscape.
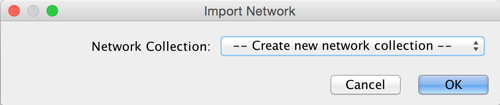
After you choose a network file, another dialog will pop up. Here, you can choose either to create a new network collection for the new network, or load the new network into an existing network collection. When you choose the latter, make sure to choose the right mapping column to map the new network to the existing network collection.
Network files in SIF, GML, and XGMML formats may also be loaded directly from the command line using the –N option.
Load Networks from a Remote Computer (URL import)
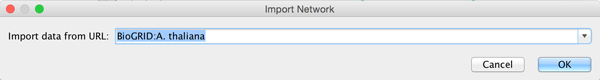
To load a network from a remote file, you can select File → Import → Network → URL.... In the import network dialog, insert the appropriate URL, either manually or using URL bookmarks. Bookmarked URLs can be accessed by clicking on the arrow to the right of the text field (see the Bookmark Manager in Preferences for more details on bookmarks). Also, you can drag and drop links from a web browser to the URL text box. Once a URL has been specified, click on the OK button to load the network.
Another issue for network import is the presence of firewalls, which can affect which files are accessible to a computer. To work around this problem, Cytoscape supports the use of proxy servers. To configure a proxy server, go to Edit → Preferences→ Proxy Settings.... This is further described in the Preferences section.
Import Networks from Unformatted Table Files
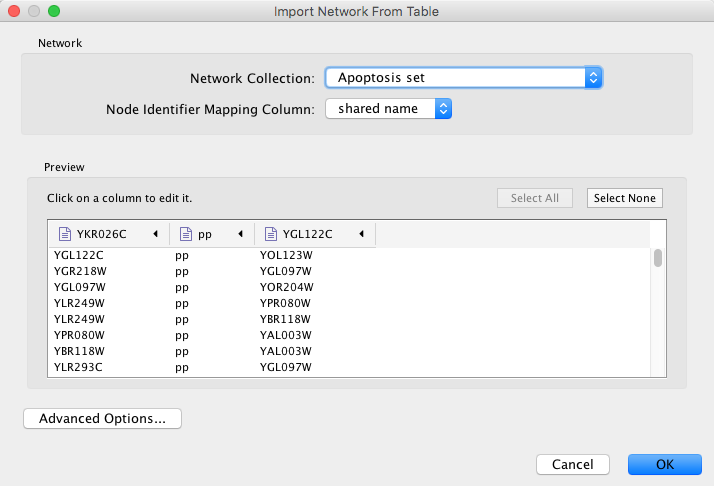
Cytoscape supports the import of networks from delimited text files and Excel workbooks using File → Import → Network → File.... An interactive GUI allows users to specify parsing options for specified files. The screen provides a preview that shows how the file will be parsed given the current configuration. As the configuration changes, the preview updates automatically. In addition to specifying how the file will be parsed, the user must also choose the columns that represent the source and target nodes as well as an optional edge interaction type.
Supported Files
The Import Network from Table function supports delimited text files and Microsoft Excel Workbooks. For Excel Workbooks with multiple sheets, one sheet can be selected for import at a time. The following is a sample table file:
source target interaction boolean data string data floating point data YJR022W YNR053C pp TRUE abcd12371 1.2344543 YER116C YDL013W pp TRUE abcd12372 1.2344543 YNL307C YAL038W pp FALSE abcd12373 1.2344543 YNL216W YCR012W pd TRUE abcd12374 1.2344543 YNL216W YGR254W pd TRUE abcd12375 1.2344543
The network table files should contain at least two columns for creating network with edges. If the file has only one column, the created network will not contain any edges. The interaction type is optional in this format. Therefore, a minimal network table looks like the following:
YJR022W YNR053C YER116C YDL013W YNL307C YAL038W YNL216W YCR012W YNL216W YGR254W
One row in a network table file represents an edge and its edge data columns. This means that a network file is considered a combination of network data and edge column data. A table may contain columns that aren't meant to be edge data. In this case, you can choose not to import those columns by clicking on the column header in the preview window. This function is useful when importing a data table like the following (1):

This data file is a tab-delimited text file and contains network data (interactions), edge data, and node data. To import network and edge data from this table, choose Unique ID A as source, Unique ID B as target, and Interactor types as interaction type. Next, turn off columns used for node data (Alternative ID A, species B, etc.). Other columns can be imported as edge data.
The network import function cannot import node table columns - only edge table columns. To import node table columns from this table, please see the Node and Edge Column Data section of this manual.
Note (1): This data is taken from the A merged human interactome datasets by Andrew Garrow, Yeyejide Adeleye and Guy Warner (Unilever, Safety and Environmental Assurance Center, 12 October 2006). Actual data files are available at http://wiki.cytoscape.org/Data_Sets/
Basic Operations
To import network from text/Excel tables, please follow these steps:
Select File → Import → Network → File... or click on
 on the tool bar.
on the tool bar. - Select a table file in the file chooser dialog.
- Define the interaction parameters by specifying which columns of data contain the Source Interaction, Target Interaction, and Interaction Type. Clicking on any column header will bring up the interface for selecting source, interaction and target:
- (Optional) Define edge table columns, if applicable. Network table files can have edge table columns in addition to network data.
- Click the OK button.
Import List of Nodes Without Edges
The table import feature supports lists of nodes without edges. If you select only a source column, it creates a network without interactions. This feature is useful with the node expansion function available from some web service clients. Please read the section Importing Networks from External Database for more detail.
Advanced Options
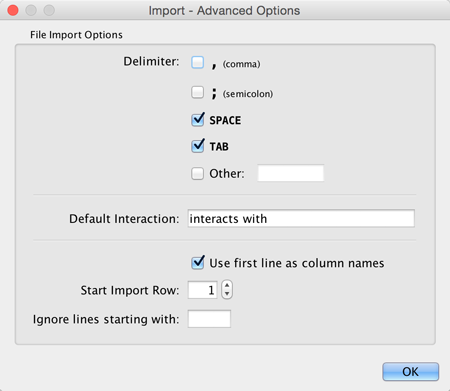
You can select several options by clicking the Advanced Options button in the main import interface.
- Delimiter: You can select multiple delimiters for text tables. By default, Tab and Space are selected as delimiters.
- Default Interaction
- Transfer first line as column names: Selecting this option will cause all edge columns to be named according to the first data entry in that column.
- Start Import Row: Set which row of the table to begin importing data from. For example, if you want to skip the first 3 rows in the file, set 4 for this option.
- Ignore lines starting with: Rows starting with this character will not be imported. This option can be used to skip comment lines in text files.
Modify Column Name/Type
In the Import Network from Table interface, you can change the name and data type of column by clicking on any column header:
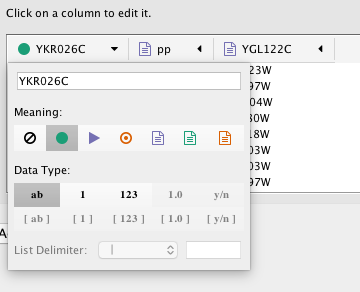
Column names and data types can be modified here.
- Modify Column Name - just enter a new column name.
- Modify Column Data Type - The following column data types are supported:
- String
- Boolean (True/False)
- Integer
- Floating Point
- List of (one of) String/Boolean/Integer/Floating Point
Cytoscape has a basic data type detection function that automatically suggests the column data type according to its entries. This can be overridden by selecting the appropriate data type from the radio buttons provided. For lists, a global delimiter must be specified (i.e., all cells in the table must use the same delimiter).
Import Networks from Public Databases
Cytoscape has a feature called Import Network from Public Databases. Users can access various kinds of databases through this function, File → Import → Network → Public Databases....
Getting Started
To get started, select File → Import → Network → Public Databases....
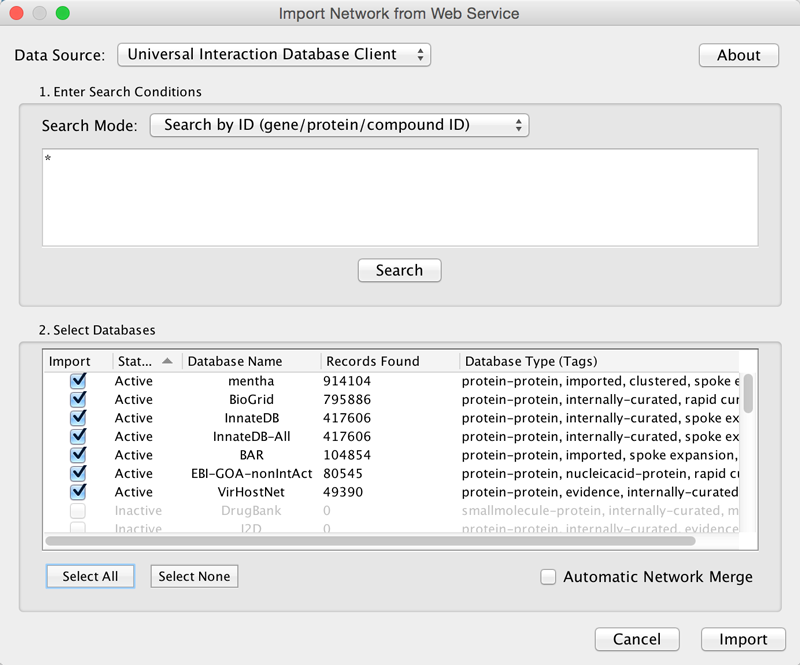
Example: Retrieving Protein-Protein Interaction Networks from Multiple Databases
Select File → Import → Network → Public Databases....
From the pull-down menu, select the Interaction databases Universal Client.
- Enter one or more search terms, such as BRCA1.
Click the Search button to start the search.
- Select databases from the hits. This selection will be saved as your default database list.
Click the Import button to import selected network data.
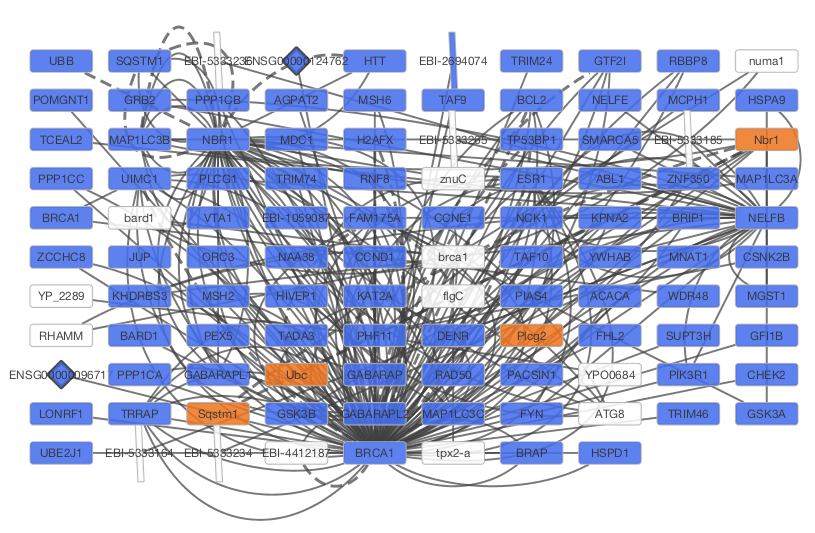
After confirming the download of interaction data, the network of BRCA1 will be imported and visualized.
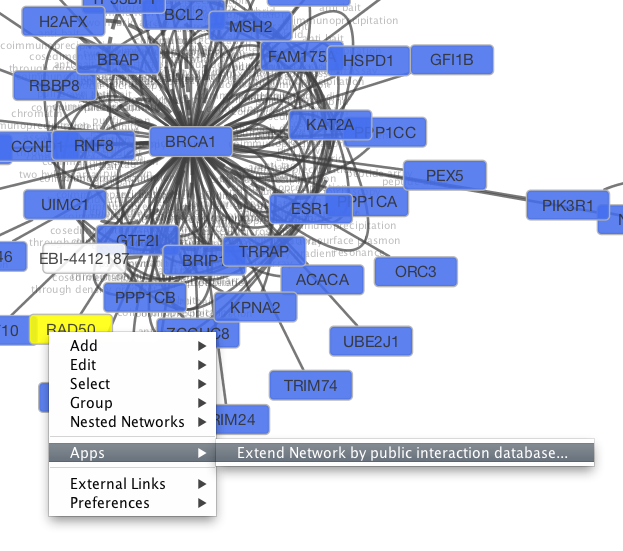
Tip: Expanding the Network: Several of the Cytoscape web services provide additional options in the node context menu. To access these options, right-click on a node and select Apps → Extend Network by public interaction database.... For example, in the screenshot, we have loaded the BRCA1 network from IntAct, and have chosen to merge this node's neighbors into the existing network.
PSICQUIC Options
PSICQUIC Web Service Client has three search modes:
- Search by ID
- Search by MIQL
- Search by Species
By default, search mode is set to Search by ID. You can search all databases by ID, such as gene symbol, Uniprot ID, or NCBI gene ID. If the search mode is set to MIQL, you can use MIQL for search. If you want to search interactions by keywords or specific functions, this is the powerful query language to filter the result. The last option is for importing all interactions for the species (i.e., interactome).
Create a New Network Manually
A new, empty network can also be created and nodes and edges manually added. To create an empty network, go to File → New → Network → Empty Network, and then manually add network components by right clicking on the network canvas or on a node.
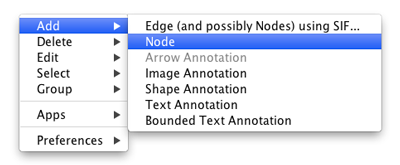
Adding a Node
To add a new node, right-click on an empty space of the network view panel. Select Add → Node item from the pop-up menu.
Adding an Edge
To add an edge to connect nodes, right-click on the source node. Select Edit → Add Edge from the pop-up menu. Next, click on the target node. The Images below show the two steps for drawing an edge between two nodes. You can abort the drawing of the edge by pressing Esc key. You can also select two or more nodes to connect and in the right-click menu select Add → Edges Connecting Selected Nodes to create edges connecting all selected nodes.
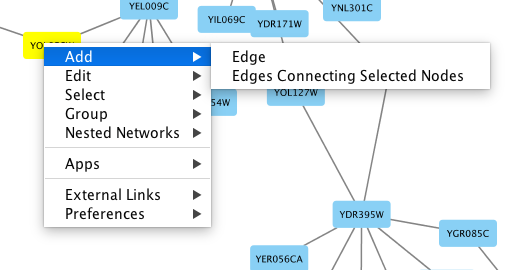
You can delete nodes and edges by selecting a number of nodes and edges, then selecting Edit → Cut. You can also delete selected nodes and edges from the Edit menu, under Edit → Delete Selected Nodes and Edges.... You can recover any nodes and edges deleted from a network by going to Edit → Undo.
Grouping nodes
Any number of nodes can be grouped together and displayed as either one group node or as the individual nodes. To create a group, select two or more nodes and right-click to select Group → Group Selected Nodes. You will be prompted to select a name for the group node. Once a group is created, you can use the right-click menu to collapse or expand the group. You can also quickly collapse/expand a group by double-clicking on the group node or any of its children to toggle back and forth.
Collapsed group
Expanded group
Adding Network Annotations
Annotations in the form of text, images or shapes can be added to the network canvas by right-clicking anywhere on the canvas and selecting one of the Annotation choices in the Add menu. You can add an image of your own, choose from a shapes library or add either plain or bounded text. Shapes and text are customizable and any added annotations can be edited from the right-click context menu.
Nested Networks
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Creating Nested Networks
There are currently two ways in which a user can create nested networks.
By importing a Nested Network Format (NNF) file. (See: NNF Network Format).
By manually constructing networks and assigning nested networks to individual nodes through the right-click node context menu. (See Nested Network Node Context Menu).
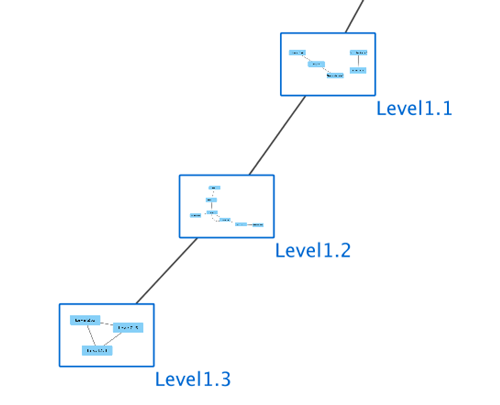
Visualization of Nested Networks
Nodes containing nested networks that are zoomed in sufficiently display an image for the nested network. If no current network view exists for the nested network the image will be a default icon, otherwise it will be a low-resolution rendering of the nested network's current layout.
Supported Network File Formats
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
- Simple interaction file (SIF or .sif format)
- Nested network format (NNF or .nnf format)
- Graph Markup Language (GML or .gml format)
- XGMML (extensible graph markup and modelling language).
- SBML
- BioPAX
- PSI-MI Level 1 and 2.5
- GraphML
- Delimited text
- Excel Workbook (.xls, .xlsx)
The SIF format specifies nodes and interactions only, while other formats store additional information about network layout and allow network data exchange with a variety of other network programs and data sources. Typically, SIF files are used to import interactions when building a network for the first time, since they are easy to create in a text editor or spreadsheet. Once the interactions have been loaded and network layout has been performed, the network may be saved to GML or XGMML format for interaction with other systems. All file types listed (except Excel) are text files and you can edit and view them in a regular text editor.
SIF Format
The simple interaction format is convenient for building a graph from a list of interactions. It also makes it easy to combine different interaction sets into a larger network, or add new interactions to an existing data set. The main disadvantage is that this format does not include any layout information, forcing Cytoscape to re-compute a new layout of the network each time it is loaded.
Lines in the SIF file specify a source node, a relationship type (or edge type), and one or more target nodes:
nodeA <relationship type> nodeB nodeC <relationship type> nodeA nodeD <relationship type> nodeE nodeF nodeB nodeG ... nodeY <relationship type> nodeZ
A more specific example is:
node1 typeA node2 node2 typeB node3 node4 node5 node0
The first line identifies two nodes, called node1 and node2, and a single relationship between node1 and node2 of type typeA. The second line specifies three new nodes, node3, node4, and node5; here "node2" refers to the same node as in the first line. The second line also specifies three relationships, all of type typeB and with node2 as the source, with node3, node4, and node5 as the targets. This second form is simply shorthand for specifying multiple relationships of the same type with the same source node. The third line indicates how to specify a node that has no relationships with other nodes. This form is not needed for nodes that do have relationships, since the specification of the relationship implicitly identifies the nodes as well.
Duplicate entries are ignored. Multiple edges between the same nodes must have different edge types. For example, the following specifies two edges between the same pair of nodes, one of type xx and one of type yy:
node1 xx node2 node1 xx node2 node1 yy node2
Edges connecting a node to itself (self-edges) are also allowed:
node1 xx node1
Every node and edge in Cytoscape has a name column. For a network defined in SIF format, node names should be unique, as identically named nodes will be treated as identical nodes. The name of each node will be the name in this file by default (unless another string is mapped to display on the node using styles). This is discussed in the section on Styles. The name of each edge will be formed from the name of the source and target nodes plus the interaction type: for example, sourceName (edgeType) targetName.
The tag <edgeType> can be any string. Whole words or concatenated words may be used to define types of relationships, e.g. geneFusion, cogInference, pullsDown, activates, degrades, inactivates, inhibits, phosphorylates, upRegulates, etc.
Some common interaction types used in the Systems Biology community are as follows:
pp .................. protein – protein interaction pd .................. protein -> DNA (e.g. transcription factor binding upstream of a regulating gene.)
Some less common interaction types used are:
pr .................. protein -> reaction rc .................. reaction -> compound cr .................. compound -> reaction gl .................. genetic lethal relationship pm .................. protein-metabolite interaction mp .................. metabolite-protein interaction
Delimiters
Whitespace (space or tab) is used to delimit the names in the simple interaction file format. However, in some cases spaces are desired in a node name or edge type. The standard is that, if the file contains any tab characters, then tabs are used to delimit the fields and spaces are considered part of the name. If the file contains no tabs, then any spaces are delimiters that separate names (and names cannot contain spaces).
If your network unexpectedly contains no edges and node names that look like edge names, it probably means your file contains a stray tab that's fooling the parser. On the other hand, if your network has nodes whose names are half of a full name, then you probably meant to use tabs to separate node names with spaces.
Networks in simple interactions format are often stored in files with a .sif extension, and Cytoscape recognizes this extension when browsing a directory for files of this type.
NNF
The NNF format is a very simple format that unlike SIF allows the optional assignment of single nested network per node. No other node columns can be specified. There are only 2 possible line formats:
- A node "node" contained in a "network:"
network node
- 2 nodes linked together contained in a network:
network node1 interaction node2
If a network name (first entry on a line) appeared previously as a node name (in columns 2 or 4), the network will be nested in the node with the same name. Also, if a name that has been previously defined as a network (by being listed in the first column), later appears as a node name (in columns 2 or 4), the previously defined network will be nested in the node with the same name. In summary: any time a name is used as both, a network name , and a node name, this implies that the network will be nested in the node of the same name. Additionally comments may be included on all lines. Comments start with a hash mark '#' and continue to the end of a line. Trailing comments (after data lines) and entirely blank lines anywhere are also permissible. Please note that if you load multiple NNF files in Cytoscape they will be treated like a single, long concatenated NNF file! If you need to embed spaces, tabs or backslashes in a name, you must escape it by preceding it with a backslash, so that, e.g. an embedded backslash becomes two backslashes, an embedded space a backslash followed by a space etc.
Examples
Example 1
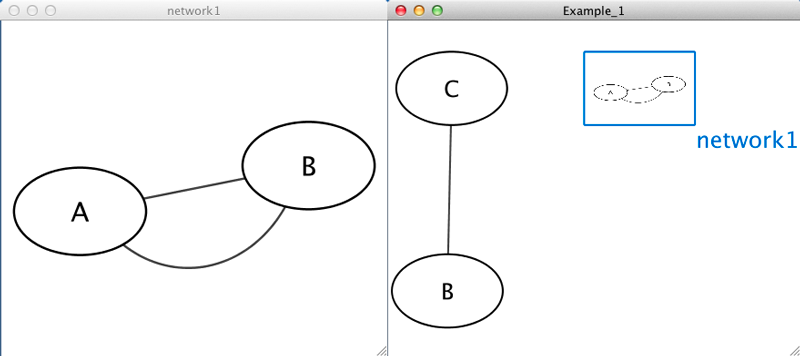
Example_1 C Example_1 network1 network1 A pp B network1 B pp A Example_1 C pp B
Example 2
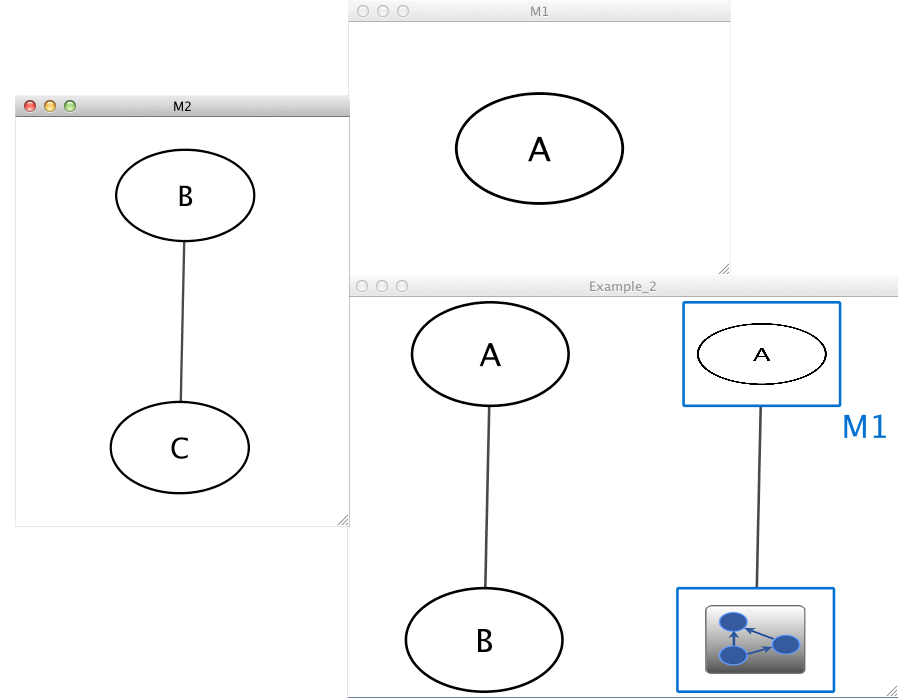
Example_2 M1 Example_2 M2 M1 A M2 B pp C Example_2 A pp B Example_2 M1 im M2
Example 3
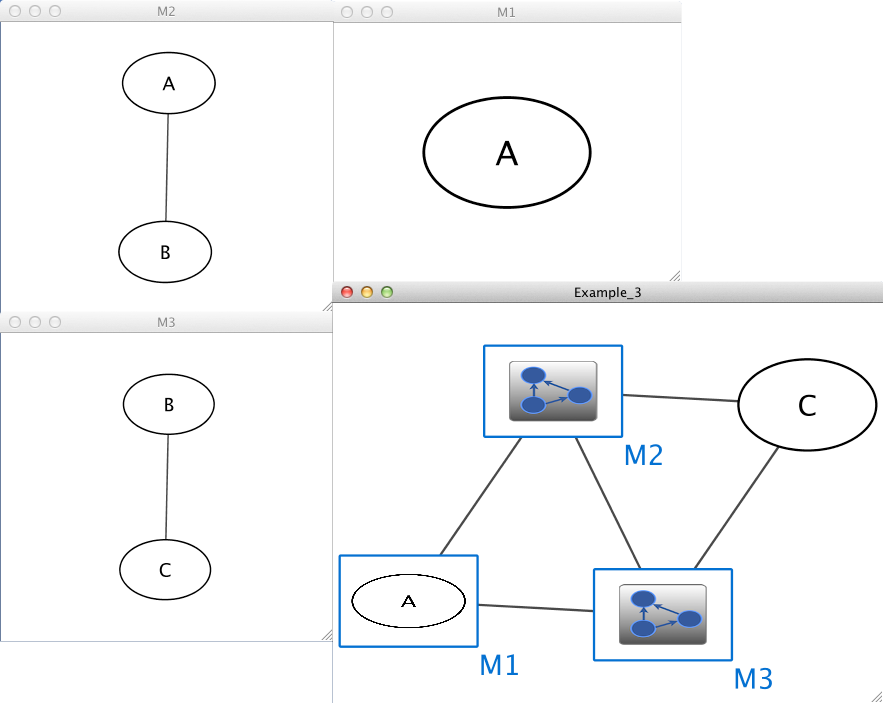
Example_3 M1 im M2 Example_3 M3 im M1 Example_3 M2 im M3 Example_3 C pp M3 Example_3 M2 pp C M1 A M2 A pp B M3 B pp C
Example 5
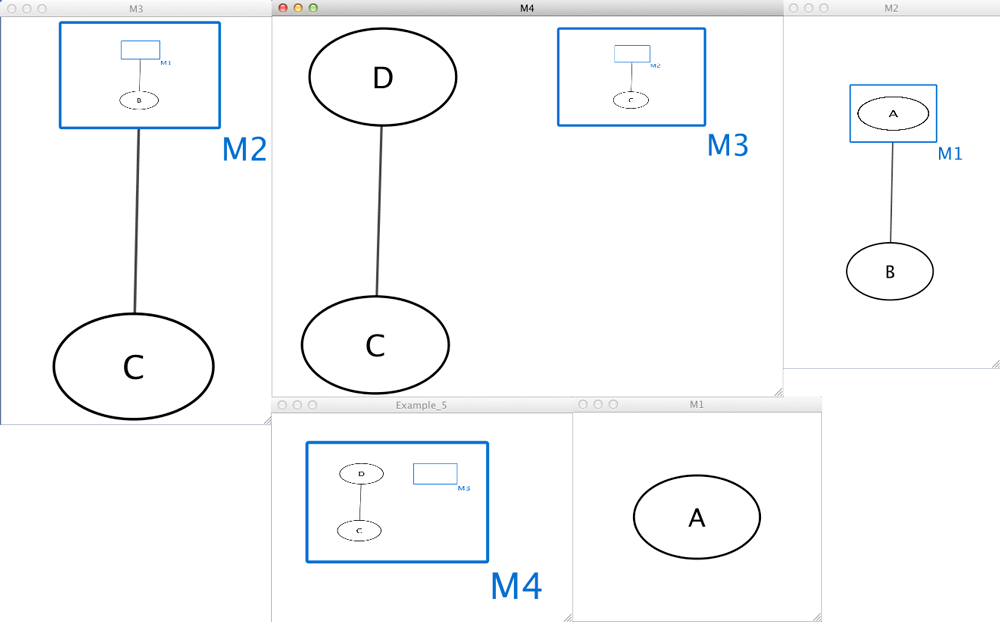
Example_5 M4 M4 D M4 M3 M3 M2 pp C M2 M1 pp B M1 A M4 C pp D
GML Format
In contrast to SIF, GML is a rich graph format language supported by many other network visualization packages. The GML file format specification is available at:
http://www.infosun.fmi.uni-passau.de/Graphlet/GML/
It is generally not necessary to modify the content of a GML file directly. Once a network is built in SIF format and then laid out, the layout is preserved by saving to and loading from GML. Properties specified in a GML file will result in a new style named Filename.style when that GML file is loaded.
XGMML Format
XGMML is the XML evolution of GML and is based on the GML definition. In addition to network data, XGMML contains node/edge/network column data. The XGMML file format specification is available at:
http://cgi5.cs.rpi.edu/research/groups/pb/punin/public_html/XGMML/
XGMML is now preferred to GML because it offers the flexibility associated with all XML document types. If you're unsure about which to use, choose XGMML.
There is a java system property "cytoscape.xgmml.repair.bare.ampersands" that can be set to "true" if you have experience trouble reading older files.
This should only be used when an XGMML file or session cannot be read due improperly encoded ampersands, as it slows down the reading process, but this is still preferable to attempting to fix such files using manual editing.
SBML (Systems Biology Markup Language) Format
The Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML) is an XML format to describe biochemical networks. SBML file format specification is available at:
BioPAX (Biological PAthways eXchange) Format
BioPAX is an OWL (Web Ontology Language) document designed to exchange biological pathways data. The complete set of documents for this format is available at:
PSI-MI Format
The PSI-MI format is a data exchange format for protein-protein interactions. It is an XML format used to describe PPI and associated data. PSI-MI XML format specification is available at:
http://psidev.sourceforge.net/mi/xml/doc/user/
GraphML
GraphML is a comprehensive and easy-to-use file format for graphs. It is based on XML. The complete set of documents for this format is available at:
http://graphml.graphdrawing.org/
Delimited Text Table and Excel Workbook
Cytoscape has native support for Microsoft Excel files (.xls, .xlsx) and delimited text files. The tables in these files can have network data and edge columns. Users can specify columns containg source nodes, target nodes, interaction types, and edge columns during file import. Some of the other network analysis tools, such as igraph (http://cneurocvs.rmki.kfki.hu/igraph/), has feature to export graph as simple text files. Cytoscape can read these text files and build networks from them. For more detail, please read the Import Free-Format Tables section of the Creating Networks section.
Cytoscape.js JSON
From Cytoscape 3.1.0 on, Cytoscape supports Cytoscape.js JSON files. You can use this feature to export your network visualizations to web browsers. Cytoscape.js has two ways to represent network data, and currently both reader and writer support only the array style graph notation. For example, this network in Cytoscape:
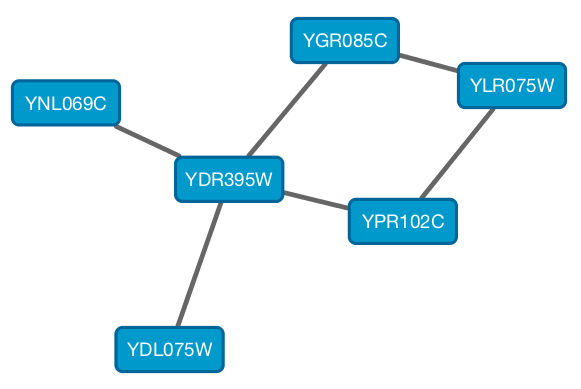
will be exported to this JSON:
{
"elements" : {
"nodes" : [ {
"data" : {
"id" : "723",
"selected" : false,
"annotation_Taxon" : "Saccharomyces cerevisiae",
"alias" : [ "RPL31A", "RPL34", "S000002233", "ribosomal protein L31A (L34A) (YL28)" ],
"shared_name" : "YDL075W",
"SUID" : 723,
"degree_layout" : 1,
"name" : "YDL075W"
},
"position" : {
"x" : 693.0518315633137,
"y" : -49.47506554921466
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "726",
"selected" : false,
"annotation_Taxon" : "Saccharomyces cerevisiae",
"alias" : [ "RP23", "RPL16B", "S000005013", "ribosomal protein L16B (L21B) (rp23) (YL15)" ],
"shared_name" : "YNL069C",
"SUID" : 726,
"degree_layout" : 1,
"name" : "YNL069C"
},
"position" : {
"x" : 627.3147710164387,
"y" : -205.99251969655353
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "658",
"selected" : false,
"annotation_Taxon" : "Saccharomyces cerevisiae",
"alias" : [ "RPL11B", "S000003317", "ribosomal protein L11B (L16B) (rp39B) (YL22)" ],
"shared_name" : "YGR085C",
"SUID" : 658,
"degree_layout" : 2,
"name" : "YGR085C"
},
"position" : {
"x" : 804.3092778523762,
"y" : -245.6235926946004
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "660",
"selected" : false,
"annotation_Taxon" : "Saccharomyces cerevisiae",
"alias" : [ "KAP108", "S000002803", "SXM1" ],
"shared_name" : "YDR395W",
"SUID" : 660,
"degree_layout" : 8,
"name" : "YDR395W"
},
"position" : {
"x" : 730.8733342488606,
"y" : -157.50702317555744
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "579",
"selected" : false,
"annotation_Taxon" : "Saccharomyces cerevisiae",
"alias" : [ "RPL11A", "S000006306", "ribosomal protein L11A (L16A) (rp39A) (YL22)" ],
"shared_name" : "YPR102C",
"SUID" : 579,
"degree_layout" : 2,
"name" : "YPR102C"
},
"position" : {
"x" : 841.1395696004231,
"y" : -130.77909119923908
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "578",
"selected" : false,
"annotation_Taxon" : "Saccharomyces cerevisiae",
"alias" : [ "GRC5", "QSR1", "RPL10", "S000004065", "ribosomal protein L10" ],
"shared_name" : "YLR075W",
"SUID" : 578,
"degree_layout" : 2,
"name" : "YLR075W"
},
"position" : {
"x" : 910.3755162556965,
"y" : -217.0562556584676
},
"selected" : false
} ],
"edges" : [ {
"data" : {
"id" : "659",
"source" : "658",
"target" : "578",
"selected" : false,
"interaction" : "pp",
"shared_interaction" : "pp",
"shared_name" : "YGR085C (pp) YLR075W",
"SUID" : 659,
"name" : "YGR085C (pp) YLR075W"
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "661",
"source" : "658",
"target" : "660",
"selected" : false,
"interaction" : "pp",
"shared_interaction" : "pp",
"shared_name" : "YGR085C (pp) YDR395W",
"SUID" : 661,
"name" : "YGR085C (pp) YDR395W"
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "724",
"source" : "660",
"target" : "723",
"selected" : false,
"interaction" : "pp",
"shared_interaction" : "pp",
"shared_name" : "YDR395W (pp) YDL075W",
"SUID" : 724,
"name" : "YDR395W (pp) YDL075W"
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "733",
"source" : "660",
"target" : "579",
"selected" : false,
"interaction" : "pp",
"shared_interaction" : "pp",
"shared_name" : "YDR395W (pp) YPR102C",
"SUID" : 733,
"name" : "YDR395W (pp) YPR102C"
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "727",
"source" : "660",
"target" : "726",
"selected" : false,
"interaction" : "pp",
"shared_interaction" : "pp",
"shared_name" : "YDR395W (pp) YNL069C",
"SUID" : 727,
"name" : "YDR395W (pp) YNL069C"
},
"selected" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"id" : "580",
"source" : "578",
"target" : "579",
"selected" : false,
"interaction" : "pp",
"shared_interaction" : "pp",
"shared_name" : "YLR075W (pp) YPR102C",
"SUID" : 580,
"name" : "YLR075W (pp) YPR102C"
},
"selected" : false
} ]
}
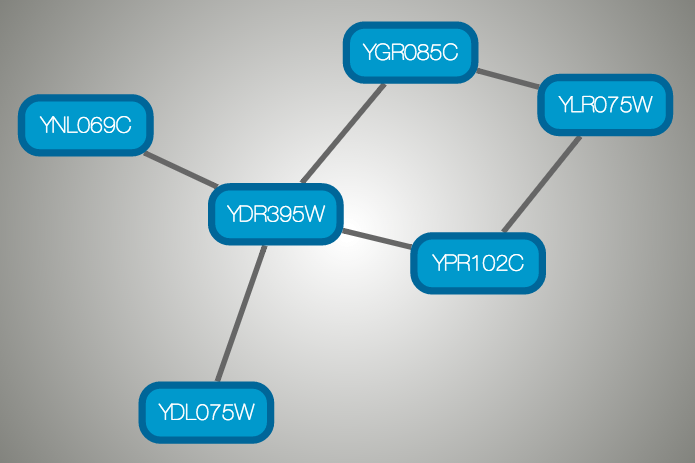
}And this is a sample visualization in Cytoscape.js:
Important Note
Export network and table to Cytoscape.js feature in Cytoscape creates a JSON file WITHOUT style. This means that you need to export the style in a separate JSON file if you apply style to your network. Please read Style section for more details.
Node and Edge Column Data
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Import Data Table Files
Cytoscape offers support for importing data from delimited text and MS Excel data tables.
Sample Data Table 1
Object Key |
Alias |
SGD ID |
AAC3 |
YBR085W|ANC3 |
S000000289 |
AAT2 |
YLR027C|ASP5 |
S000004017 |
BIK1 |
YCL029C|ARM5|PAC14 |
S000000534 |
The data table file should contain a primary key column and at least one data column. The maximum number of data columns is unlimited. The Alias column is an optional feature, as is using the first row of data as column names. Alternatively, you can specify each column name from the File → Import → Table → File... user interface.
Basic Operation
Select File → Import → Table → File....
- Select a data file. The file can be either a text or Excel (.xls/.xlsx) file.
In the Target Table Data section, choose where to import the data to. You can choose an existing network collection, a specific network only, or you can choose to import the data to an Unassigned Table (described below).
Depending on what you choose in the Where to import Table Data drop-down, you will need to select a network collection or specific network. You will also need to select Importing Type, that is whether the data is node, edge or network table columns.
If the table is not properly delimited in the preview panel, change the delimiter in the Advanced Options panel. The default delimiter is tab. This step is not necessary for Excel Workbooks.
- By default, the first column is designated as the primary key. Change the key column if necessary.
Click OK to import.
Unassigned Table
As of Cytoscape 3.1. it is possible to import data tables without assigning them to existing networks, meaning the data doesn't have to correspond to any nodes/edges currently loaded. If a data table is imported as unassigned and a network is later imported that maps to the data in terms of nodes or edges, the data will link automatically. This is useful when loading a large dataset (for example expression data), defining a Style for visualizing the data on networks and later loading individual networks to view the data, for example from an online database. This feature allows the data to be automatically linked to any network that is applicable, without having to load the data for each network.
Legacy Cytoscape Attributes Format
In addition to tabular data, the simple attribute file format used in previous versions of Cytoscape is still supported. Node and edge data files are simply formatted: a node data file begins with the name of the column on the first line (note that it cannot contain spaces). Each following line contains the name of the node, followed by an equals sign and the data value. Numbers and text strings are the most common data types. All values for a given column must have the same type. For example:
FunctionalCategory YAL001C = metabolism YAR002W = apoptosis YBL007C = ribosome
An edge data file has much the same structure, except that the name of the edge is the source node name, followed by the interaction type in parentheses, followed by the target node name. Directionality counts, so switching the source and target will refer to a different (or perhaps non-existent) edge. The following is an example edge data file:
InteractionStrength YAL001C (pp) YBR043W = 0.82 YMR022W (pd) YDL112C = 0.441 YDL112C (pd) YMR022W = 0.9013
Since Cytoscape treats edge data as directional, the second and third edge data values refer to two different edges (source and target are reversed, though the nodes involved are the same).
Each data column is stored in a separate file. Node and edge data files use the same format, and have the suffix ".attrs".
Node and edge data may be loaded via the File → Import → Table menu, just as data table files are.
When expression data is loaded using an expression matrix, it is automatically loaded as node data unless explicitly specified otherwise.
Node and edge data columns are attached to nodes and edges, and so are independent of networks. Data values for a given node or edge will be applied to all copies of that node or edge in all loaded network files, regardless of whether the data file or network file is imported first.
Detailed file format (Advanced users)
Every data file has one header line that gives the name of the data column, and optionally some additional meta-information about that data column. The format is as follows:
columnName (class=JavaClassName)
The first field is always the column name: it cannot contain spaces. If present, the class field defines the name of the class of the data values. For example, java.lang.String or String for Strings, java.lang.Double or Double for floating point values, java.lang.Integer or Integer for integer values, etc. If the value is actually a list of values, the class should be the type of the objects in the list. If no class is specified in the header line, Cytoscape will attempt to guess the type from the first value. If the first value contains numbers in a floating point format, Cytoscape will assume java.lang.Double; if the first value contains only numbers with no decimal point, Cytoscape will assume java.lang.Integer; otherwise Cytoscape will assume java.lang.String. Note that the first value can lead Cytoscape astray: for example,
floatingPointDataColumn firstName = 1 secondName = 2.5
In this case, the first value will make Cytoscape think the values should be integers, when in fact they should be floating point numbers. It's safest to explicitly specify the value type to prevent confusion. A better format would be:
floatingPointDataColumn (class=Double) firstName = 1 secondName = 2.5
or
floatingPointDataColumn firstName = 1.0 secondName = 2.5
Every line past the first line identifies the name of an object (a node in a node data file or an edge in a edge data file) along with the String representation of the data value. The delimiter is always an equals sign; whitespace (spaces and/or tabs) before and after the equals sign is ignored. This means that your names and values can contain whitespace, but object names cannot contain an equals sign and no guarantees are made concerning leading or trailing whitespace. Object names must be the Node ID or Edge ID as seen in the left-most column of the Table Panel if the data column is to map to anything. These names must be reproduced exactly, including case, or they will not match.
Edge names are all of the form:
sourceName (edgeType) targetName
Specifically, that is
sourceName space openParen edgeType closeParen space targetName |
Note that tabs are not allowed in edge names. Tabs can be used to separate the edge name from the "=" delimiter, but not within the edge name itself. Also note that this format is different from the specification of interactions in the SIF file format. To be explicit: a SIF entry for the previous interaction would look like
sourceName edgeType targetName
or
sourceName whiteSpace edgeType whiteSpace targetName |
To specify lists of values, use the following syntax:
listDataColumnName (class=java.lang.String) firstObjectName = (firstValue::secondValue::thirdValue) secondObjectName = (onlyOneValue)
This example shows a data column whose value is defined as a list of text strings. The first object has three strings, and thus three elements in its list, while the second object has a list with only one element. In the case of a list every data value uses list syntax (i.e. parentheses), and each element is of the same class. Again, the class will be inferred if it is not specified in the header line. Lists are not supported by Styles and so can’t be mapped to network properties.
Newline Feature
Sometimes it is desirable to for data values to include linebreaks, such as node labels that extend over two lines. You can accomplish by inserting \n into the data value. For example:
newlineDataColumn YJL157C = This is a long\nline for a label.
Table Panel
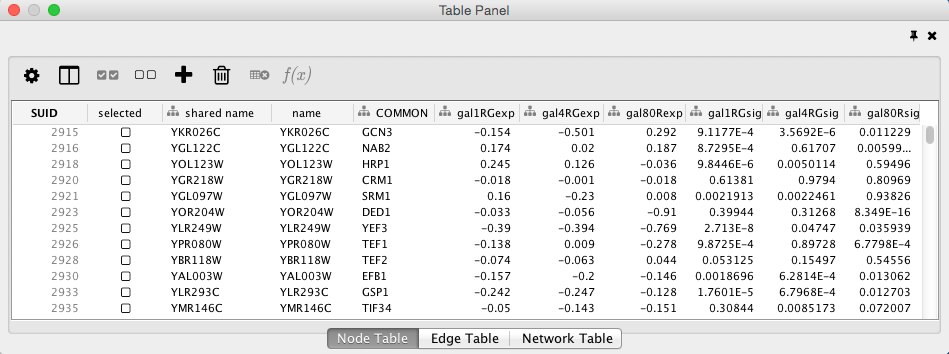
When Cytoscape is started, the Table Panel appears in the bottom right of the main Cytoscape window. This browser can be hidden and restored using the F5 key or the View → Show/Hide Table Panel menu option. Like other Panels, the browser can be undocked by pressing the little icon in the top right corner.
To swap between displaying node, edge, and network Data Tables use the tabs on the bottom of the Table Panel. By default, the Table Panel displays columns for all nodes and edges in the selected network. To display columns for only selected nodes/edges, click the Change Table Mode button  at the top left. To change the columns that are displayed, click the Show Column
at the top left. To change the columns that are displayed, click the Show Column  button and choose the columns that are to be displayed (select various columns by clicking on them, and then click elsewhere on the screen to close the column list).
button and choose the columns that are to be displayed (select various columns by clicking on them, and then click elsewhere on the screen to close the column list).
Most column values can be edited by double-clicking the cell (only the ID cannot be edited). Newline characters can be inserted into String columns either by pressing Enter or by typing "\n". Once finished editing, click outside of the editing cell in the Table Panel or press Shift-Enter to save your edits. Pressing Esc while editing will undo any changes.
Rows in the panel can be sorted alphabetically by specific column by clicking on a column heading. A new column can be created using the Create New column  button, and must be one of four types – integer, string, real number (floating point), or boolean. Columns can be deleted using the Delete Columns...
button, and must be one of four types – integer, string, real number (floating point), or boolean. Columns can be deleted using the Delete Columns...  button. NOTE: Deleting columns removes them from Cytoscape, not just the Table Panel! To remove columns from the panel without deleting them, simply unselect the column using the Select Columns
button. NOTE: Deleting columns removes them from Cytoscape, not just the Table Panel! To remove columns from the panel without deleting them, simply unselect the column using the Select Columns  button.
button.
Import Data Table from Public Databases
It is also possible to import node data columns from public databases via web services, for example from BioMart.
Basic Operation
- Load a network, for example galFiltered.sif.
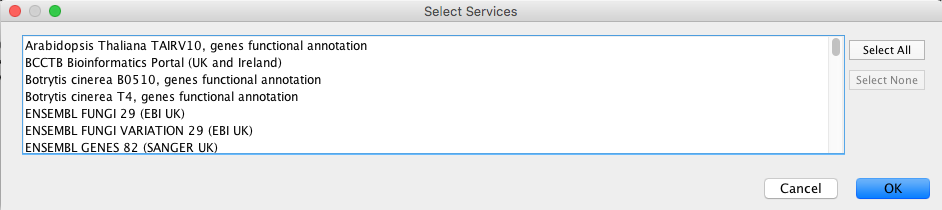
Select File → Import → Table → Public Databases....
You will first be asked to select from a set of web services. For this example, we will choose ENSEMBL GENES 73 (SANGER UK).
In the Import Data Table from Web Services dialog, select a Data Source. Since galFiltered.sif is a yeast network, select ENSEMBL GENES - SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE.
For Key Column in Cytoscape, select shared name for Column and Ensembl Gene ID for Data Type.
The type of identifier selected under Data Type must match what is used in the selected Column in the network.
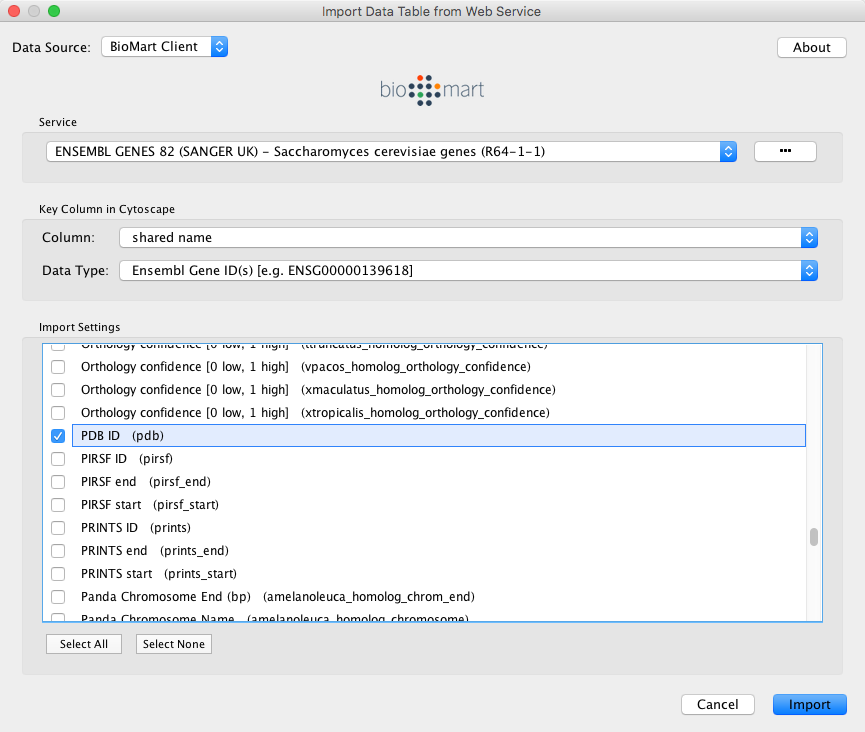
- Select the data columns you want to import.
Select Import.
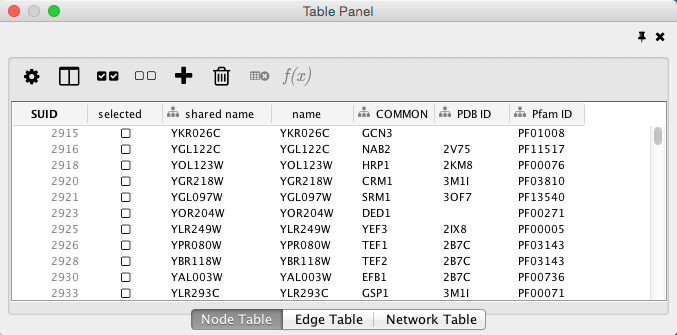
When import is complete, you can see the newly imported data columns in the Table Panel.
Ontology and Annotation Import
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
GO 8150 biological_process
- GO 7582 physiological processes
- GO 8152 metabolism
- GO 44238 primary metabolism
- GO 19538 protein metabolism
- GO 6412 protein biosynthesis
- GO 19538 protein metabolism
- GO 44238 primary metabolism
- GO 8152 metabolism
Graphical View of GO Term 6412: protein biosynthesis
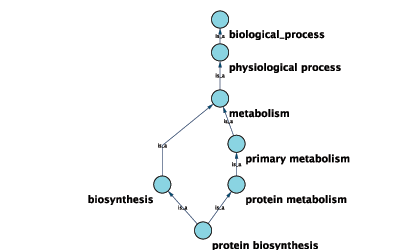
Cytoscape can use this ontology DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) to annotate objects in networks. The Ontology Server (originally called "BioDataServer") is a Cytoscape feature which allows you to load, navigate, and assign annotation terms to nodes and edges in a network. Cytoscape 2.4 now has an enhanced GUI for loading ontology and associated annotation, enabling you to load both local and remote files.
Ontology and Annotation File Format
The standard file formats used in the Cytoscape Ontology Server are OBO and Gene Association. The GO website details these file formats:
Ontologies and Definitions: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.downloads.shtml#ont
Current Annotations: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.current.annotations.shtml
Default List of Ontologies
Cytoscape provides a list of ontologies available in OBO format. If an Internet connection is available, Cytoscape will import ontology and annotation files directly from the remote source. The table below lists the included ontologies.
Ontology Name |
Description |
Gene Ontology Full |
This data source contains a full-size GO DAG, which contains all GO terms. This OBO file is written in version 1.2 format. |
Generic GO slim |
A subset of general GO Terms, including higer-level terms only. |
Yeast GO slim |
A subset of GO Terms for annotating Yeast data sets maintained by SGD. |
Molecule role (INOH Protein name/family name ontology) |
A structured controlled vocabulary of concrete and abstract (generic) protein names. This ontology is a INOH pathway annotation ontology, one of a set of ontologies intended to be used in pathway data annotation to ease data integration. This ontology is used to annotate protein names, protein family names, and generic/concrete protein names in the INOH pathway data. INOH is part of the BioPAX working group. |
Event (INOH pathway ontology) |
A structured controlled vocabulary of pathway-centric biological processes. This ontology is a INOH pathway annotation ontology, one of a set of ontologies intended to be used in pathway data annotation to ease data integration. This ontology is used to annotate biological processes, pathways, and sub-pathways in the INOH pathway data. INOH is part of the BioPAX working group. |
Protein-protein interaction |
A structured controlled vocabulary for the annotation of experiments concerned with protein-protein interactions. |
Pathway Ontology |
The Pathway Ontology is a controlled vocabulary for pathways that provides standard terms for the annotation of gene products. |
PATO |
PATO is an ontology of phenotypic qualities, intended for use in a number of applications, primarily phenotype annotation. For more information, please visit the PATO wiki (http://www.bioontology.org/wiki/index.php/PATO:Main_Page). |
Mouse pathology |
The Mouse Pathology Ontology (MPATH) is an ontology for mutant mouse pathology. This is Version 1. |
Human disease |
This ontology is a comprehensive hierarchical controlled vocabulary for human disease representation. For more information, please visit the Disease Ontology website (http://diseaseontology.sourceforge.net/). |
Although Cytoscape can import all kinds of ontologies in OBO format, annotation files are associated with specific ontologies. Therefore, you need to provide the correct ontology-specific annotation file to annotate nodes/edges/networks in Cytoscape. For example, while you can annotate human network data using the GO Full ontology with human Gene Association files, you cannot use a combination of the human Disease Ontology file and human Gene Association files, because the Gene Association file is only compatible with GO.
Gene Association File
The Gene Association files provide annotation only for the Gene Ontology. It is a species-specific annotation file for GO terms. Gene Association files will only work with Gene Ontology annotation.
Sample Gene Association File (gene_association.sgd - annotation file for yeast):
SGD |
S000003916 |
AAD10 |
GO:0006081 |
SGD_REF:S000042151|PMID:10572264 |
ISS |
P |
aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase (putative) |
YJR155W gene |
taxon:4932 |
SGD |
S000005275 |
AAD14 |
GO:0008372 |
SGD_REF:S000069584 |
ND |
C |
aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase (putative) |
YNL331C gene |
taxon:4932 |
Import Ontology and Annotation
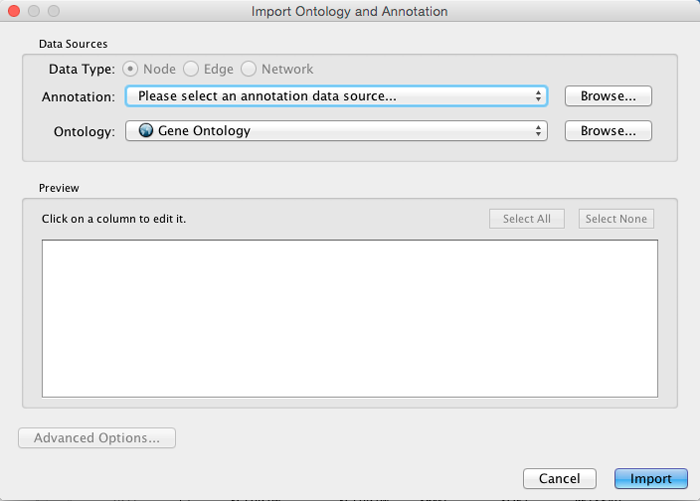
Cytoscape provides a graphical user interface to import both ontology and annotation files at the same time.
Note: All data sources in the preset list are remote URLs, meaning a network connection is required.
Select File → Import → Ontology and Annotation... to open the "Import Ontology and Annotation" interface. From the Annotation drop-down list, select a gene association file for your network. For example, if you want to annotate the yeast network, select "Gene Association file for Saccharomyces cerevisiae".
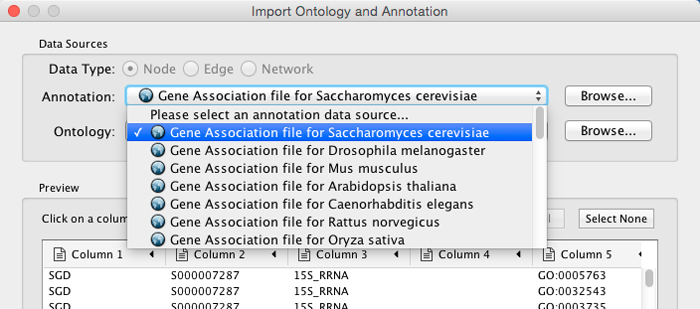
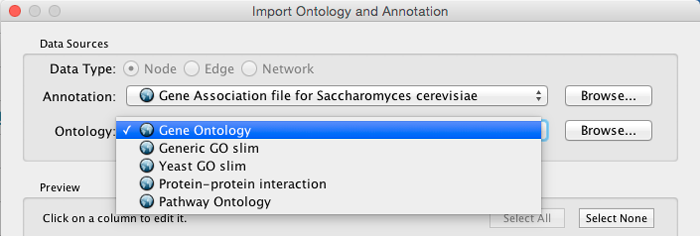
* Select an Ontology data (OBO file) from the Ontology drop-down list. If the file is not loaded yet, it will be shown in red. The first three files are Gene Ontology files. You can load other ontologies, but you need your own annotation file to annotate networks.
Once you click the Import button, Cytoscape will start loading OBO and Gene Association files from the remote sources. If you choose GO Full it may take a while since it is a large data file.
- When Cytoscape finishes importing files, the import window will be automatically closed. All columns mapped by this function have the prefix "annotation" and look like this: annotation.[column_name].
Note: Cytoscape supports both OBO formats: version 1.0 and 1.2.
Column Data Functions and Equations
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Column Formulas
Introduction
Column data values may be formulas. A typical example is =ABS($otherColumn + LOG(10.2)). Formulas are modeled after Excel™ but only support references to other columns at the same node, edge or network. Since Cytoscape column names may contain embedded spaces, optional braces around the column name (required if the name is not simply a letter followed by one or more letters or digits) is allowed e.g. ${a name with spaces}. Backslashes, opening braces and dollar signs in column names have to be escaped with a leading backslash. For example the column name ex$am{p\le would have to be written as ${ex\$am\{p\\le}. Finally, column names are case sensitive.
String constants are written with double-quotes ". In order to embed a double-quote or a backslash in a string they have to be escaped with a leading backslash, therefore the string "\ must be written as "\"\\". Formula results must be compatible with the type of the column that they have been assigned to. The rules are rather lax though, for example anything can be interpreted as a string and all numeric values will be accepted for a boolean (or logical) column data where non-zero will be interpreted as true and zero as false. For integer columns, floating point values will be converted using the rules of the Excel™ INT function. Parentheses can be used for grouping and to change evaluation order. The operator precedence rules follow those of standard arithmetic.
Operators
Currently supported operators are the four basic arithmetic operators and the ^ exponentiation operator. +, -, *, and \ are left-associative and ^ is right-associative. The string concatenation operator is &. Supported boolean or logical operators are the comparison operators <, >, <=, >=, =, and <> (not equal).
Supported Functions
Currently we support the following functions:
Numeric Functions
- Abs -- Returns the absolute value of a number.
- ACos -- Returns the arccosine of a number.
- ASin -- Returns the arcsine of a number.
- ATan2 -- Returns the arctangent of two numbers x and y.
- Average -- Returns the average of a group of numbers.
- Cos -- Returns the cosine of an angle given in radians.
- Cosh -- Returns the hyperbolic sine of its argument.
- Count -- Returns the number of numeric values in a list.
- Degrees -- Returns its argument converted from radians to degrees.
- Exp -- Returns e raised to a specified number.
- Ln -- Returns the natural logarithm of a number.
- Log -- Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base.
- Max -- Returns the maximum of a group of numbers.
- Median -- Returns the median of a list of numbers.
- Min -- Returns the minimum of a group of numbers.
- Mod -- Calculates the modulus of a number.
- Pi -- Returns an approximation of the value of π.
- Radians -- Returns its argument converted from degrees to radians.
- Round -- Rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places.
- Sin -- Returns the sine of an angle given in radians.
- Sinh -- Returns the hyperbolic sine of its argument.
- Sqrt -- Calculates the square root of a number.
- Tan -- returns the tangent of its argument in radians.
- Tanh -- returns the hyperbolic tangent of its argument in radians.
- Trunc -- Truncates a number.
String Functions
- Concatenate -- Concatenates two or more pieces of text.
- Left -- Returns a prefix of s string.
- Len -- Returns the length of a string.
- Lower -- Converts a string to lowercase.
- Mid -- Selects a substring of some text.
- Right -- Returns a suffix of a string.
- Substitute -- Replaces some text with other text.
Text -- Format a number using the Java DecimalFormat class' conventions.
- Upper -- Converts a string to uppercase.
- Value -- Converts a string to a number.
Logical/Boolean Functions
- And -- Returns the logical conjunction of any number of boolean values.
- Not -- Returns the logical negation of a boolean value.
- Or -- Returns the logical disjunction of any number of boolean values.
List Functions
- First -- Returns the first entry in a list.
- Last -- Returns the last entry in a list.
- Nth -- Returns the n-th entry in a list.
Statistical Functions
- Largest -- the kth largest value in a list.
GeoMean -- the geometric mean of a set of numbers.
HarMean -- the harmonic mean of a set of numbers.
- Mode -- the mode of a set of numbers.
NormDist -- Returns the pdf or CDF of the normal distribution.
- Permut -- Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects.
StDev - sample standard deviation.
- Var -- sample variance.
Miscellaneous Functions
- Combin - Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects.
- If -- Returns one of two alternatives based on a boolean value.
ListToString -- Returns a string representation of a list.
- Now -- Returns a string representation of the current date and time.
- Today -- returns a string representation of the current date.
Pitfalls
The possibly biggest problem is the referencing of other columns that have null values. This is not allowed and leads to errors. In order to mitigate this problem we support the following optional syntax for column references: ${columnName:defaultValue}. The interpretation is that if columnName is null, then the default value will be used, otherwise the value of the referenced value will be used instead. The referenced column must still be a defined column and not an arbitrary name! The other potential problem is when there are circular column reference dependencies. Circular dependencies will be detected at formula evaluation time and lead to a run-time error.
The Formula Builder
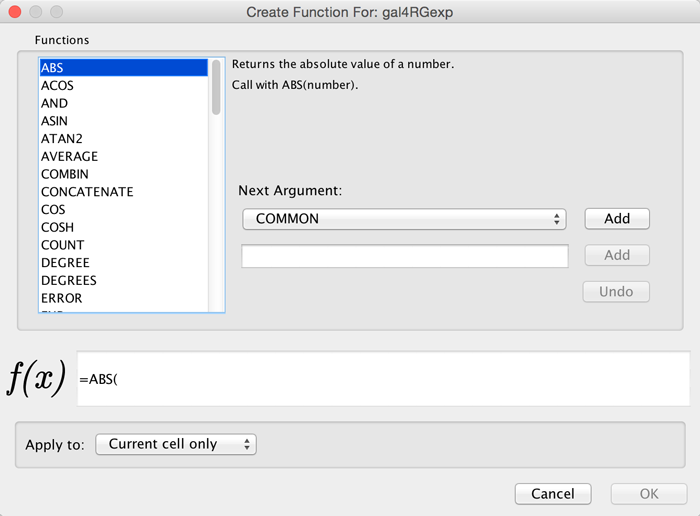
In order to ease the creation of formulas as well as to facilitate discovery of built-in functions we provide a Function Builder in the Table Panel. After selecting a non-list column cell, you can invoke it by clicking on  . This should bring up the Function Builder which looks like this:
. This should bring up the Function Builder which looks like this:
Select a function on the left hand side of the dialog - here, we've selected the ABS function. Next to the list of functions, you can specify one or more arguments. This can either be a column (selected from the drop-down list) or a constant specified in the box below. If you select a column, the value of that column (in the row containing the formula) will be used, and the function result will be updated dynamically when that value changes. Click Add to add an argument - you can add one or more depending on how many arguments the function accepts. At the bottom of the dialog is a preview of the current formula. Under Apply to, you can select whether the formula will apply to the current cell only, the cell selection, or the entire column. Click OK when you are satisfied with the result, or Cancel to discard any changes.
The Function Builder is a useful tool for discovery of the list of built-in functions, which has the return type matching the data type of the column. Arguments can either be selected from a list of named columns, or constant values can be entered in a text entry field. A major shortcoming at this time is that the Formula Builder won't let you compose functions with function calls as arguments. If you need the most general functionality, please type the expression directly into a cell.
A Note for App Writers
It is relatively easy to add your own built-in formula functions. A simple function can probably be implemented in 15 to 20 minutes. It can then be registered via the parser and becomes immediately available to the user. It will of course also show up in the drop-down list in the Function Builder.
Finding and Filtering Nodes and Edges
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Search Bar
You can search for nodes and edges by column value directly through Cytoscape's tool bar. For example, to select nodes or edges with a column value that starts with "STE", type ste* in the search bar. The search is case-insensitive. The * is a wildcard character that matches zero or more characters, while "?" matches exactly one character. So ste? would match "STE2" but would not match "STE12". Searching for ste* would match both.
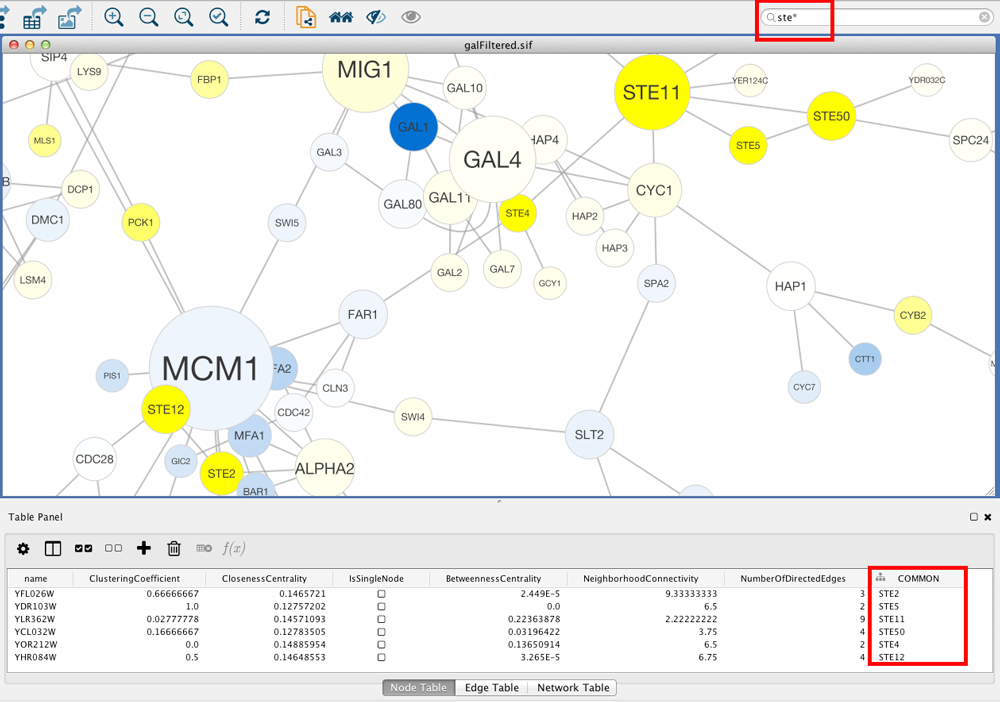
To search a specific column, you can prefix your search term with the column name followed by a :. For example, to select nodes and edges that have a "COMMON" column value that starts with "STE", use common:ste*. If you don't specify a particular column, all columns will be searched.
Columns with names that contain spaces, quotes, or characters other than letters and numbers currently do not work when searching a specific column. This will be fixed in a future release.
To search for column values that contain special characters you need to escape those characters using a "\". For example, to search for "GO:1232", use the query GO\:1232. The complete list of special characters is:
+ - & | ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \Note: Escaping characters only works when searching all columns. It currently does not work for column-specific searching. This will be fixed in a future release.
Filters
Cytoscape 3 provides a new user interface for filtering nodes and edges. These tools can be found in the Select panel:
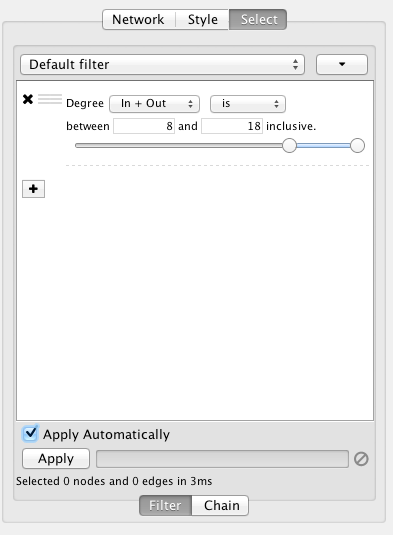
There are two types of filters. On the Filter tab are narrowing filters, which can be combined into a tree. On the Chain tab are chainable filters, which can be combined in a linear chain.
Narrowing Filters
Narrowing filters are applied to the entire network, and are used to select a subset of nodes or edges in a network based on user-specified constraints. For example, you can find edges with a weight between 0 and 5.5, or nodes with degree less than 3. A filter can contain an arbitrary number of sub-filters.
To add a filter click on the "+" button. To delete a filter (and all its sub-filters) click the "x" button. To move a filter grab the handle  with the mouse and drag and drop the filter on its intended destination. Dropping a filter on top of another filter will group the filters into a composite filter.
with the mouse and drag and drop the filter on its intended destination. Dropping a filter on top of another filter will group the filters into a composite filter.
Interactive Filter Application Mode
Due to the nature of narrowing filters, Cytoscape can apply them to a network efficiently and interactively. Some filters even provide slider controls to quickly explore different thresholds. This is the default behavior on smaller networks. For larger networks, Cytoscape automatically disables this interactivity. You can override this by manually checking the Apply Automatically box above the Apply button:
Cytoscape comes packaged with the following narrowing filters:
Column Filter
This filter will match nodes or edges that have particular column values. For numeric columns sliders are provided to set minimum and maximum values, or the values may be entered manually.
From string columns, a variety of matching options are provided:
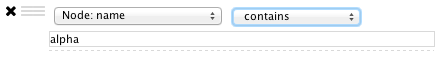
For example, column values can be checked to see if they contain or match exactly the text entered in the text box. More complex matching criteria can be specified by using a Java-style regular expression.
By default string matching is case insensitive. Case sensitive matching requires the use of a regular expression that starts with "(?-i)". For example to match the text "ABC" in a case sensitive way use the following regular expression: "(?-i)ABC".
Cytoscape uses Java regular expression syntax.
Degree Filter
The degree filter matches nodes with a degree that falls within the given minimum and maximum values, inclusive. You can choose whether the filter operates on the in-degree, out-degree or overall (in + out) degree.
Topology Filter
The topology filter matches nodes having a certain number of neighbors which are within a fixed distance away, and which match a sub-filter. The thresholds for the neighborhood size and distance can be set independently, and the sub-filter is applied to each such neighbor node.
The topology filter will successfully match a node if the sub-filter matches against the required number of neighbor nodes.
Grouping and Organizing Filters
By default, nodes and edges need to satisfy the constraints of all your filters. You can change this so that instead, only the constraints of at least one filter needs to be met in order to match a node or edge. This behavior is controlled by the Match all/any drop-down box. This appears once your filter has more than one sub-filter. For example, suppose you wanted to match nodes with column COMMON containing ste or cdc, but you only want nodes with degree 5 or more, you'd first construct a filter that looks like this:
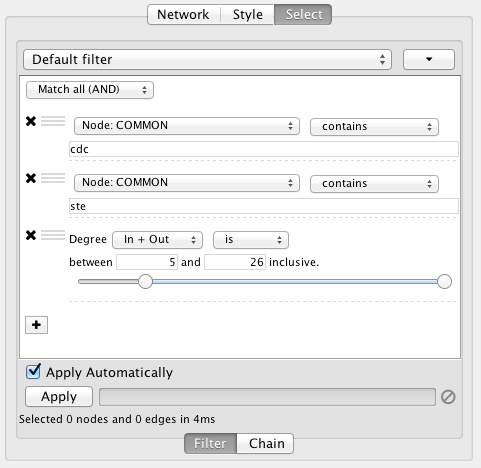
This filter will match nodes where COMMON contains ste and cdc. To change this to a logical or operation, drag either of the column filters by its handle  onto the other column filter to create a new group. Now change the group's matching behavior to Match any:
onto the other column filter to create a new group. Now change the group's matching behavior to Match any:
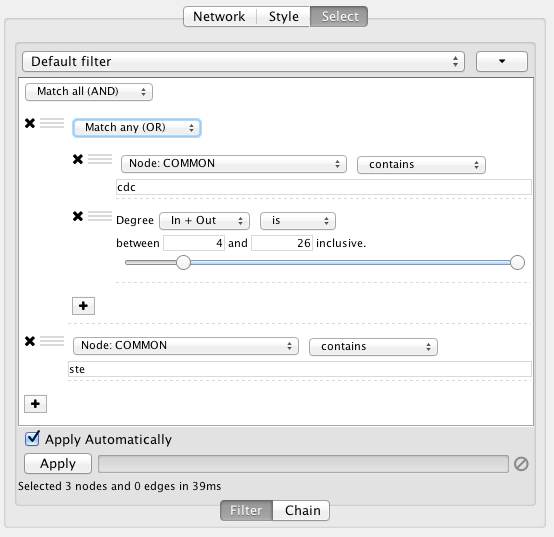
You can also reorder filters by dropping them in-between existing filters.
Chainable Filters
Chainable filters are combined in an ordered list. The nodes and edges in the output of a filter become the input of the next filter in the chain. The first filter in the chain gets its input from the current selection or from a filter on the Filter tab. The output of the last filter becomes the new selection.
You can specify the input to the first filter in the chain by selecting a Start with, where Current selection refers to the nodes and edges currently selected. You can also choose a narrowing filter, which produces a different set of selected nodes and edges.
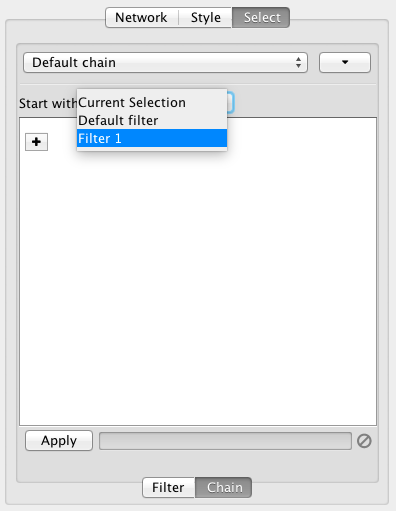
Chainable filters can be reordered by dragging one by the handle and dropping it between existing filters.
Cytoscape currently bundles the following chainable filters:
Edge Interaction Transformer
This transformer will go through all the input edges and selectively add their source nodes, target nodes, or both, to the output. This is useful for adding nodes that are connected to edges that match a particular filter.
Output options:
- Add (default): Automatically includes all input nodes and edges in the output, and adds source or target nodes from input edges to the output.
- Replace with: Does not automatically include input nodes and edges in the output. Only outputs nodes that match the filter.
A sub-filter may be added as well. When a sub-filter is present the source/target nodes must match the filter to be included in the output.
Node Adjacency Transformer
This transformer is used to add nodes and edges that are adjacent to the input nodes. A sub-filter may be specified as well.
Note that pressing the Apply button repeatedly may cause the selection to continuously expand. This allows adjacent nodes that are at greater distances to be added.
Output options:
- Add (default): Automatically includes all input nodes and edges in the output, and adds selected adjacent nodes and edges.
- Replace with: Only outputs the adjacent nodes/edges.
Select options:
- Adjacent nodes: Output nodes that are adjacent to the input nodes.
- Adjacent edges: Output edges that are adjacent (incident) to the input nodes.
- Adjacent nodes and edges (default): Output both nodes and edges that are adjacent to the input nodes.
Edge direction options. (Hidden by default, click the small arrow icon to reveal.):
- Incoming: Only include adjacent nodes/edges when the adjacent edge is incoming.
- Outgoing: Only include adjacent nodes/edges when the adjacent edge is outgoing.
- Incoming and Outgoing (default): Ignore the directionality of adjacent edges.
Sub-filter options. (Available when a sub-filter has been added.):
- Adjacent nodes (default): The sub-filter is only applied to adjacent nodes. (Edges to the adjacent nodes are still included in the output.)
- Adjacent edges: The sub-filter is only applied to adjacent edges. (Nodes connected to the adjacent edges are still included in the output.)
- Adjacent nodes and edges: Both the adjacent edge and its connected node must match the filter. Note that for a filter to match an edge and a node at the same time it should be a compound filter that is set to "Match any (OR)".
Working with Narrowing and Chainable Filters
The name of active filter appears in the drop-down box at the top of Select panel. Beside this is the options button which will allow you to rename, remove or export the active filter. It also lets you create a new filter, or import filters.
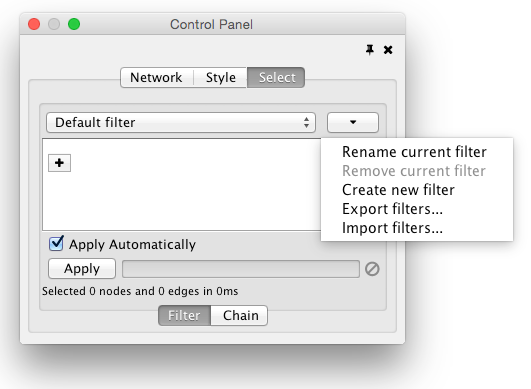
At the bottom of the Select panel, there is an Apply button that will re-apply the active filter. On the opposite side of the progress bar is the cancel button, which will let you interrupt a long-running filter.
The Select Menu
The Select → Nodes and Select → Edges menus provide several mechanisms for selecting nodes and edges. Most options are fairly straightforward; however, some need extra explanation.
Select → Nodes → From ID List File... selects nodes based on node identifiers found in a specified file. The file format is simply one node id per line:
Node1 Node2 Node3 ...
Navigation and Layout
Styles
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
What are Styles?
One of Cytoscape's strengths in network visualization is the ability to allow users to encode any table data (name, type, degree, weight, expression data, etc.) as a property (such as color, size of node, transparency, or font type) of the network. A set of these encoded or mapped table data sets is called a Style and can be created or edited in the Style panel of the Control Panel. In this interface, the appearance of your network is easily customized. For example, you can:
Specify a default color and shape for all nodes.
Set node sizes based on the degree of connectivity of the nodes. You can visually see the hub of a network...
...or, set the font size of the node labels instead.
Visualize gene expression data along a color gradient.
Encode specific physical entities as different node shapes.
Use specific line types to indicate different types of interactions.
Control edge transparency (opacity) using edge weights.
Control multiple edge properties using edge score.
Browse extremely-dense networks by controlling the opacity of nodes.
Show highly-connected region by edge bundling and opacity.
Add photo/image/graphics on top of nodes.
Cytoscape 3 has several sample styles. Below are a few examples of these applied to the galFiltered.sif network :
Introduction to the Style interface
The Style interface is located under the Style panel of the Control Panel.
This interface allows you to create/delete/view/switch between different styles using the Current Style options. The panel displays the mapping details for a given style and is used to edit these details as well.
At the top of the interface, there is a drop-down menu for selecting a pre-defined style. There is also an Options drop-down with options to rename, remove, create and copy a Style, and an option to create a legend for the selected Style.
- The main area of the interface is composed of three tabs, for Node, Edge and Network.
Each tab contains a list of properties relevant to the current style. At the top of the list a Properties drop-down allows you to add additional properties to the list.
- Each property entry in the list has 3 columns:
The Default Value shows just that, the default value for the property. Clicking on the Default Value column for any property allows you to change the default value.
Mapping displays the type of mapping currently in use for the property. Clicking on the Mapping column for any property expands the property entry to show the interface for editing the mapping. Details on the mapping types provided here.
Bypass displays any style bypass for a selected node or edge. Note that a node/edge or subset of nodes/edges must be selected to activate the Bypass column. Clicking on the Bypass column for selected node(s)/edge(s) allows you to enter a bypass for that property for selected node(s)/edge(s).
The Default Value is used when no mapping is defined for a property, or for nodes/edges not covered by a mapping for a particular property. If a Mapping is defined for a property, this defines the style for all or a subset of nodes/edges, depending on how the mapping is defined. A Bypass on a specific set of nodes/edges will bypass and override both the default value and defined mapping.
Introduction to Style
The Cytoscape distribution includes several predefined styles to get you started. To examine a few styles, try out the following example:
Step 1. Load some sample data
Load a sample session file: From the main menu, select File → Open..., and select the file sampleData/galFiltered.cys.
The session file includes a network, some annotations, and sample styles. By default, the style galFiltered Style is selected. Gene expression values for each node are colored along a color gradient between blue and yellow (where blue represents a low expression ratio and yellow represents a high expression ratio, using thresholds set for the gal1RGexp experiment bundled with Cytoscape in the sampleData/galExpData.csv file). Also, node size is mapped to the degree of the node (number of edges connected to the node) and you can see the hubs of the network as larger nodes. See the sample screenshot below:

Step 2. Switch between different styles
You can change the style by making a selection from the Current Style drop-down list, found at the top of the Style panel.
For example, if you select Sample1, a new style will be applied to your network, and you will see a white background and round blue nodes. If you zoom in closer, you can see that protein-DNA interactions (specified with the label "pd") are drawn with dashed edges, whereas protein-protein interactions (specified with the label "pp") are drawn with solid edges (see sample screenshot below).
Finally, if you select Solid, you can see the graphics below:
This style does not have mappings except node/edge labels, but you can modify the network graphics by editing the Default Value for any property.
Additional sample styles are available in the sampleStyles.xml file in the sampleData directory. You can import the sample file from File → Import → Styles....
List of Node, Edge and Network Properties
Cytoscape allows a wide variety of properties to be controlled. These are summarized in the tables below.
Node Properties |
Description |
Border Line Type |
The type of line used for the border of the node. |
Border Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the border of the node. Zero means totally transparent, and 255 means totally opaque. |
Border Width |
The width of the node border. |
Label |
The text used for the node label. |
Label Font Face |
The font used for the node label. |
Label Font Size |
The size of the font used for the node label. |
Label Position |
The position of the node label relative to the node. |
Label Transparency |
The opacity of the node label. Zero means totally transparent, and 255 means totally opaque. |
Label Width |
The maximum width of the node label. If the node label is wider than the specified width, Cytoscape will automatically wrap the label on space characters. Cytoscape will not hyphenate words, meaning that if a single word (i.e. no spaces) is longer than maximum width, the word will be displayed beyond the maximum width. |
Nested Network Image Visible |
A boolean value that indicates whether a nested network should be visualized (assuming a nested network is present for the specified node). |
Padding (Compound Node) |
Internal padding of the compound node (a node that contains other nodes). |
Paint |
The color of the whole node, including its border, label and selected paint. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Paint. |
Border Paint |
The color of the border of the node. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Border Paint. |
Image/Chart 1-9 |
A user-defined graphic (image, chart or gradient) that is displayed on the node. These properties (maximum of nine) can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Custom Paint n → Image/Chart n. |
Image/Chart Position 1-9 |
The position of each graphic (image, chart or gradient). These properties (maximum of nine) can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Custom Paint n → Image/Chart Position n. |
Fill Color |
The color of the node. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Fill Color. |
Label Color |
The color of the node label. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Label Color. |
Selected Paint |
The fill color of the node when selected. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Selected Paint. |
Shape |
The shape of the node. |
Shape (Compound Node) |
The shape of the compound node (a node that contains other nodes). |
Size |
The size of the node. Width and height will be equal. This property is mutually exclusive of Node Height and Node Width. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Size. |
Image/Chart Size 1-9 |
The size of the related node Image/Chart. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Image/Chart Size n. |
Height |
The height of the node. Height will be independent of width. This property is mutually exclusive of Node Size. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Height. |
Width |
The width of the node. Width will be independent of height. This property is mutually exclusive of Node Size. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Width. |
Fit Custom Graphics to node |
Toggle to fit Image/Chart size to node size. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Fit Custom Graphics to node. |
Lock node width and height |
Toggle to ignore Width and Height, and to use Size for both values. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Lock node width and height. |
Tooltip |
The text of the tooltip that appears when a mouse hovers over the node. |
Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the node. Zero means totally transparent, and 255 means totally opaque. |
Visible |
Hides the node if set to false. By default, this value is set to true. |
X Location |
X location of the node. Default value of this will be ignored. The value will be used only when mapping function is defined. |
Y Location |
Y location of the node. Default value of this will be ignored. The value will be used only when mapping function is defined. |
Z Location |
Z location of the node. Default value of this will be ignored. The value will be used only when mapping function is defined. |
Edge Properties |
Description |
Bend |
The edge bend. Defines how the edge is rendered. Users can add multiple handles to define how to bend the edge line. |
Curved |
If Egde Bend is defined, edges will be rendered as straight or curved lines. If this value is set to true, edges will be drawn as curved lines. |
Label |
The text used for the edge label. |
Label Font Face |
The font used for the edge label. |
Label Font Size |
The size of the font used for the edge label. |
Label Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the edge label. Zero means totally transparent, and 255 means totally opaque. |
Line Type |
The type of stoke used to render the line (solid, dashed, etc.) |
Paint |
The color of the whole edge (including the stroke and arrows) when it is selected or unselected. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Paint. |
Color (Selected) |
The color of the whole edge (stroke and arrows) when selected. This property can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Selected) → Color (Selected). |
Source Arrow Selected Paint |
The selected color of the arrow on the source node end of the edge. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Selected) → Source Arrow Selected Paint. |
Stroke Color (Selected) |
The color of the edge line when selected. It can be added to the list from the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Selected) → Stroke Color (Selected). |
Target Arrow Selected Paint |
The selected color of the arrow on the target node end of the edge. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Selected) → Target Arrow Selected Paint. |
Color (Unselected) |
The color of the whole edge (stroke and arrows) when it is not selected. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Unselected) → Color (Unselected). |
Source Arrow Unselected Paint |
The color of the arrow on the source node end of the edge. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Unselected) → Source Arrow Unselected Paint. |
Stroke Color (Unselected) |
The color of the edge line. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Unselected) → Stroke Color (Unselected). |
Target Arrow Unselected Paint |
The color of the arrow on the target node end of the edge. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Unselected) → Target Arrow Unselected Paint. |
Label Color |
The color of the edge label. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Label Color. |
Source Arrow Shape |
The shape of the arrow on the source node end of the edge. |
Target Arrow Shape |
The shape of the arrow on the target node end of the edge. |
Tooltip |
The text of the tooltip that appears when a mouse hovers over the edge. |
Transparency |
The opacity of the of the edge. Zero means totally transparent, and 255 means totally opaque. |
Visible |
Hides the edge if set to false. By default, this value is set to true. |
Width |
The width of the edge line. |
Edge color to arrows |
If true then Color (Unselected) is used for the whole edge, including its line and arrows. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Paint → Color (Unselected) → Edge color to arrows. |
Network Properties |
Description |
Background Paint |
The background color of the network view. |
Center X Location |
The X location of network view center. |
Center Y Location |
The Y location of network view center. |
Edge Selection |
Edges are selectable or not. If this is false, users cannot select edges. |
Node Selection |
Nodes are selectable or not. If this is false, users cannot select nodes. |
Scale Factor |
The zoom level of the network view. |
Size |
The size (width and height) of the network view. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Size. |
Height |
The height of the network view. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Height. |
Width |
The width of the network view. It can be found in the drop-down menu Properties → Size → Width. |
Title |
The title of the network view. |
Available Shapes and Line Styles
Available Shapes and Line Styles |
Sample |
Node Shapes |
|
Line Types |
|
Arrow Shapes |
|
How Mappings Work
For each property, you can specify a default value or define a dynamic mapping. Cytoscape currently supports three different types of mappings:
Passthrough Mapping
- The values of network column data are passed directly through to properties. A passthrough mapping is typically used to specify node/edge labels. For example, a passthrough mapping can label all nodes with their common gene names.
Discrete Mapping
- Discrete column data are mapped to discrete properties. For example, a discrete mapping can map different types of molecules to different node shapes, such as rectangles for gene products and ellipses for metabolites.
Continuous Mapping
- Continuous data are mapped to properties. Depending on the property, there are three kinds of continuous mapping:
Continuous-to-Continuous Mapping: for example, you can map a continuous numerical value to node size.
Color Gradient Mapping: This is a special case of continuous-to-continuous mapping. Continuous numerical values are mapped to a color gradient.
Continuous-to-Discrete Mapping: for example, all values below 0 are mapped to square nodes, and all values above 0 are mapped to circular nodes.
- However, note that there is no way to smoothly morph between circular nodes and square nodes.
- Continuous data are mapped to properties. Depending on the property, there are three kinds of continuous mapping:
The table below shows mapping support for each property.
Legend
Symbol |
Description |
- |
Mapping is not supported for the specified property. |
+ |
Mapping is fully supported for the specified property. |
o |
Mapping is partially supported for the specified property. Support for “continuous to continuous” mapping is not supported. |
Node Mappings
Node Property |
Passthrough Mapping |
Discrete Mapping |
Continuous Mapping |
|
Color |
Fill Color |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Transparency |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Border Paint |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Border Transparency |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Label Color |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Label Transparency |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Numeric |
Size/Width/Height |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Label Font Size |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Border Width |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Label Width |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Padding (Compound Node) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Image/Chart Size |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Other |
Border Line Type |
+ |
+ |
o |
Shape |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Shape (Compound Node) |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Label |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Tooltip |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Label Font Face |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Label Position |
- |
+ |
o |
|
Nested Network Image Visible |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Image/Chart |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Image/Chart Position |
- |
+ |
o |
|
Edge Mappings
Edge Properties |
Passthrough Mapping |
Discrete Mapping |
Continuous Mapping |
|
Color |
Color |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Transparency |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Target Arrow Color |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Source Arrow Color |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Label Color |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Label Transparency |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Numeric |
Width |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Label Font Size |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Label Width |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Other |
Line Type |
+ |
+ |
o |
Bend |
- |
+ |
o |
|
Curved |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Source Arrow Shape |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Target Arrow Shape |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Label |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Tooltip |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Label Font Face |
- |
+ |
o |
|
Text Passthrough Mapping
In Cytoscape 2.8.0 and later versions, the Passthrough Mapping can recognize some text representations of values. This means, if you have a string column named Node Size Values, you can directly map those values as the Node Size by setting "Node Size Values" as controlling column with Node Size "Passthrough Mapping". The following value types are supported:
Colors: Standard color names supported by all browsers or RGB representation in hex
Numerical Values: Automatically mapped to the specified property.
Images: URL String. If the URL is valid and an actual image data exists there, Cytoscape automatically downloads the image and maps it to the node.
Examples
- Color Passthrough Mapping
- Node Size Passthrough Mapping
- Image Passthrough Mapping
Images, Charts and Gradients
Cytoscape allows you to set custom graphics to nodes. Using the Style interface, you can map Image/Chart properties to nodes like any other property. Cytoscape provides a set of images and you can also add your own images in the Image Manager, as well as remove or modify existing ones.
Taxonomy Icon set used in this section is created by Database Center for Life Science (DBCLS) and is distributed under Creative Commons License (CC BY 2.1.)
Managing Images
The Image Manager is available under the menu option View → Open Image Manager...:
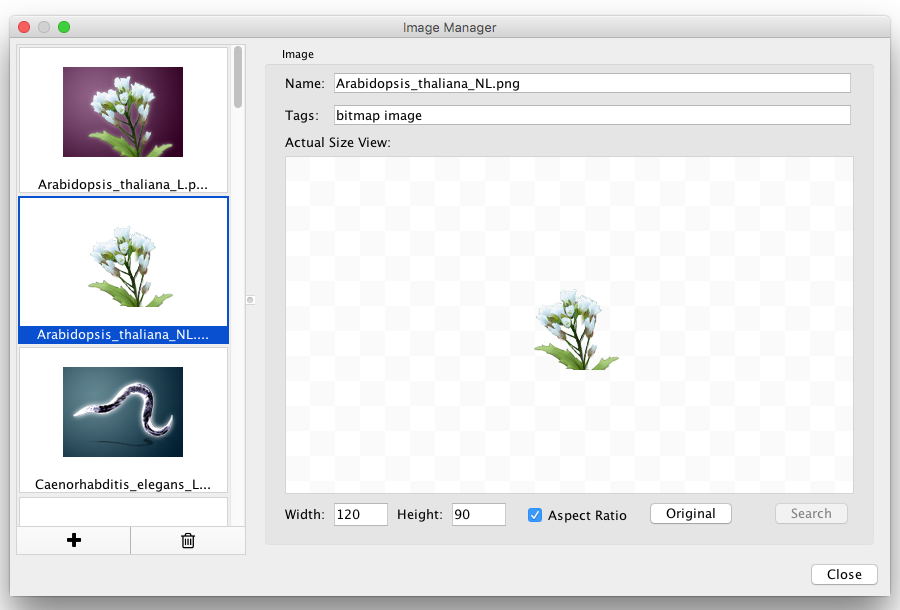
- You can add images by drag-and-drop of image files and URLs. If you want to add images from a web browser or local file system, you can drag images from them and drop those images onto the list of images on the left.
Note: When you drag and drop images from web browser, make sure that you are actually dragging the URL for the image. In some cases, images are linked to an HTML page or scripts, and in such cases, this drag and drop feature may not work.
If you want to add one or more images from a folder, press the + button on the bottom of the Image Manager window and then select the images you want to add.
To remove images from the current session's image library, simply select one or more images from the list and press the Remove Selected Images button (trash icon).
Images can be resized by defining specific Width and Height values. If the Aspect Ratio box is checked, the width-height ratio is always synchronized. You can resize the image to the original size by pressing the Original button.
Using Graphics in Styles
Node graphics are used and defined like any other property, through the Style interface. There are nine Image/Chart properties.
Cytoscape provides three kinds of graphics (selectable via tabs on the Graphics dialog):
Images: You can select one of the provided images or add your own (click the Open Image Manager... button to add more images to the list).
Charts: The following chart types are available:
 Bar ,
Bar ,  Box,
Box,  Heat Map,
Heat Map,  Line,
Line, 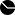 Pie,
Pie,  Ring.
Ring. Gradients: You can also set Linear and Radial gradients to nodes.
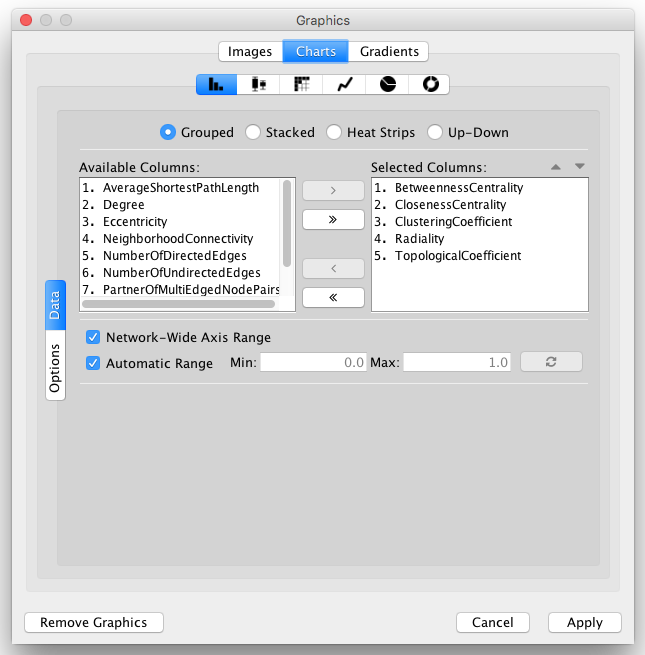
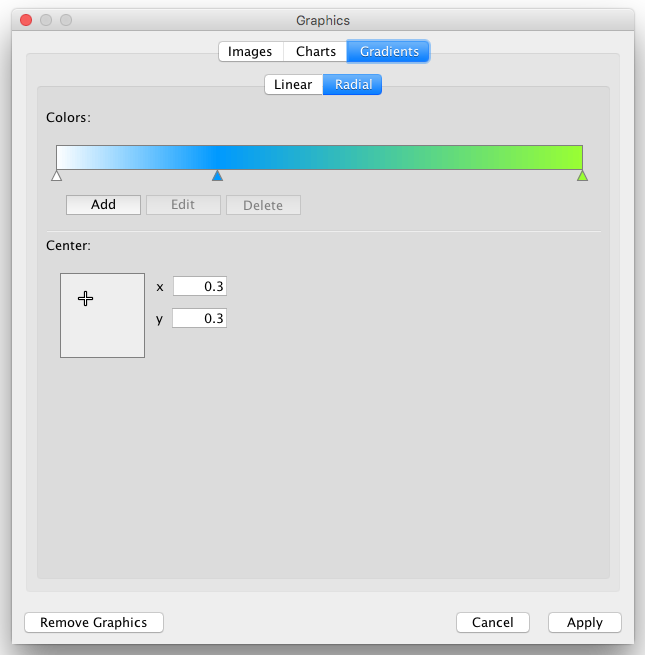
To add a graphic, first add one Image/Chart property to the properties list in the Style interface (on the Node tab, select Properties → Paint → Custom Paint n → Image/Chart n). Next, click the Default Value column of the Image/Chart property to bring up the Graphics dialog. Select an image, a chart or a gradient and then click Apply.
By default, graphics are automatically resized to be consistent with the Node Size property.
To remove an image, chart or gradient, click the Remove Graphics button on the Graphics dialog.
Graphics Positions
Each Image/Chart property is associated with a position. You can edit its position by using the UI available in the Default Value column for the Image/Chart Position property that has the same number. For instance, the Image/Chart Position 2 value modifies the position of Image/Chart 2.
Note: Setting graphics positions for Linear or Radial gradients has no effect, as they are always centered on the node.
Z-Ordering
The number that appears with the Image/Chart property represents an ordering of layers. Basic node color and shape are always rendered first, then node Image/Chart 1, 2, ..., through 9.
Saving and Loading Images
In general, saving and loading images is automatic. When you quit Cytoscape, all of the images in the Image Manager will be saved automatically. There are two types of saving:
- To a session file
When you save the current session to a file, the images used in the current styles will be saved to that file. For example, if you have a style with a discrete mapping for Image/Chart 1, all images used in the style will be saved to the session file. Other images will not be saved in your session file. This is because your image library can be huge when you add thousands of images to the Image Manager and it takes a very long time to save and load the session file.
Automatic saving to CytoscapeConfiguration/images3 directory
When you select File → Quit (Windows and Linux) or Cytoscape → Quit Cytoscape (Mac OS X), all of the images in the Image Manager will be saved automatically to your Cytoscape settings directory. Usually, they are saved in YOUR_HOME_DIRECTORY/CytoscapeConfiguration/images3.
In any case, images will be saved automatically to your system or session and will be restored when you restart Cytoscape or load a session.
Styles Tutorials
The following tutorials demonstrate some of the basic Style features. Each tutorial is independent of the others.
Tutorial 1: Creating a Basic Style and Setting Default Values
The goal of this tutorial is to learn how to create a new Style and set some default values.
Load a sample network: From the main menu, select File → Import → Network → File..., and select sampleData/galFiltered.sif.
Create some node/edge statistics: The Network Analyzer calculates some basic statistics for nodes and edges. From the main menu, select Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network, and click OK. Once the result is displayed, simply close the window. All statistics are stored as regular table data.
Select the Style panel in the Control Panel.
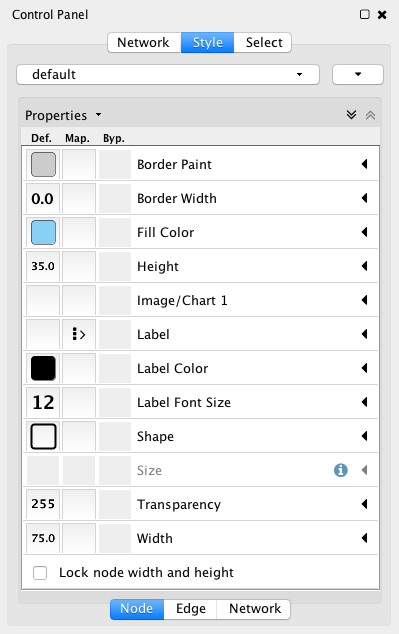
Create a new style: Click the Options
 drop-down, and select Create New Style. Enter a name for your new style when prompted.
drop-down, and select Create New Style. Enter a name for your new style when prompted. 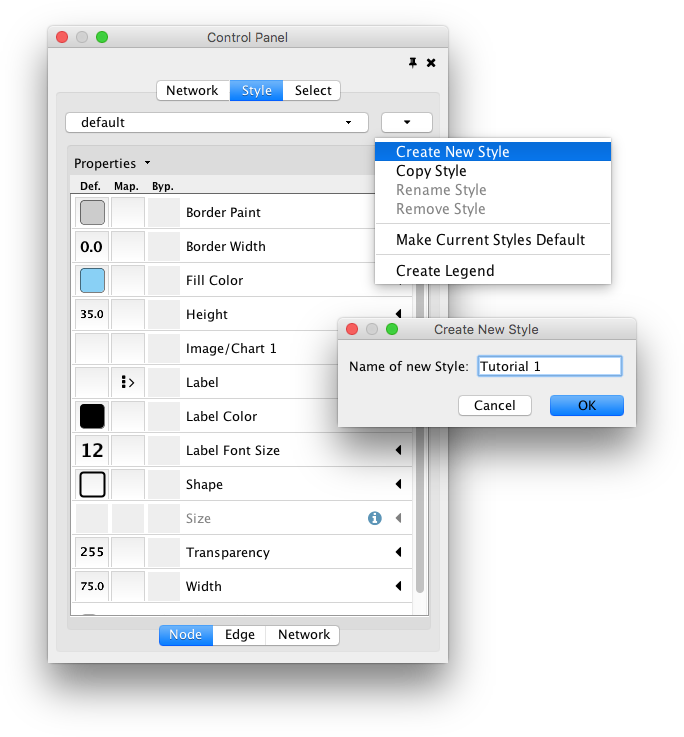
Since no mappings are set up yet, only default values are defined for some of the properties. From this panel, you can create node/edge mappings for all properties.
Change the default node color and shape: To set the default node shape to triangles, click the Default Value column for the Shape property. A list of available node shapes will be shown. Select the Triangle item and click the Apply button. You can edit other default values in the same way. In the example shown below, the node shape is set to Round Rectangle, while Fill Color is set to white. The new Style is automatically applied to the current network, as shown below.
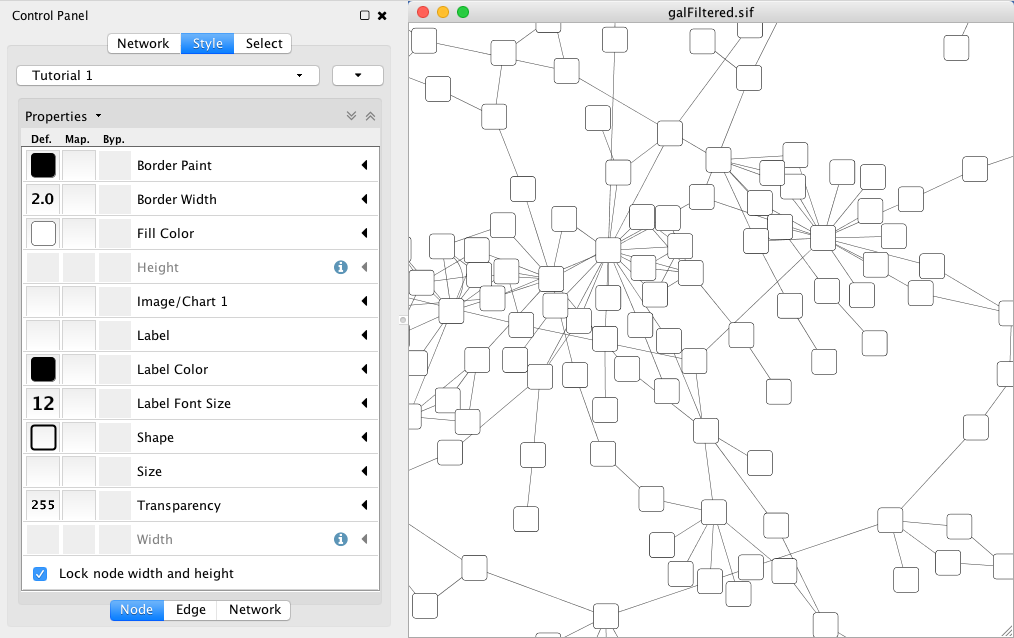
Tutorial 2: Creating a New Style with a Discrete Mapping
Now you have a network with a new Style. The following section demonstrates how to create a new style that has a discrete mapping. The goal is to draw protein-DNA interactions as dashed lines, and protein-protein interactions as solid lines.
Find the property: In the Edge tab of the Style panel, find the Stroke Color (Unselected) property. If it is not already visible in the properties sheet, add it by selecting the drop-down item Properties → Paint → Color (Unselected) → Stroke Color (Unselected).
Choose a data column to map to: Expand the entry for Stroke Color (Unselected) by clicking the arrow icon on the right. Click the Column entry and select "interaction" from the drop-down list that appears.
Set the mapping type: Under Mapping Type, select "Discrete Mapping". All available column values for "interaction" will be displayed, as shown below.
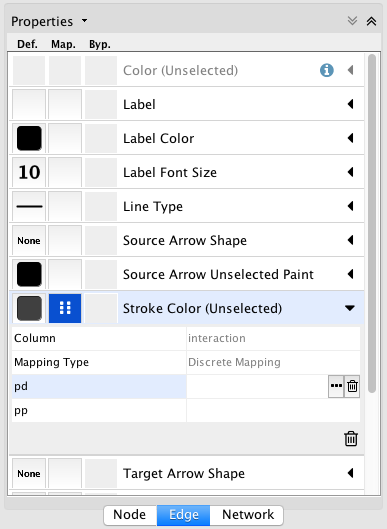
Set the mapped values: Click the empty cell next to "pd" (protein-DNA interactions). On the right side of the cell, click on the ... button that appears. A popup window will appear; select green or similar, and the change will immediately appear on the network window.
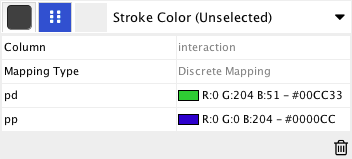
Repeat step 4 for "pp" (protein-protein interactions), but select a darker color. Then repeat steps 3 through 4 for the Line Type property, by selecting the correct line style ("Dash" or "Solid") from the list.
Now your network should show "pd" interactions as dashed green lines and "pp" interactions as solid lines. A sample screenshot is provided below.
Tutorial 3: Creating a New Style with a Continuous Mapping
At this point, you have a network with some edge mappings. Next, let's create mappings for nodes. The following section demonstrates how to create a new style using a continuous mapping. The goal is to superimpose node statistics (in this example, node degree) onto a network and display it along a color gradient.
Find the property: In the Node tab of the Style panel, find the Fill Color property. If it is not already visible in the properties sheet, add it by selecting the drop-down item Properties → Paint → Fill Color.
Set the node table column: Expand the entry for Fill Color by clicking the arrow icon on the right. Click the Column entry and select "Degree" from the drop-down list that appears.
Set the mapping type: Set the "Continuous Mapping" option as the Mapping Type. This automatically creates a default mapping.
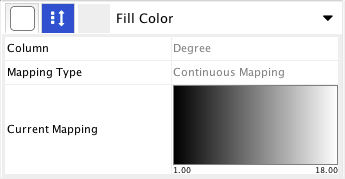
Define the points where colors will change: Double-click on the black-and-white gradient rectangle next to Current Mapping to open the Continuous Mapping Editor. Note the two smaller triangles at the top of the gradient.
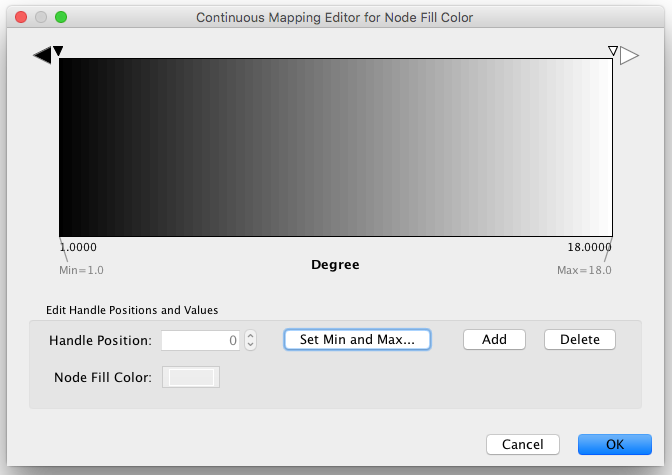
Define the colors between points: Double-click on the larger leftmost triangle (facing left) and a color palette will appear. Set the color white and repeat for the smaller left-side triangle. For the triangle on the right, set the color green and then choose the same color for the smaller right-side triangle.
The color gradients will immediately appear on the network. All nodes with degree 1 will be set to white, and all values between 1 and 18 will be painted with a white/green color gradient (see the sample screenshot below).
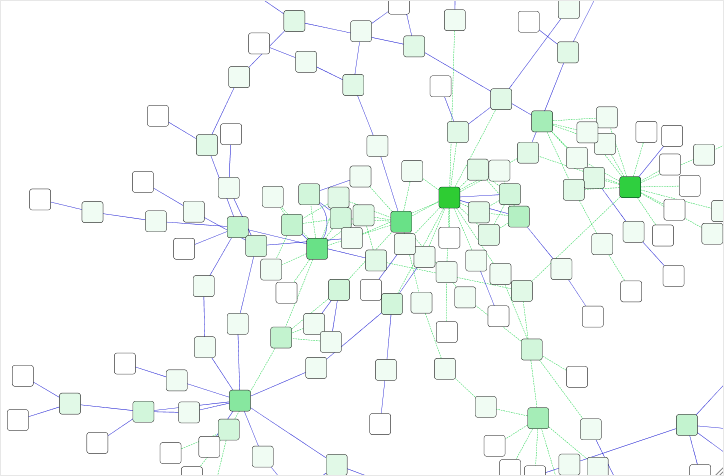
Repeat for other properties: You can create more continuous mappings for other numeric table data. For example, edge data table column "EdgeBetweenness" is a number, so you can use it for continuous mapping. The following is an example visualization which mapps Edge Width to "EdgeBetweenness".
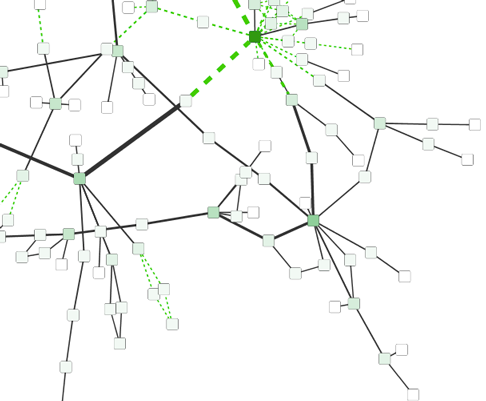
Tutorial 4: Setting Automatic Values to a Discrete Mapping
The goal of this section is to learn how to generate automatic values for discrete mappings.
Switch the Current Style to Minimal. Now your network looks like the following:
Create a discrete mapping for Fill Color. Select "AverageShortestPathLength" (generated by the Network Analyzer) as the controlling property.
Right-click the Fill Color cell, then select Mapping Value Generators → Rainbow. Cytoscape will automatically generate different colors for all the property values as shown below:
Create a discrete mapping for Label Font Size. Select "AverageShortestPathLength" as controlling property (Column field).
Right-click the Label Font Size cell, then select Mapping Value Generators → Number Series. Type 3 for the first value and click OK. Enter 3 for increment.
Apply Layout → yFiles Layouts → Organic. The final view is shown below:
This mapping generator utility is useful for categorical data. The following example shows a discrete mapping that maps the species column to node color.
Tutorial 5: Using Images in Styles
This tutorial is a quick introduction to the node image feature. You can assign up to nine images per node as a part of a Style.
In this first example, we will use the presets that Cytoscape 3 has. In general, you can use any type of bitmap graphics. User images should be added to the Image Manager before using them in a Style.
If you are continuing from the previous tutorials, skip to the next step. Otherwise, load a network and run the Network Analyzer (Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network...). This creates several new table columns (statistics for nodes and edges).
Click the Style panel in the Control Panel, and select the Solid style.
If the property Image/Chart 1 is not in the properties sheet yet, add it from the drop-down Properties → Paint → Custom Paint 1 → Image/Chart 1.
Click the Default Value cell of the Image/Chart 1 entry in order to open the Graphics dialog.
Select any of the images from the list and click Apply.
Click the Default Value cell of node Transparency and set the value to zero.
Set the Default Value of node Size to 80.
Set the Default Value of node Label Font Size to 10, to increase readability.
Also change the edge Width to 6. Now your network looks like the following:
Open the Image Manager under View → Open Image Manager.... Drag and Drop this
 icon to the image list which automatically adds it to the manager.
icon to the image list which automatically adds it to the manager. 
Create a Continuous Mapping for Image/Chart 2 and select "BetweennessCentrality" as its controlling property. Double-click the Current Mapping value cell to open the Continuos Mapping Editor.
In the Continuos Mapping Editor, add a handle position by clicking in the Add button, and move the handle to 0.2. Double-click the region over 0.2 and set the new icon you have just added in the last step.
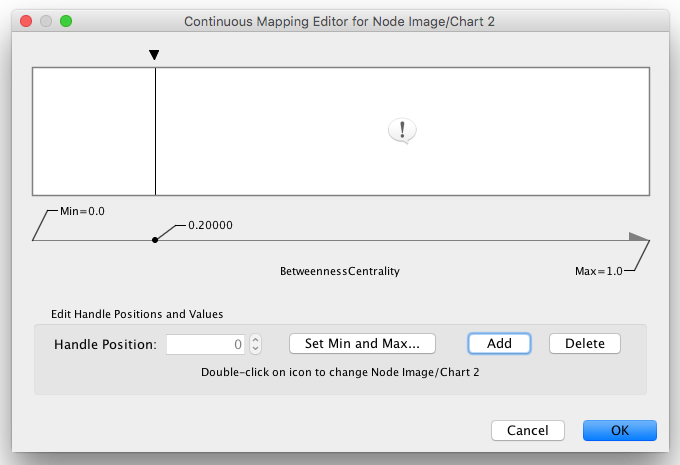
Add the property Image/Chart Position 2 from the drop-down option Properties → Paint → Custom Paint 2 → Image/Chart Position 2. Click its Default Value cell to move the position of the graphics to upper left.
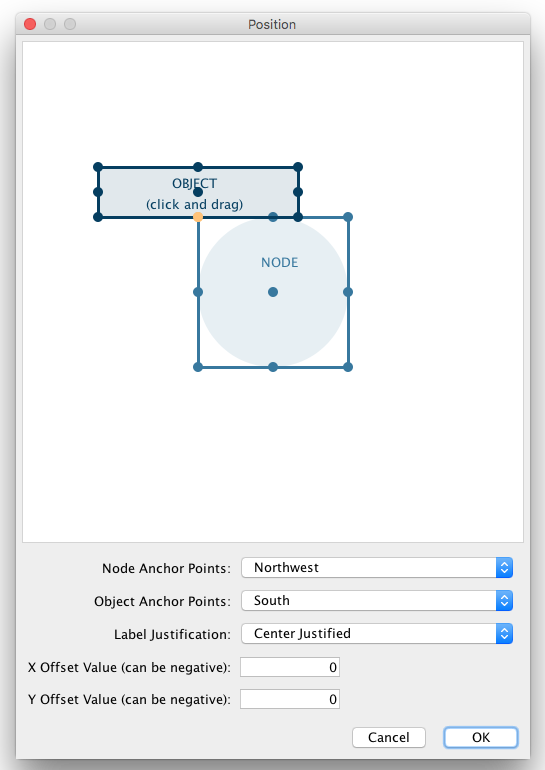
Now the important nodes in the network (nodes with high betweenness centrality) are annotated with the icon:
Tutorial 6: Creating Node Charts
The goal of this tutorial is to learn how to create and customize node charts from data stored in the Node tables.
Start a new session and load a sample network. From the main menu, select File → Import → Network → File..., and select sampleData/galFiltered.sif.
Create some node/edge statistics using the Network Analyzer. Network Analyzer calculates some basic statistics for nodes and edges. From the main menu, select Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network..., and click OK. Once the result is displayed, simply close the window. All statistics are stored as regular table data.
Select the Style panel in the Control Panel.
Create a new style: Click the Options
 drop-down, and select Create New Style. Enter a name for your new style when prompted.
drop-down, and select Create New Style. Enter a name for your new style when prompted. If the property Image/Chart 1 is not in the properties sheet yet, add it from the drop-down Properties → Paint → Custom Paint 1 → Image/Chart 1.

Click the Default Value cell of the Image/Chart 1 entry in order to open the Graphics dialog.

Click the Charts tab and make sure the Bar Chart option is selected.
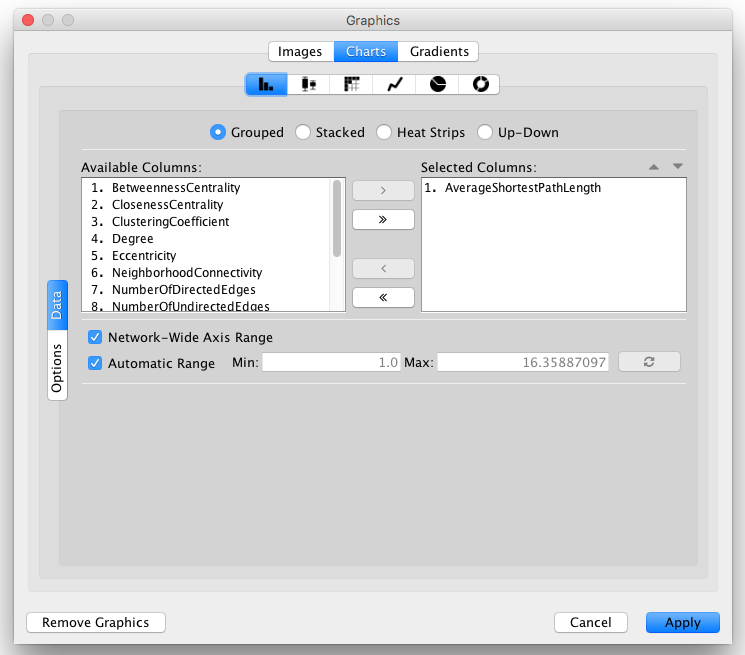
Select data columns: Now you have to choose the columns in the Node table that contains the data you want to be displayed as charts. The Available Columns list displays all node columns that can be used as chart data (i.e. single or list columns of numerical types).
First click the Remove All button to remove the current selected columns (by default, Cytoscape selects the first column in the Available Columns list).
Now select all centrality and coefficient columns from Available Columns list and click the Add Selected button.
Click the Apply button to create bar charts with the selected data columns and default options.
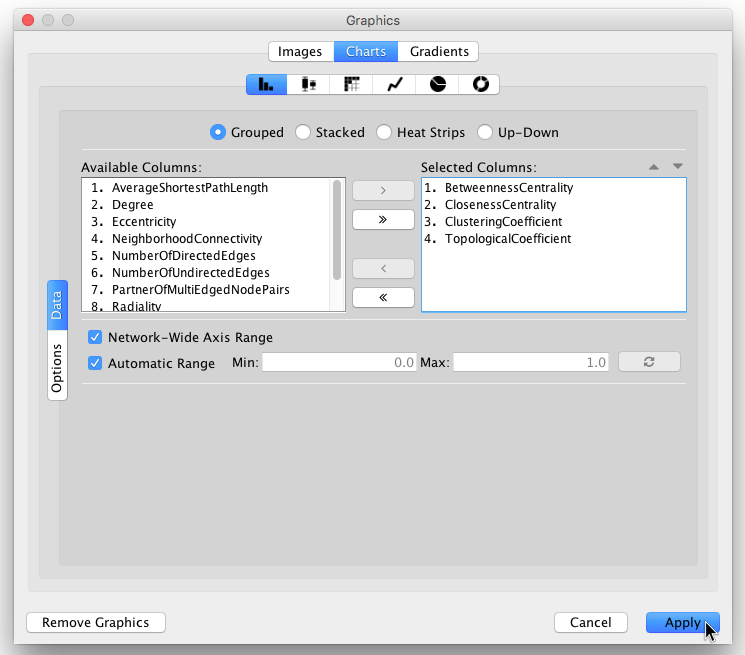
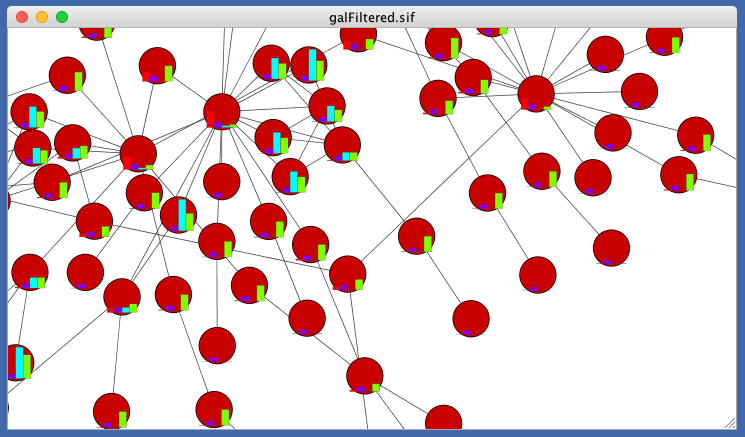
The network view doesn't look so good yet, so let's make a few changes to its Style before we continue. In the example shown below, the node Shape is set to Rectangle, while the node Fill Color is set to white.
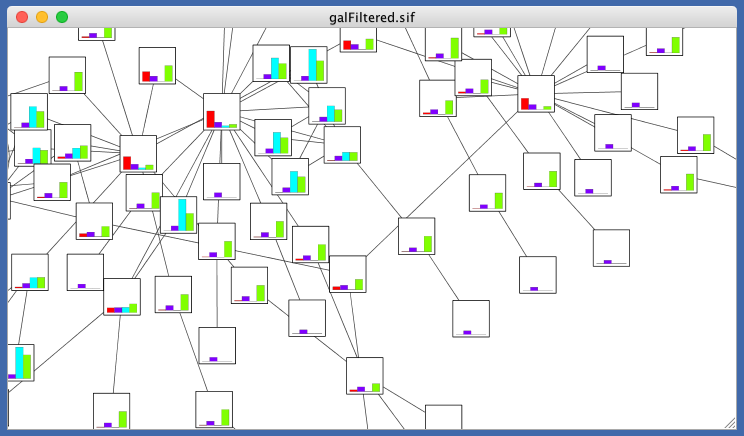
- Focus on one node to see the chart details. For example search for and then focus on node "YMR043W".
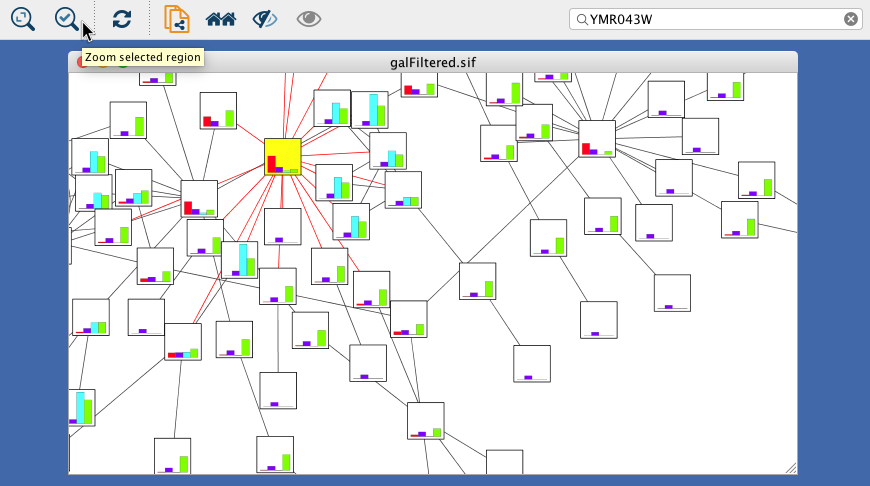
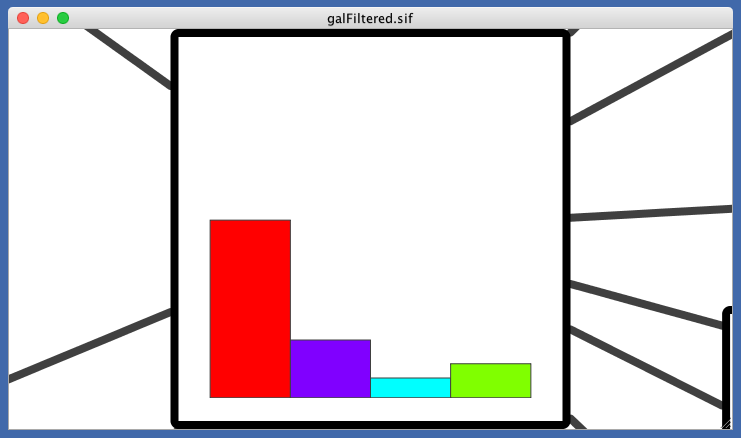
Change other chart options: Click the Default Value cell of the Image/Chart 1 property again in order to open the Graphics dialog, and then select the Options tab on the Bar Chart editor.
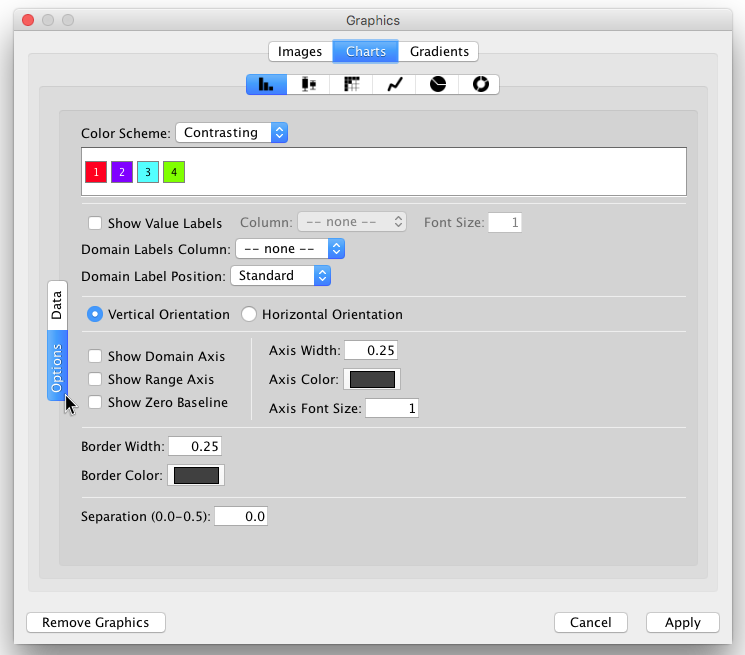
On this panel, you can:Choose another Color Scheme or set all the colors individually (just click on each color).
Show/Hide Value and Domain Labels and also set the Domain Label Position.
Change the chart Orientation.
- Show/Hide Axes.
- Change the line width and color for axes and bars.
- Increase or reduce the separation between bars (up to 50% of the total chart width).
Note: Other charts provide different options.
Check both Show Domain Axis and Show Range Axis and apply the graphics again. Now the node chart should look like this:
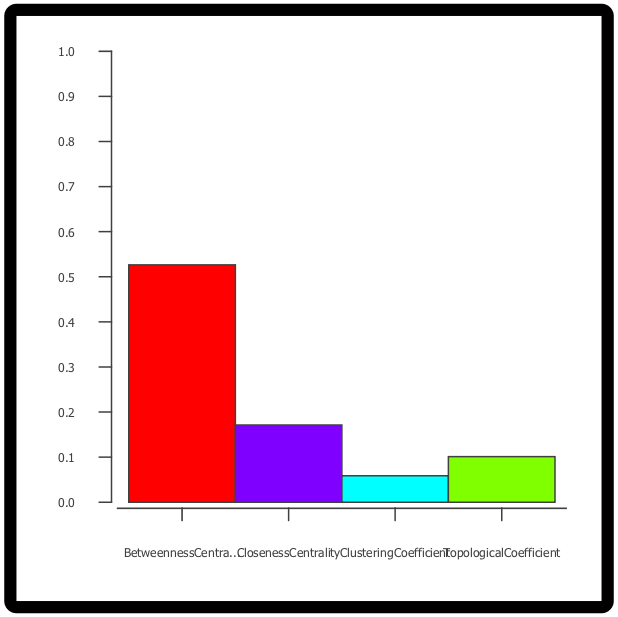
- The default domain labels are not very useful, so let's set better labels:
On the Node Table (Table Panel), create a new List Column of type String and name it "domain_labels".
Edit any of the cells of the created column (double-click it) and type ["Bet. Cent.","Closen. Cent","Clust. Coeff.","Topol. Coeff."].
Right-click the same cell and select the option Apply to entire column.
Open the chart editor again and select the Options panel.
Select "domain_labels" on the Domain Labels Column drop-down button.
Select "Up 45o" on the Domain Labels Position drop-down button. The labels should look like this now:
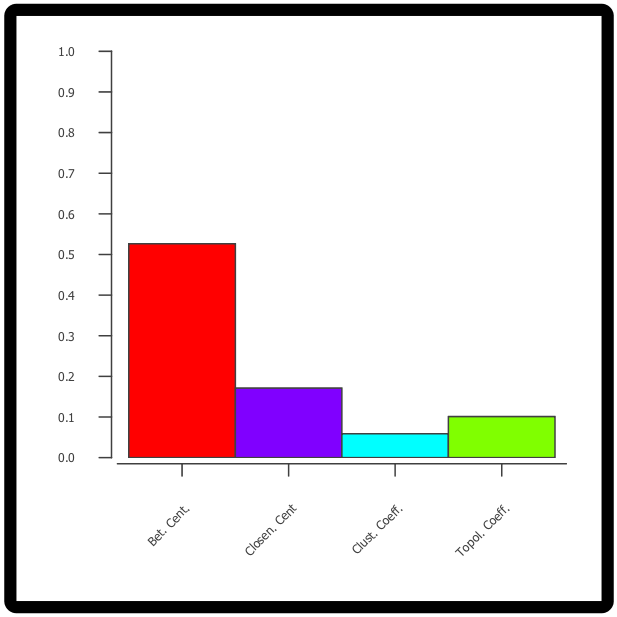
Advanced Topics
Discrete Mappings
Several utility functions are available for Discrete Mappings. You can use these functions by right-clicking on any property entry (shown below).
Automatic Value Generators
Mapping Value Generators - Functions in this menu category are value generators for discrete mappings. Users can set values for discrete mappings automatically by selecting these functions.
Rainbow and Rainbow OSC - These functions try to assign as diverse a set of colors as possible for each data value.
Random Numbers and Random Colors - Randomized numbers and colors.
Number Series - Set a series of numbers to the specified mapping. Requires a starting number and increment.
Fit label width - This function is only for node Width and Size. When a discrete mapping for node Width or Size is available, you can fit the size of each node to its label automatically by selecting this function. See the example below:
Edit Selected Values at Once
You can set multiple values at once. First, you need to select discrete mapping rows in which you want to change values then right-click and select Edit → Edit Selected Discrete Mapping Values. A dialog pops up and you can enter the new value for the selected rows.
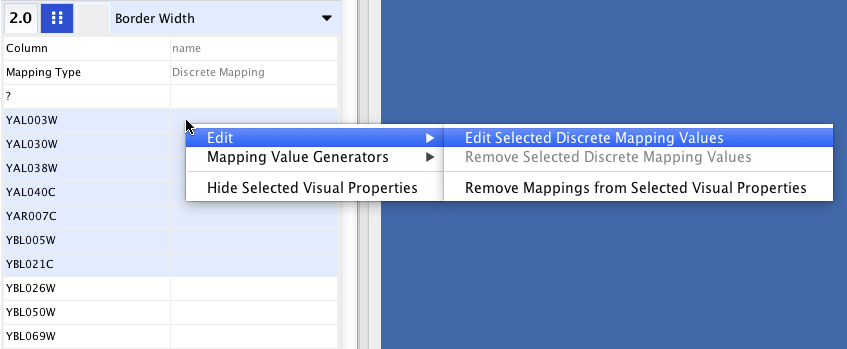
Working with Continuous Mapping Editors
There are three kinds of Continuous Mapping Editors. Each of them are associated with a specific property type:
Editor Type |
Supported Data Type |
Properties |
Color Gradient Editor |
Color |
node/edge/border/label colors |
Continuous-Continuous Editor |
Numbers |
size/width/transparency |
Continuous-Discrete Editor |
All others |
font/shape/text/graphics/position/etc. |
Range Settings Panel
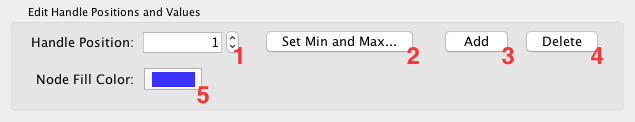
Each continuous mapping editor has a range settings section (labelled Edit Handle Positions and Values) with the following fields and buttons.
Handle Position - This box displays the current value for the selected slider handle. You can also directly type the value in this box to move the slider to an exact location.
Set Min and Max... - Click this button to set the overall range of this editor. The first time you open the editor, the Min and Max values are set by the range of the data column you selected (i.e. the minimum and maximum values of the mapped column).
Add - Adds a new handle to the editor.
Delete - Deletes the selected handle from the slider widget.
Handle Value (e.g. Node Fill Color) - Click this button to edit the value (e.g. a color) assigned to the selected handle.
Gradient Editor
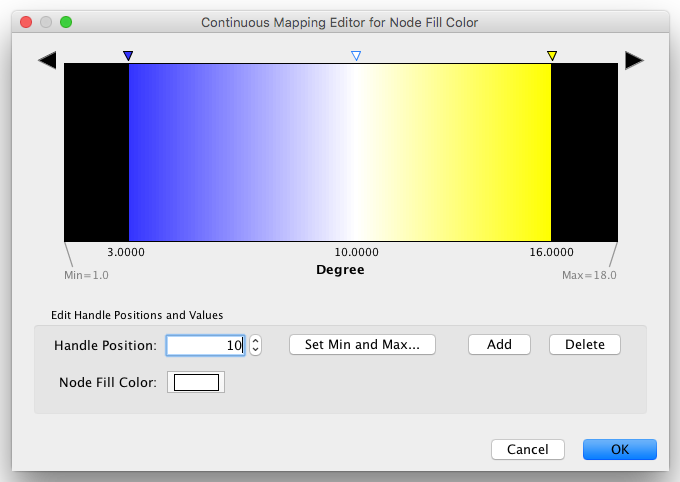
The Gradient Editor is an editor for creating continuous mappings for colors. To change the color of each region, just double-click the handles (small triangles on the top). A Color gradient will be created only when the editor has two or more handles (see the example below).
1 handle (no gradient) |
2 handles |
|
|
Continuous-Continuous Editor
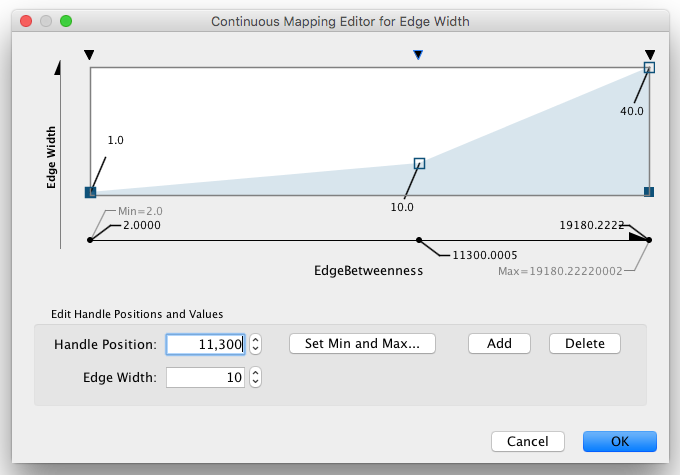
The Continuous-Continuous Editor is for creating mappings between numerical data and numerical properties (e.g. size, transparency). To change the value assigned on the Y-axis (the property shown in the example above is edge Width), drag the small squares or double-click them to directly type an exact value.
Continuous-Discrete Editor
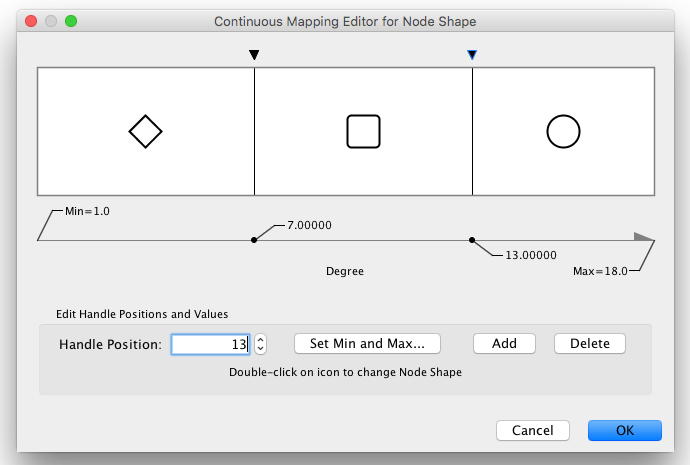
The Continuous-Discrete Editor is used to create mappings from numerical column values to discrete properties, such as fonts, shapes, or line styles. To edit a value for a specific region, double-click the icon on the track.
Managing Styles
All Cytoscape Style settings are initially loaded from a default file that cannot be altered by users. When users make changes to the properties, a session_syle.xml file is saved in the session file. This means that if you save your session, you will not lose your properties. No other style files are saved during normal operation.
Saving Styles
Styles are automatically saved with the session they were created in. Before Cytoscape exits, you will be prompted to make sure you save the session before quitting. It is also possible to save your styles in a file separate from the session file. To do this, navigate to the menu option File → Export → Styles..., and save the selected styles to a file. This feature can be used to share styles with other users.
You can also change the default list of styles for all future sessions of Cytoscape. To do this, click the Options  drop-down in the Style section, and select Make Current Styles Default. This will save the current styles as a default_vizmap.xml file to your CytoscapeConfiguration directory (found in your home directory). These styles will then be loaded each time Cytoscape is started.
drop-down in the Style section, and select Make Current Styles Default. This will save the current styles as a default_vizmap.xml file to your CytoscapeConfiguration directory (found in your home directory). These styles will then be loaded each time Cytoscape is started.
Style File Formats
The Cytoscape-native Style format is Style XML. If you want to share Style files with other Cytoscape users, you need to export them to this format.
From version 3.1.0 on, Cytoscape can also export Cytoscape.js compatible JSON file. Since Cytoscape.js is an independent JavaScript library, and there are some differences between Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js, not all properties are mapped to JSON. The following properties are not supported by the exporter:
- Custom Graphics and their locations
- Edge Bends
- Nested Networks
- Network Background (Note: This can be set manually as standard CSS in Cytoscape.js)
The Continuous-Discrete Editor is used to create mappings from numerical data values to discrete properties, such as fonts, shapes, or line styles. To edit a value for a specific region, double-click on the icon on the track.
Importing Styles
To import existing styles, navigate to the menu option File → Import → Styles... and select a styles.xml (Cytoscape 3 format) file. Imported properties will supplement existing properties or override existing ones if the properties have the same name. You can also specify a style file using the -V command line option. Properties loaded from the command line will override any default properties. Note that legacy .props files can only be loaded via the File → Import → Styles... menu, but not by command line.
App Manager
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
What are apps?
Cytoscape's capabilities are not fixed. They can be expanded with apps. They can extend Cytoscape in a variety of ways. One app can have the ability to import data from an online database. Another app could provide a new method for analyzing networks. You can install apps after you have installed Cytoscape. Most apps were made by Cytoscape users like you.
If you're familiar with Cytoscape 2.x, you probably know that Cytoscape apps were called plugins. Starting in Cytoscape 3.0, we are calling them apps. Cytoscape 2.x plugins cannot be used in Cytoscape 3.0.
Installing Apps
You can install apps through the App Store or within Cytoscape. In this section, we'll talk about installing apps through Cytoscape. You can learn how to install apps through the App Store here.
To install apps within Cytoscape, go to the menu bar and choose Apps → App Manager. At the top of the App Manager window, make sure you have the Install tab selected.
There are three ways you can find apps:
If you know the name of an app you're looking for, enter it in the Search field. The App Manager will list the apps whose names or descriptions match the Search field in the middle panel.
If you have a general idea of what sort of app you're looking for, double-click on the apps by tag folder, then click on one of the tags that interests you. The apps with that tag are listed in the middle panel.
If you're not sure what sort of app you and want to see everything, click the all apps folder. In the middle pane, you will see a list of all the apps.
When you click on an app in the middle panel, the App Manager shows its short description and icon in the right panel. If you want more information about the app, click the View on App Store button on the bottom-right. If you want to go ahead and install the app, click the Install button.
If you've downloaded an app to your computer, you can install it by clicking the Install from File button on the bottom-left.
Managing your Installed Apps
You can see a list of all apps you have installed by clicking the Currently Installed tab at the top. When you click on an app in the list, you'll see a description of your app at the bottom. At the bottom, you'll see a couple buttons where you can:
Uninstall an app. This deletes the app from your computer. If you want to reinstall the app, you will have to find it again in the Install from App Store tab or in the App Store site and reinstall it there.
Disable an app. This temporarily disables the app. The app stays on your computer, but Cytoscape does not load it. You can enable the app by first selecting the disabled app in the list, then click Enable.
Command Tool
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Second, and arguably more useful, it will read script files and execute them. Each line in the script file is a command that is sent to a app. Script files may be entered on the Cytoscape command line using the "-S" flag to Cytoscape, through the File → Run Script File... menu item, or through Tools → Execute Command File.
Cytoscape commands consist of three parts: a command class, or namespace; a command within that namespace; and a series of arguments or options provided as a series of name=value pairs. For example, to import an XGMML format file from the Command Line Dialog or a command script, you would use:
network import file filePath="path-to-file"
where network is the namespace, import file is the command, and there is only one argument: filePath="path-to-file". If there were more arguments they would appear on the same line separated by spaces.
The Command Tool also uses the Command API to provide help. "help" by itself will list all of the command classes (or namespaces) and "help " followed by a namespace will list all of the commands supported by that namespace. Details of a specific command are available by typing "help " followed by the namespace and command (e.g. "help layout force-directed"). The Command Tool registers the "command" namespace and supports a single command: run, which takes a file argument. Here is the help for the command run command from the command namespace:
help command run
command run file=<File> Similarly, the help for the "network import file" example from above is:
help network import file network import file arguments: dataTypeList=<String>: List of column data types ordered by column index (e.g. "string,int,long,double,boolean,intlist" or just "s,i,l,d,b,il") defaultInteraction=<String>: Default interaction type delimiters=<ListMultipleSelection [,,;, ,\t]>: Text Delimiters delimitersForDataList=<ListSingleSelection (\||\|/|,)>: Text Delimiters for data list type file=<File>: Data Table file firstRowAsColumnNames=true|false: First row used for column names indexColumnSourceInteraction=<int>: Column for source interaction indexColumnTargetInteraction=<int>: Column for target interaction indexColumnTypeInteraction=<int>: Column for interaction type NetworkViewRendererList=<ListSingleSelection ()>: Network View Renderer RootNetworkList=<ListSingleSelection (-- Create new network collection --|Network)>: Network Collection startLoadRow=<int>: Start Load Row TargetColumnList=<ListSingleSelection ()>: Node Identifier Mapping Column
Merge
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Merge Networks
The Advanced Network Merge interface is available from Tools → Merge → Networks... and allows for merging of two or more networks.
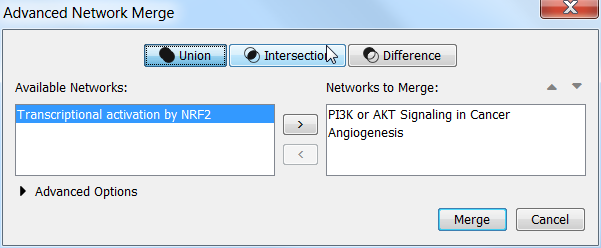
Basic Operations
- With the buttons select either "union", "intersection" or "difference".
Networks available for merge are listed under Networks to merge. Select a network from the list and click the right arrow to transfer the network to Selected networks. Click Merge to continue. The merged network will be displayed as a separate network.
Advanced Options
The Advanced Network Merge interface includes an expandable Advanced Network Merge panel, where you can specify the details of how to merge the networks. The options available here are:
Matching columns: This specifies the network columns that should be used for merging. Typically, the "name" column or some other column containing identifier information is used here.
How to merge columns?: A table lets the user specify for each of the individual network columns, what the corresponding column in the merged network should be named and its data type.
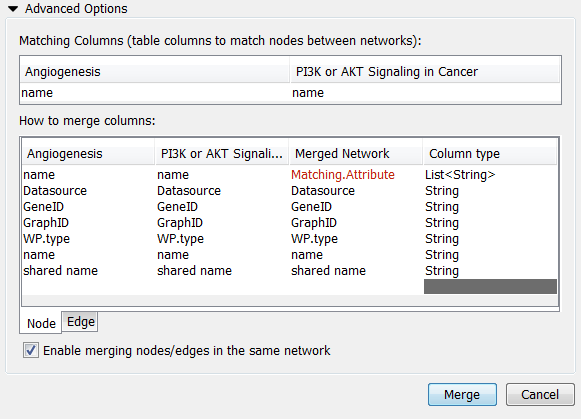
Merge Tables
NetworkAnalyzer
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
- Number of nodes, edges and connected components.
- Network diameter, radius and clustering coefficient, as well as the characteristic path length.
- Charts for topological coefficients, betweenness, and closeness.
- Distributions of degrees, neighborhood connectiveness, average clustering coefficients, shortest path lengths, number of shared neighbors and stress centrality.
NetworkAnalyzer also constructs the intersection, union and difference of two networks. It supports the extraction of connected components as separate networks and the removal of self-loops.
Network Analysis
Analyze Network
To run NetworkAnalyzer, select Tools → NetworkAnalyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network.
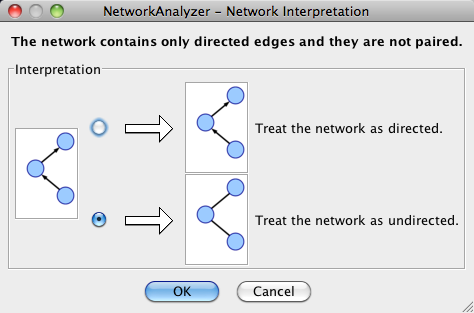
The NetworkAnalyzer will determine whether your network contains directed or undirected edges. At this point, you can choose to ignore edge direction information.
When results are calculated, they will appear in the Results Panel.
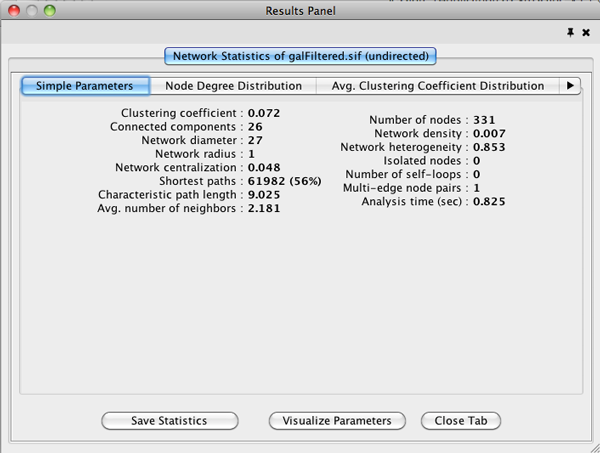
The results have multiple tabs. Details on the network parameters can be found here.
Simple Parameters
Node Degree Distribution
Avg. Clustering Coefficient Distribution
Topological Coefficients
Shortest Path Distribution
Shared Neighbors Distribution
Neighborhood Connectivity Distribution
Betweenness Centrality
Closeness Centrality
Stress Centrality Distribution
You can also save the statistics for later use by using the Save Statistics button.
Analyze Subset of Nodes
An exhaustive topological analysis of very large networks can be a time consuming task. The computation of local parameters for the nodes is significantly faster than the computation of global (path-related) parameters. Examples of local parameters are node degree, neighborhood connectivity, topological and clustering coefficients. Betweenness and closeness centralities, as well as stress, are global parameters.
NetworkAnalyzer provides the Analyze Subset of Nodes option for computing local parameters for a subset of nodes. If one or more nodes in the network are selected before starting an analysis, only the sub-network induced by the selected nodes is analyzed. Moreover, only local parameters are computed. Shared neighbors distribution and shortest path lengths distribution, among others, are not displayed in the results.
Batch Analysis
The Batch Analysis option is used to perform topological analysis on all networks stored in specific directory, using all possible interpretations for every network. Batch analysis consists of three simple steps:
Selecting directories: The user selects the input and output directories. The input directory should contain network files that can be loaded into Cytoscape. Sub-directories of the input directory are not considered. The output directory is the one that will contain all analysis results after the batch analysis. In order to avoid file overwriting, NetworkAnalyzer requires that the output directory is empty (contains no files) before the batch analysis starts.
Analysis: NetworkAnalyzer scans the input directory and loads all supported networks into Cytoscape, one at a time. Each loaded network is inspected and then it is analyzed considering all possible interpretations for it. The analysis step is complete after all networks are analyzed. Note that depending on the number of networks and their sizes, this might be a very time-consuming step.
Inspection of results: After the analysis is complete, the button Show Results is enabled, and it displays the results dialog. The dialog contains a table of all topological analyses performed. Every row in the results table lists the loaded network, its interpretation and the resulting network statistics file that was saved in the output directory. By clicking on a network name and on statistics file name, the user can load the network and topology analysis results, respectively.
Load Network Statistics
Existing network statistics can be loaded from a file saved previously in NetworkAnalyzer.
Plot Parameters
The Plot Parameters dialog offers a possibility to plot two parameters against each other. The parameters to be plotted can be chosen from two drop-down menus. The Table Column 1 menu provides the values for the domain/category axis, and the Table Column 2 menu specifies the values for the range/value axis. The plot is updated each time a different parameter is selected in one of the menus.
Generate Style from Statistics
NetworkAnalyzer computed parameters can be visualized as node/edge size and color, if the Store node / edge parameters in node / edge table option in NetworkAnalyzer Settings is enabled. Parameters loaded from a .netstats file cannot be visualized because the network itself is not stored in the network statistics file. If, after performing topological analysis, the network is modified by introducing or removing nodes or edges, it is recommended (and sometimes required) to run NetworkAnalyzer again before visualizing any parameters.
The visualization is initiated by the Generate Style from Statistics... menu option. There are two ways of mapping computed parameters.
Map to node / edge size: The computed parameter is mapped to the size of the nodes or edges. Mapping can be straight or inverse, that is, low parameter values can be mapped to small sizes or to large sizes. The smallest node size is set to 10 and the largest one to 100. Regarding edges, size reflects the edge line width and varies between 1 and 8. Refer to the Styles section for details.
- Map to node / edge color: A computed parameter is mapped to the color of the nodes or edges. Two mapping styles are possible - mapping low parameter values to bright colors or to dark colors. By default, the brightest color is green and the darkest color is red. The mapping also uses a middle (intermediate) color, which allows for fine-grained perception of differing values through the color gradient. The default middle color is yellow.
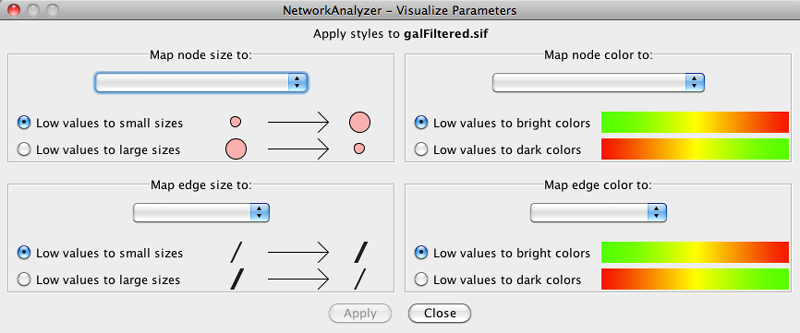
NetworkAnalyzer Settings
The following settings can be configured by the user:
Store node / edge parameters in node / edge table: For every node in a network, NetworkAnalyzer computes its degree (in- and out-degrees for directed networks), its clustering coefficient, the number of self-loops, and a variety of other parameters. NetworkAnalyzer also computes edge betweenness for each edge in the network. If the respective options are enabled, NetworkAnalyzer can stores the computed values as columns of the corresponding nodes and edges. This enables the users to use the values in Styles or to select nodes or edges based on the values. A complete list of the computed node and edge columns is available here.
Use expandable dialog interface for the display of network statistics: If this option is enabled, analysis results are presented in a window in which all charts are placed below each other in expandable boxes. If this option is disabled, analysis results are presented in a window that contains tabs for the group of simple parameters and for every complex parameter (default). Users who wish to simultaneously view two or more complex parameters of one network, should enable this option.
NetworkAnalyzer allows the user to change the default colors of parameter visualization.
Background color for parameter visualization: The color of the background in the network view. It is initially set to the default Cytoscape background color.
Bright color to map parameters: This color defines the brightest color that parameters can be mapped to. By default its value is green.
Middle color: This color defines the intermediate color, that parameters can be mapped to. By default its value is yellow.
Dark color: This color defines the darkest color that parameters can be mapped to. By default its value is red.
Location of the help documents: URL of the original help web page for NetworkAnalyzer. This also enables the local download and storage of this help page.
Subnetwork Creation
NetworkAnalyzer allows for the creation of sub-networks of connected components. The user selects a number of connected components from a list and each selected components is visualized as a sub-network.
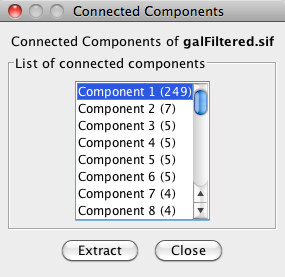
Cytoscape Preferences
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Managing Properties
The Cytoscape properties editor, accessed via Edit → Preferences → Properties…, is used to specify default properties. Any changes made to these properties will be saved in .props files under the CytoscapeConfiguration subdirectory of the user's home directory.
Cytoscape properties are configurable using the Add, Modify and Delete buttons as seen below.
App properties may also be edited in the same way as editing Cytoscape properties. For example, to edit the properties of Linkout, select 'linkout' from the combobox of the Preferences Editor. Some apps may store properties inside session files in addition to (or instead of) storing them in the CytoscapeConfiguration directory.
Managing Bookmarks
Cytoscape contains a pre-defined list of bookmarks, which point to sample network files located on the Cytoscape web server. Users may add, modify, and delete bookmarks through the Bookmark manager, accessed by going to Edit → Preferences → Bookmarks….
There are currently several types of bookmarks (based on data categories), including network and table. Network bookmarks are URLs pointing to Cytoscape network files. These are normal networks that can be loaded into Cytoscape. Table bookmarks are URLs pointing to data table files.
Managing Proxy Servers
You can define and configure a proxy server for Cytoscape by going to Edit → Preferences → Proxy Settings….
After the proxy server is set, all network traffic related to loading a network from URL will pass through the proxy server. Cytoscape apps use this capability as well. The proxy settings are saved in cytoscape3.props. Each time you click the OK button after making a change to the proxy settings, an attempt is made to connect to a well known site on the Internet (e.g., google.com) using your settings. For both success and failure you are notified and for failure you are given an opportunity to change your proxy settings.
If you no longer need to use a proxy to connect to the Internet, simply set the Proxy type to "direct" and click the OK button.
Managing Group View
The configuration of Cytoscape group view may also be edited through Edit → Preferences → Group Preferences….
Linkout
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
The external links are specified in a linkout.props file which is internal to Cytoscape. The defaults include a number of links such as Entrez, SGD, iHOP, and Google, as well as a number of species-specific links. In addition to the default links, users can customize the External Links menu and add (or remove) links by editing the linkout properties (found under Edit → Preferences → Properties...).
External links are listed as ‘key’-‘value’ pairs in the linkout.props file where key specifies the name of the link and value is the search URL. The LinkOut menus are organized in a hierarchical structure that is specified in the key. Linkout key terms specific for nodes start with the keyword nodelinkouturl, for edges this is edgelinkouturl.
For example, the following entry:
nodelinkouturl.Model Organism DB.SGD (yeast)=http://www.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/locus.fpl?locus=%ID%
places the SGD link under the Model Organism DB submenu. This link will appear in Cytoscape as:
In a similar fashion one can add new submenus.
The %ID% string in the URL is a place-holder for the node label. When the popup menu is generated this marker is substituted with the node label. In the above example, the generated SGD link for the YNL050C protein is:
http://www.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/locus.fpl?locus=YNL050C
If you want to query based on a different column, you need to specify a different node label using Styles.
For edges the mechanism is much the same; however here the placeholders %ID1% and %ID2% reflect the source and target node label respectively.
Currently there is no mechanism to check whether the constructed URL query is correct and if the node label is meaningful. Similarly, there is no ID mapping between various identifiers. For example, a link to NCBI Entrez from a network that uses Ensembl gene identifiers as node labels will produce a link to Entrez using the Ensembl ID, which results in an incorrect link. It is the user's responsibility to ensure that the node label that is used as the search term in the URL link will result in a meaningful link.
Adding and Removing Links
The default links are defined in a linkout.props file contained inside the Linkout JAR bundle under the framework/system/org/cytoscape/linkout-impl subdirectory of the Cytoscape installation. These links are normal Java properties and can be edited by going to Edit → Preferences → Properties... and selecting linkout from the box (shown below). Linkouts can be modified, added or removed using this dialog; however, note that the modifications would not be stored in the file. To change a URL permanently, you would need to edit the linkout.props file directly.
In addition, new links can be defined when starting Cytoscape from command line by specifying individual properties. The formatting of the command is cytoscape.sh -P [context_menu_definition]=[link] . context_menu_definition specifies the context menu for showing the linkout menu item. The structure of this definition is "." separated and the first item needs to be either nodelinkouturl or edgelinkouturl. The former will add the linkout item as a node context menu and the latter will add it as an edge context menu. The rest of the definition would define the hierarchy of the menu.
For instance this command:
cytoscape.sh -P nodelinkouturl.yeast.SGD=http://db.yeastgenome.org/cgi-bin/locus.pl?locus\=%ID%
will add this menu item:
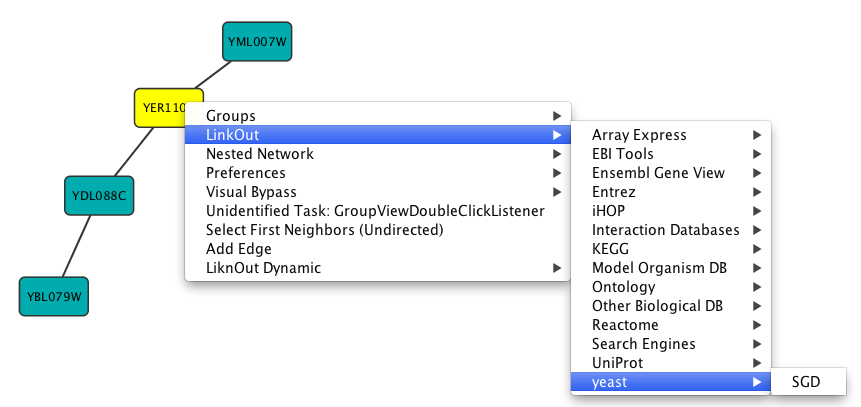
To remove a link from the menu, simply delete the property using Edit → Preferences → Properties... and selecting commandline. Linkouts added in the command line will be available for the running instance of Cytoscape.
Panels
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
What are Panels?
Panels are floatable/dockable panels designed to cut down on the number of pop-up windows within Cytoscape and to create a more unified user experience. They are named based on their functions -- Control Panel, Table Panel, Tool Panel and Result Panel. The following screenshot shows the file galFiltered.sif loaded into Cytoscape, with a force-directed layout, Rotate tools showing in the Tool Panel, and with results from Network Analyzer (Tools → Network Analysis → Analyze Network). The Control Panel (at the left-hand side of the screen) contains the Network Manager, Network Overview, Styles and Select tabs. On the bottom of the panel, there is another panel called Tool Panel. In the Table Panel, the Node Table is shown. In addition, analysis results from Network Analyzer are shown in Result Panel (at the right-hand side).
The user can then choose to resize, hide or float Panels. For example, in the screenshot below, the Network, Table and Results panels are floating and the Tool Panel is hidden:
Basic Usage
Cytoscape includes four Panels: the Control Panel on the left, Tool Panel on the bottom of the Control Panel, the Table Panel on the bottom right, and the Result Panel on the right. By default, only the Control Panel and the Data Panel will appear. The Result Panel may appear, depending on the mix of Cytoscape apps that you currently have installed. The Tool Panel will appear when you select the following commands under the Layout menu: Rotate, Scale, and Align and Distribute.
All panels can be shown or hidden using the View → Show/Hide functions.
In addition, Panels can be floated or docked using icon buttons at the top right corner of each Panel. The Float Window control  will undock any panel which is useful when you want assign the network panel as much screen space as possible. To dock the window again, click the Dock Window icon
will undock any panel which is useful when you want assign the network panel as much screen space as possible. To dock the window again, click the Dock Window icon  . Clicking the Hide Panel icon
. Clicking the Hide Panel icon  will hide the panel; this can be shown again by choosing View → Show and selecting the relevant panel.
will hide the panel; this can be shown again by choosing View → Show and selecting the relevant panel.
Rendering Engine
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
What is Level of Detail (LOD)?
Cytoscape 3.0 retains the rendering engine found in version 2.8. It is to be able to display large networks (>10,000 nodes), yet retain interactive speed. To accomplish this goal, a technique involving level of detail (LOD) is being used. Based on the number of objects (nodes and edges) being rendered, an appropriate level of detail is chosen. For example, by default, node labels (if present) are only rendered when less than 200 nodes are visible because drawing text is a relatively expensive operation. This can create some unusual behavior. If the screen currently contains 198 nodes, node labels will be displayed. If you pan across the network, such that now 201 nodes are displayed, the node labels will disappear. As another example, if the sum of rendered edges and rendered nodes is greater than or equal to a default value of 4000, a very coarse level of detail is chosen, where edges are always straight lines, nodes are always rectangles, and no anti-aliasing is done. The default values used to determine these thresholds can be changed by setting properties under Edit → Preferences → Properties....
Low LOD vs High LOD
Network with Low LOD |
Network with High LOD |
|
|
With low LOD values, all nodes are displayed as square and anti-aliasing is turned off. With high LOD values, anti-aliasing is turned on and nodes are displayed as actual shape user specified in the Style.
Parameters for Controlling LOD
NOTE: The greater these thresholds become, the slower performance will become. If you work with small networks (a few hundred nodes), this shouldn't be a problem, but for large networks it will produce noticeable slowing. The various thresholds are described below.
render.coarseDetailThreshold |
If the sum of rendered nodes and rendered edges equals to or exceeds this number, a very coarse level of detail will be chosen and all other detail parameters will be ignored. If the total number of nodes and edges is below this threshold, anti-alias will be turned on; this value defaults to 4000. |
|
render.nodeBorderThreshold |
If the number of rendered nodes equals to or exceeds this number, node borders will not be rendered; this value defaults to 400. |
|
render.nodeLabelThreshold |
If the number of rendered nodes equals to or exceeds this number, node labels will not be rendered; this value defaults to 200. |
|
render.edgeArrowThreshold |
If the number of rendered edges equals to or exceeds this number, edge arrows will not be rendered; this value defaults to 600. |
|
render.edgeLabelThreshold |
If the number of rendered edges equals to or exceeds this number, edge labels will not be rendered; this value defaults to 200. |
|
When printing networks or exporting to formats such as PostScript, the highest level of detail is always chosen, regardless of what is currently being displayed on the screen.
Force to Display Detail
If you want to display every detail of the network regardless of LOD values, you can toggle to full details mode by View → Show Graphics Details (or CTR+SHIFT+F on Windows/Linux, Command+SHIFT+F for Mac). This option forces the display of all graphics details. If the network is large, this option slows down rendering speed. To hide details, select the menu item again (View → Hide Graphics Details).
Publish Your Data
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Publish Your Visualizations
When you finish your data analysis and visualization, you need to publish your data to share the results. Cytoscape has several options to do it, with most options suitable for Cytoscape users and other options suitable for programmers wanting to create unusual or complex network viewers. They're further explained below.
- A session file
- A static image
- An interactive web application
- Full web application
- Simple network view (for web application developers)
As a Session File
The easiest way to share your results with others is simply saving everything as a session file (which is a zipped session archive). You can save your current session by clicking Save Session icon. You can save to a thumb drive, a shared file system, or even a cloud drive directory such as Dropbox -- if you save to a shared drive, beware not to have two people work on the same session file with Cytoscape at the same time, as unpredictable results may occur.
As a Static Image
Cytoscape can generate publication-quality images from network views. By selecting File → Export → Network View as Graphics..., you can export the current network view into the following formats:
- JPG
- PNG
- PS (Post Script)
- SVG
We recommend using PDF for publications because it is a standard vector graphics format, and it is easy to edit in other applications such as Adobe Illustrator.
Known Issues
For PDF export, there is an option to Export Texts as Fonts. This option does not work for two-byte characters such as Chinese or Japanese. To avoid corrupted texts in the exported images, please uncheck this option when you publish networks including those non-English characters.
As an Interactive Web Application (New in 3.2.0)
The Web is an excellent platform for data sharing and collaboration, and Cytoscape provides a number of ways to publish your network on the web, with each choice representing tradeoffs between ease, simplicity, and customization options. All solutions leverage the cytoscape.js drawing library, and so enable not only viewing but also Cytoscape-style interactive browsing of networks and attributes.
The simplest choice is CyNetShare, where you save your network (and optionally a style) on a public file system, then interactively view the network in a browser. Like Google Maps, you can generate and publish a URL that allows collaborators to also view your network.
Alternatively, Cytoscape can generate an entire web site showing a single page containing the viewer with your network pre-loaded. You can load this directly onto your own web server to become part of your web site.
Finally, Cytoscape can generate the skeleton of a web site for further customization by JavaScript programmers.
These features are available as Export menu items under the File menu, and are described in sections below.
For example, here is a network in Cytoscape:
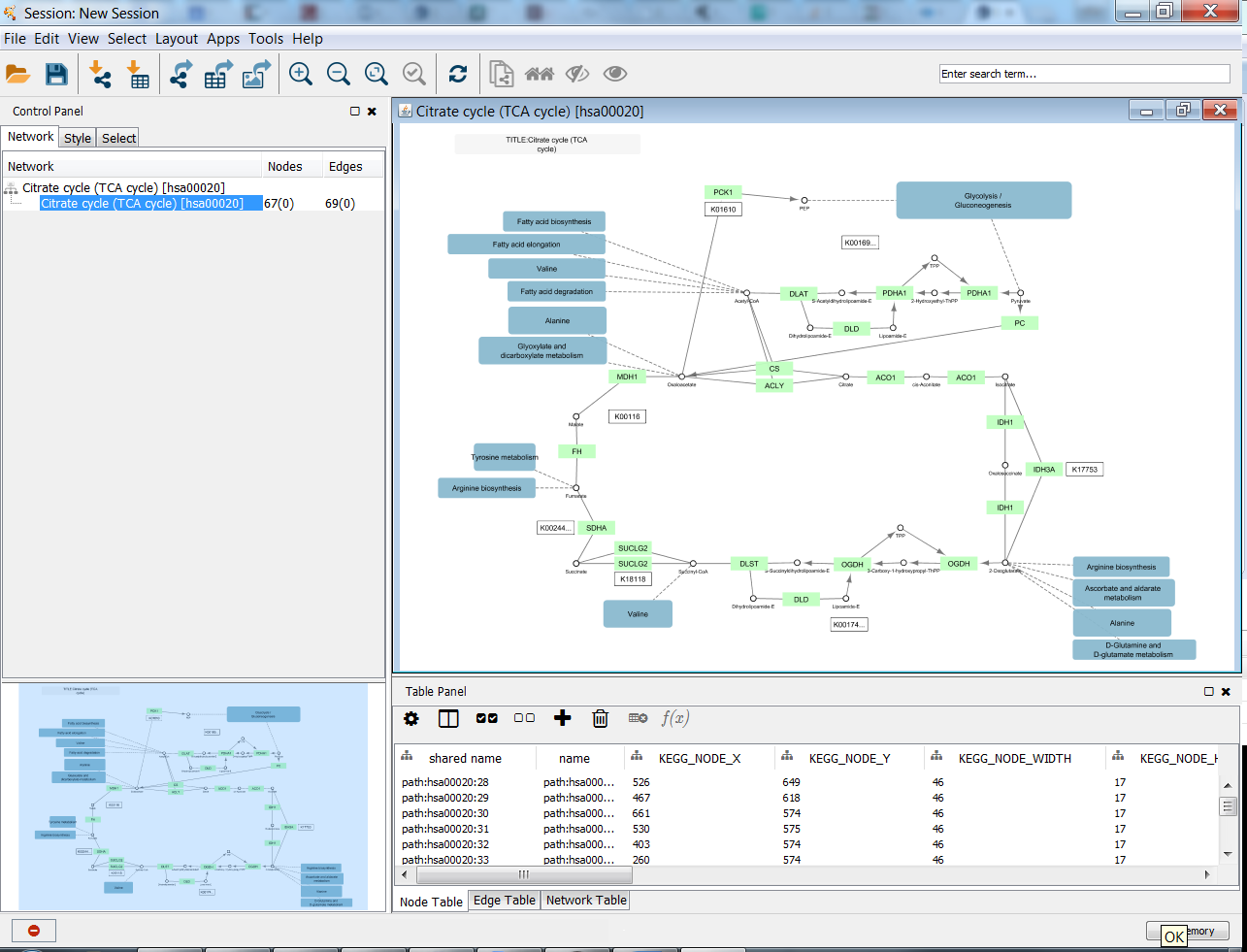
Here is the same network as an interactive web visualization:
Note that web browsers can render small networks (e.g., 1000 nodes) quickly and effectively, but attempting to render large ones (e.g., 5000 nodes) will take a very long time.
A word about exporting styles styles to interactive web applications: Our web applications are based on the cytoscape.js display library, which renders a subset of Cytoscape styles. For more information, see the Export Styles to Cytoscape.js section below.
Sharing via CyNetShare
CyNetShare is a browser-based web application that renders JSON-formatted networks and attributes saved in public directories. Optionally, you can specify visual styles that the web application will use to draw your network as it appears in Cytoscape. CyNetShare is similar to Google Maps in that once you have loaded your network and have tweaked its appearance to suit, you can have CyNetShare generate a new URL that you can e-mail or post as a link on your own web site. That URL will bring up CyNetShare preloaded with your network for anyone to see.
To use CyNetShare:
Select File → Export → Network and View... to export your network to a public directory. Choose the Cytoscape.js JSON (*.cyjs) export file format.
Optionally, select File → Export → Style... to export your style settings. Choose the Style for cytoscape.js (*.json) export file format.
- Use your public directory system to determine direct URLs for the files you exported.
Start CyNetShare
- Enter the network's URL as the Graph URL.
- Optionally, enter the style's URL.
Click the Visualize button.
The CyNetShare User Guide is provided on the CyNetShare web page:
Note that if you specify a style URL, the style is added to the list of styles available in CyNetShare's Visual Style dropdown, and you can apply the style by selecting it in the list.
Note that the mechanics of generating a URL for a file in a public directory system is a fast moving topic. Until recently, systems like Dropbox (and others) allowed users to create a URL that resolved directly to a file -- a "direct" URL would be appropriate for use with CyNetShare. As of this writing, some public directory systems (e.g., Dropbox) generate "shareable" URLs instead, which resolve to a web page that allows file download -- a "shareable" URL makes CyNetShare hang. Systems that offer "shareable" URLs may offer "direct" URLs as part of their premium (or Pro) package. To tell if your public directory system generates a "direct" URL, have it generate a URL for a file, then paste the URL into the address field of a browser and observe whether the browser displays the file itself (good!) or a download page for the file (bad!).
A simple strategy for always getting a "direct" URL is to store your file in a public directory served up by a web server, if you have access to one -- a URL served by a web server might appear as: http://myserver.com/~mypublicdir/netstyle.json.
Alternately, you can use Gist to create a shareable document having a "direct" URL. To try this:
- Use Cytoscape to generate your network as a .cyjs file on your local disk
- Use an editor to open the file and copy its contents to the clipboard
Use a web browser to surf to Gist
- Paste the contents into a Gist document
Select Create public Gist
Select Raw to place the "direct" URL into your browser's address field
Use that URL with CyNetShare
Generating a Full Web Application
The full page export option is designed for users who want to publish their network as a complete single-page application. Cytoscape creates a zip archive containing a complete JavaScript-based web application that works as a basic viewer (like CyNetShare) for Cytoscape-generated network visualizations. You can unzip the archive onto a web server (or your PC) and view the network via a web browser on PCs and tablets.
To generate an entire web page as a zip archive, select File → Export → Network View(s) as Web Page ....
To view the web page, unzip the archive into a folder on your PC or web server. The folder will contain an index.html file, the network data, and other files. You can open the index.html file in your browser (usually from your browser's File → Open menu item.)
Depending on your browser's security settings, you may not be able to open the index.html file directly if it is stored on your PC -- you may need to start a web server on your PC. An easy way to set up a local web server is by running the Python simple HTTP server. If you have Python installed on your machine, just go into the web archive folder and type:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8000
and use your browser to open:
http://localhost:8000/
Testing the archive on your PC will serve as an easy test of the web page, but to publish it to collaborators, you should unzip your archive onto a web server.
Here is an example exported file from Cytoscape:
Note that because Cytoscape uses the latest HTML5-based web technologies, it cannot support older or non-conformant web browsers such as Internet Explorer. We strongly recommend using the latest version of modern web browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Apple Safari.
Generating a Simple Network View (For Web Application Developers)
The Simple Network View export option is designed for users who want to publish their data as a complete single-page application, but are interested in customizing the web viewer application themselves. Cytoscape creates a zip archive containing a partial JavaScript-based web application based on the cytoscape.js library and including simple "boilerplate" code and the current network view. The user can create a custom viewer by customizing this code.
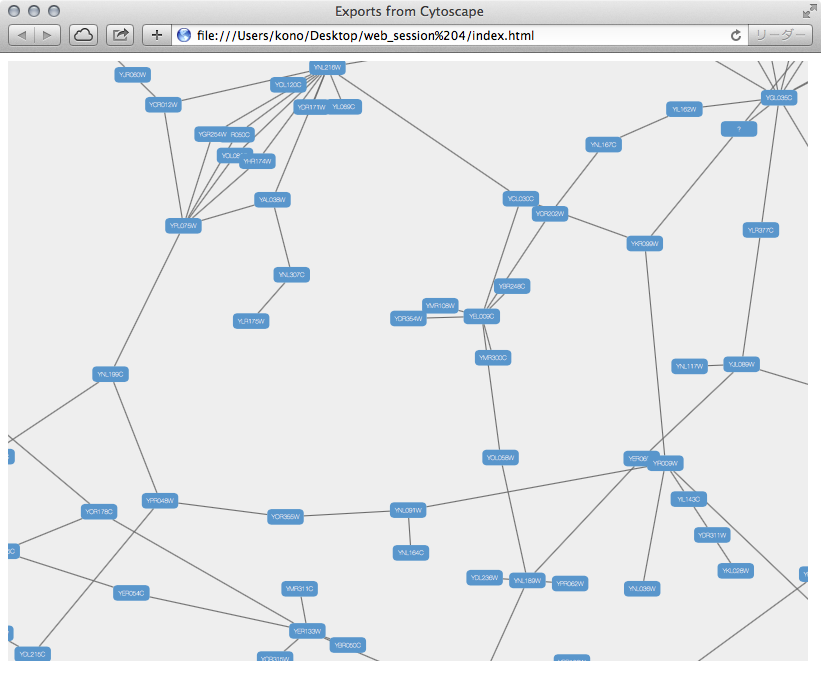
To generate an entire web page as a zip archive, select File → Export → Network View(s) as Web Page ..., and choose the Simple viewer for current network only format.
For instructions on testing the customized web application, see Generating a Full Web Application above.
Customize Export Template (For Web Application Developers)
The code generated by Cytoscape for the Full Web Application and the Simple Network View web applications is minimalistic. While you can directly modify this code yourself to create your own page design or add new features, the modifications will apply to a single exported network. If you are a web application developer, you can change the application code generated for all exports by editing HTML5 template code resource files in your ~/CytoscapeConfiguration/web directory:
In this folder, you can find full and simple sub directories corresponding to Full Web Application and the Simple Network View described above.
Requirements
To build these project, you need the following tools installed:
- Node.js
- gulp
- grunt
Full Export Template
This is an AngularJS based web application built with grunt (at least for now -- we have plans to migrate to gulp). Source code and more documentations are available here:
* https://github.com/idekerlab/cyjs-full-export
To build the project into dist directory, type:
grunt
Simple Export Template
This template is generated by a simple gulp project. The source code is available here:
To build the project into dist directory, type:
gulp
Use Your Custom Templates for Export
Once you have your own builds, you can deploy your templates by replacing the contents of full and simple with your own builds.
Cytoscape.js and Cytoscape
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
What is Cytoscape.js?
Cytoscape.js is a JavaScript library for interactive network visualization. It is a building block for web applications and is NOT a complete web application. If you have network data sets and want to share visualizations created with Cytoscape, you can build your own website using Cytoscape.js and this new Export to Cytoscape.js feature.
Examples
- A network visualized with Cytoscape 3.1.0
- Same network exported to Cytoscape.js (Rendered with Google Chrome and Cytoscape.js 2.0.3)
Interactive example (galFiltered.sif rendered with Cytoscape.js 2.0.3)
Differences and Shared Concepts
Although Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js are two completely independent software packages, they are sharing higher level concepts. The following is the list of similarities and differences between the two:
Cytoscape
Desktop application for network visualization written in Java programming language
- Needs desktop or laptop computers to run
- Users have to install Java runtime
- High performance application for large scale network analysis and visualization
Expandable by Apps
Use Styles to map data to network properties, such as node color, edge width, node shape, etc.
Cytoscape.js
A JavaScript library for network visualization, NOT a complete web application nor mobile app
- Runs on most of modern web browsers, including tablets and smart phones
- No plugins are required to run. Modern web browser is the only requirement
- Need to write code to set up your web site or web application
Expandable by Extensions
Use CSS-based Styles to map data to network properties
In a long term, Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js will be more integrated, and as the first step Cytoscape now supports reading and writing Cytoscape.js network/table JSON files. In addition, Cytoscape can convert Styles to Cytoscape.js Style object.
Data Exchange between Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js
Since Cytoscape.js is a JavaScript library, its basic data exchange format is JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). All of these import/export functions are part of standard Cytoscape user interface, and you can read/write Cytoscape.js JSON files just like other standard files such as SIF.
Export Network and Table to Cytoscape.js
Cytoscape.js stores network data (graph) and its data table in the same object. Cytoscape writes such data complex as JSON, i.e., both network and data tables will be exported as a single JSON file. You can select a network and export it from File → Export → Network.
Cytoscape only supports one of the Cytoscape.js supported JSON formats, which is:
{
elements:{
nodes:[],
edges:[]
}
}SUID will be used as unique identifier for nodes and edges in the JSON. For more information about this format, please visit Cytoscape.js web site.
Important Note about Data Compatibility
Cytoscape creates JSON file directly from data table and tries to extract as much data as possible from the original table. However, since table column names will be directly converted into JavaScript variable names, invalid characters will be replaced by underscore (_):
- Original Data Table Column Names:
Gene Name KEGG.pathway
- The Names above will be replaced to:
Gene_Name KEGG_pathway
You should be careful when you plan to use this feature for data roundtrip: from Cytoscape to Cytoscape.js back to Cytoscape. For such use cases, we strongly recommend to use JavaScript-safe characters only in your table column names. Naming your columns only with alphanumeric characters and underscore (_) is the best practice. (For actual data entries, all characters are allowed. This restriction is only for table column names.)
Export Styles to Cytoscape.js
Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js are sharing a concept called Style. This is a collection of mappings from data point to network property. Cytoscape can export its Styles into CSS-based Cytoscape.js JSON.
You can export all Styles into one JSON file from File → Export → Style and select Cytoscape.js JSON as its format.
Limitations
Cytoscape.js does not support all of Cytoscape Network Properties. Those properties will be ignored or simplified when you export to JSON Style file.
Currently, the following Visual Properties will not be exported to Cytoscape.js JSON:
- Custom Graphics and its positions
- Edge Bends
- Tooltips
- Node Label Width
- Node Border Line Type
- Arrow Colors (they are always same as edge color)
Cytoscape.js and Cytoscape compatibility charts
The following two charts detail the compatibility of specific Cytoscape features in Cytoscape.js.
Import Cytoscape.js data into Cytoscape
Cytoscape.js network JSON files can be loaded from standard Cytoscape file menu: File → Import → Network →. Both File and URL are supported.
Build Your Own Web Application with Cytoscape.js
Although Cytoscape can export networks, tables, and Style as Cytoscape.js-compatible JSON, users have to write some JavaScript code to visualize the data files with Cytoscape.js. Details of web application development with Cytoscape.js is beyond the scope of this document. If you need examples and tutorials about web application development with Cytoscape.js, please visit the following web site:
Questions?
If you have questions and comments about web application development with Cytoscape and Cytoscape.js, please send yours to our mailing list.
Programmatic Access to Cytoscape Features (Scripting)
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
Programmatic Access to Cytoscape Features
In this chapter, you will learn how to use Cytoscape from the command line and scripts. These features replace the Scripting module in past versions of Cytoscape.
Topics
Commands
RESTful API
Command REST API
cyREST
Background
Cytoscape's intuitive graphical user interface is useful for interactive network data integration, analysis, and visualization. It provides great features for exploratory data analysis, but what happens if you have hundreds of data files or need to ask someone to execute your data analysis workflows? It is virtually impossible to apply the same operations to hundreds of networks manually using a GUI. More importantly, although you can save your results as session files, you cannot save your workflows if you perform your data analysis with point-and-click GUI operations. Cytoscape has several options that support scripting and automating your workflows: Commands and RESTful API.
The Command feature allows you to script a number of Cytoscape commands and menu items, and commands can have parameter values that would normally be provided by a user via Cytoscape dialog box. For example, session open file="C:\myfile.cys" loads a session from a file similarly to the File → Open menu item. You can create a command script file that Cytoscape can execute via the Tools → Execute Command File menu item or on the Cytoscape command line at startup.
The RESTful API feature allows you to access Cytoscape from a separate application, thereby orchestrating Cytoscape operations from that application. The application may be written in a general programming language (e.g., Python) that keeps its own data structures, performs complex flow control, or directly manipulates Cytoscape nodes, edges, attributes, and visual styles.
The Command feature is useful for executing sequences of commands, whereas the RESTful API feature is useful when Cytoscape is to be used as a service relative to an application.
Commands
Commands is the built-in Cytoscape feature to automate your workflow as simple script. You can learn more about this feature in this section:
RESTful API
In some cases, you may need to use fully featured programming languages, such as Python, R, Ruby, or JavaScript to script your workflow. Such languages enable complex control and data structures, and Cytoscape would be called as a service. For such use cases, accessing Cytoscape via REST API is the right option.
Cytoscape offers two flavors of REST-style control: REST Commands and cyREST. REST Commands uses a REST interface to issue script commands. cyREST uses a REST interface to access the Cytoscape data model as a document via a formal API.
1. REST API for Commands
In addition to running Command scripts, Command module has REST API to enable command execution from another program.
By default, this feature is disabled. To enable the REST API server for Commands, please follow these steps:
- Open a terminal session:
PowerShell or Command (For windows)
Terminal or iTerm2 (For Mac)
- Terminal (For Linux)
- Start Cytoscape from command-line. You must specify a TCP/IP port number as a parameter -- in this example, port 8888 will be opened for Command:
- For Mac/Linux
./cytoscape.sh -R 8888
For Windows./cytoscape.bat -R 8888
- For Mac/Linux
- To test the Command interface, open the following URL with your web browser:
http://localhost:8888/v1/commands
- If you see list of available commands, you are ready to use Command API
2. cyREST

cyREST is a language-agnostic, programmer-friendly RESTful API module for Cytoscape. If you want to build your own workflow with R, Python or other programming languages along with Cytoscape, this is the option for you. You can use popular tools, including IPython/Jupyter Notebook and RStudio as your orchestration tool for your data visualization workflow with Cytoscape.
(Sample Jupyter Notebook written with cyREST and py2cytoscape)
Currently, cyREST is available as an App for Cytoscape 3.2.1 and later, and requires the Java 8 (or later) virtual machine. As of Cytoscape v3.3, cyREST is installed automatically with Cytoscape. Please visit the link below for more information.
Cytoscape Privacy Policy
This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
- On the Cytoscape download web page, we log the date, time, browser signature, and IP address to which we deliver Cytoscape.
- For a news feed fetched for display on the Cytoscape Welcome screen, we log the date and time the news was fetched, the browser signature, and the IP address for the workstation running Cytoscape.
This policy may change from time to time, and if it does, we will notify you via the Cytoscape Welcome screen news feed and via our normal mass notification media. We will also update this section of the user manual.
Note that some internal Cytoscape Apps and Apps available through the Cytoscape App Store connect with third party services via the Internet. Once an App links to such a service, you are subject to the privacy policy of that service.
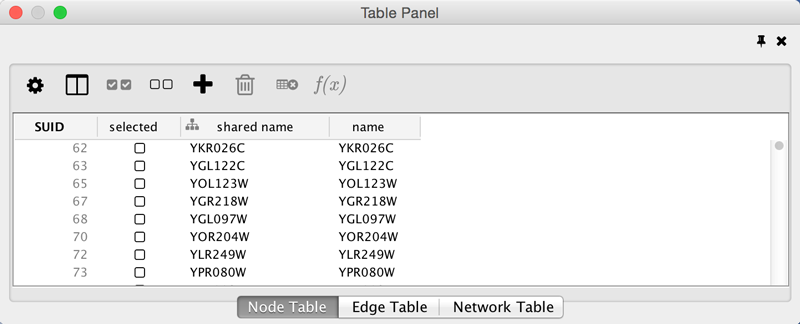
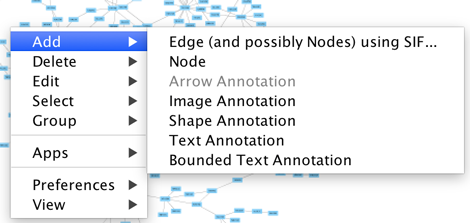
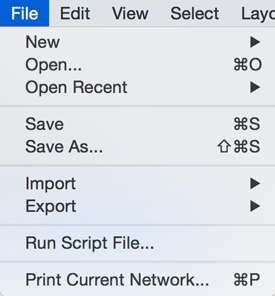
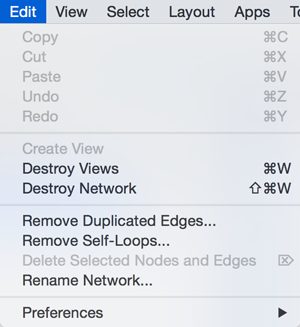
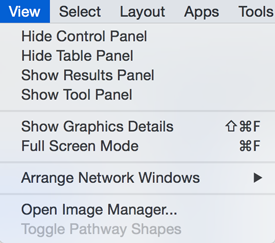
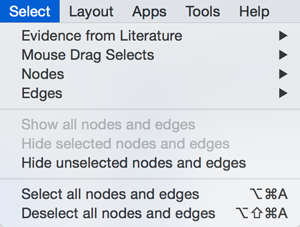
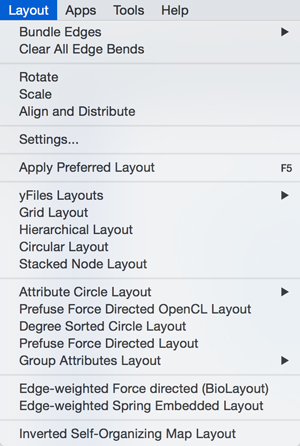
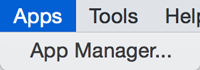
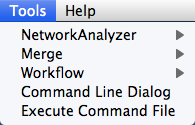

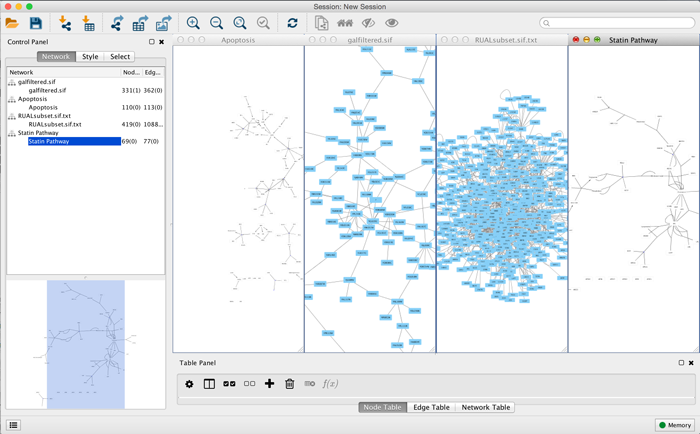
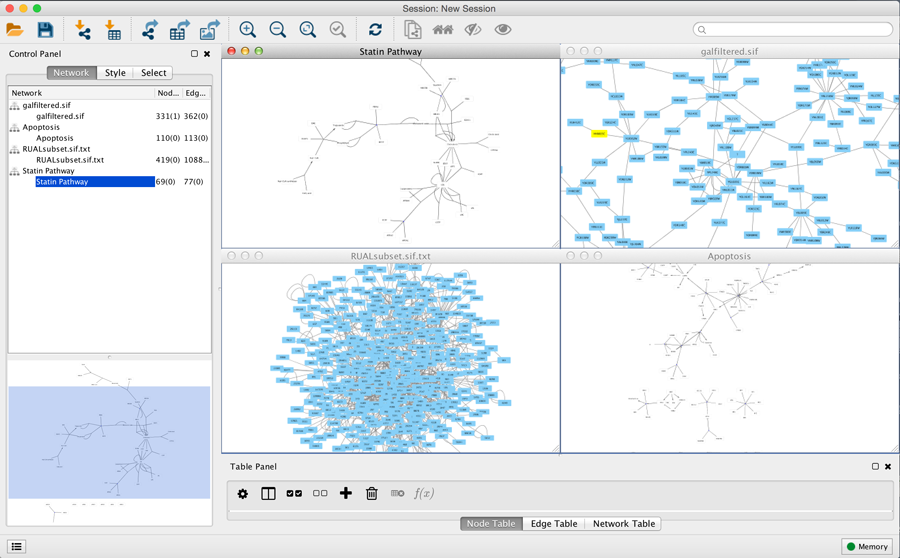
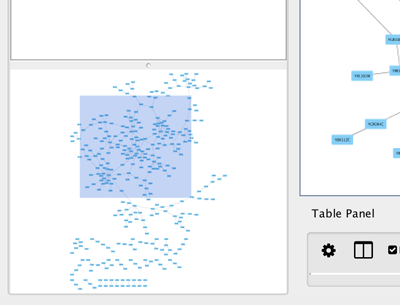
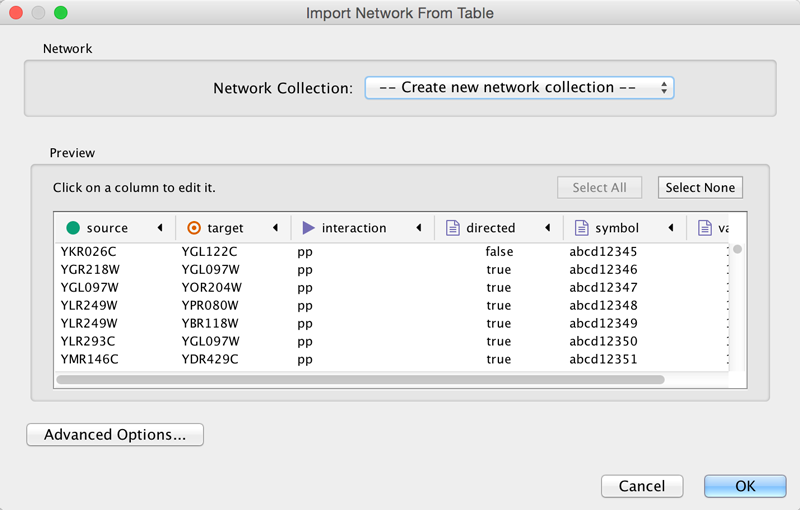
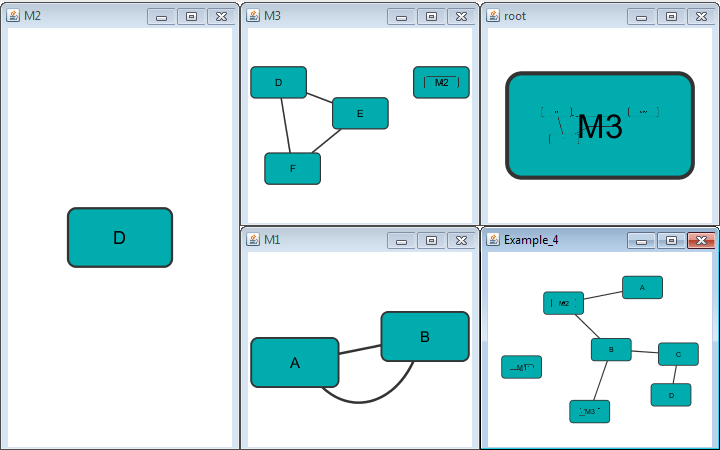
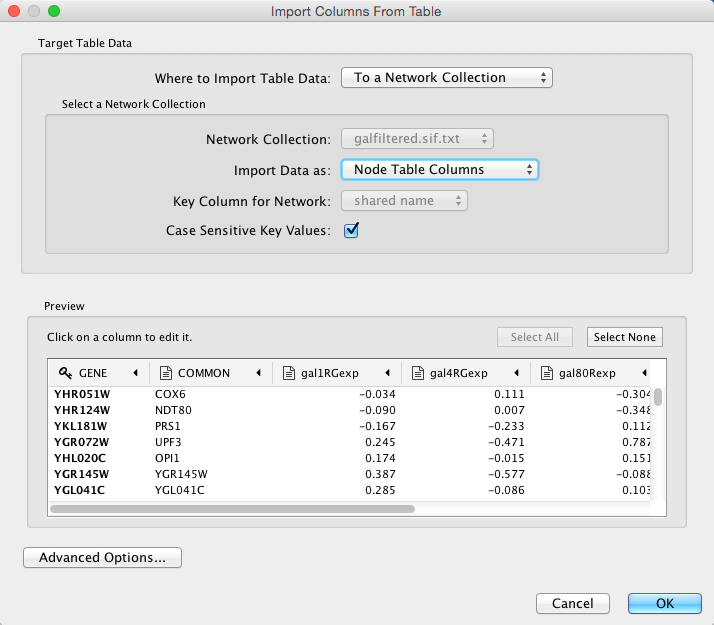
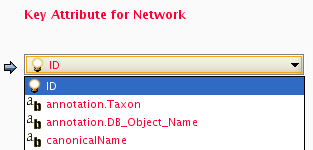
 The Attribute Browser has an Attribute Batch Editor. This enables you to set and modify attribute values for selected nodes or edges of a specified attribute at once. For example, if you want to create a new attribute called Modules and set module names for each group of selected nodes, you can use Set command from this editor.
The Attribute Browser has an Attribute Batch Editor. This enables you to set and modify attribute values for selected nodes or edges of a specified attribute at once. For example, if you want to create a new attribute called Modules and set module names for each group of selected nodes, you can use Set command from this editor. 




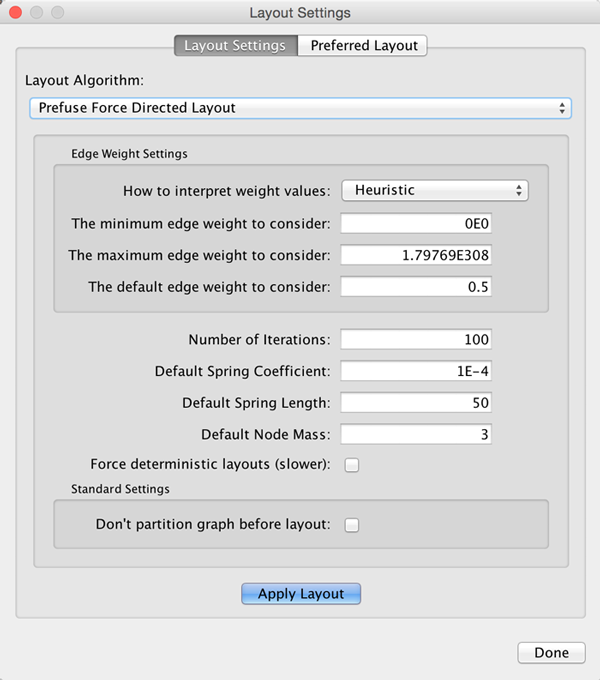
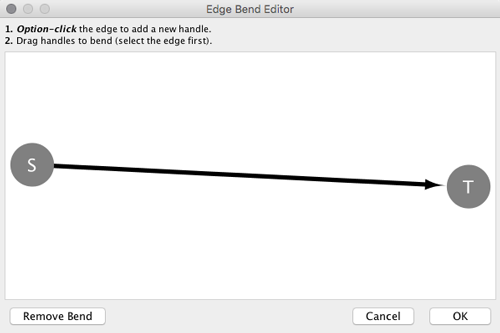
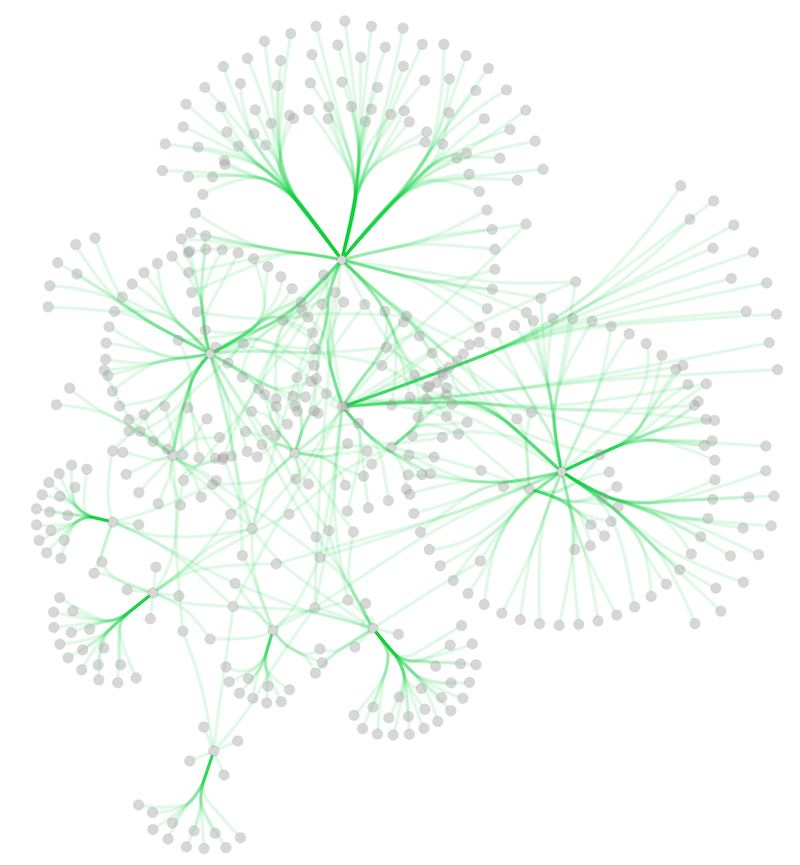






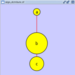
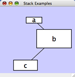
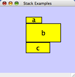
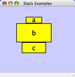
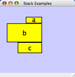
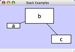
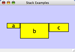
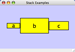
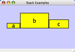
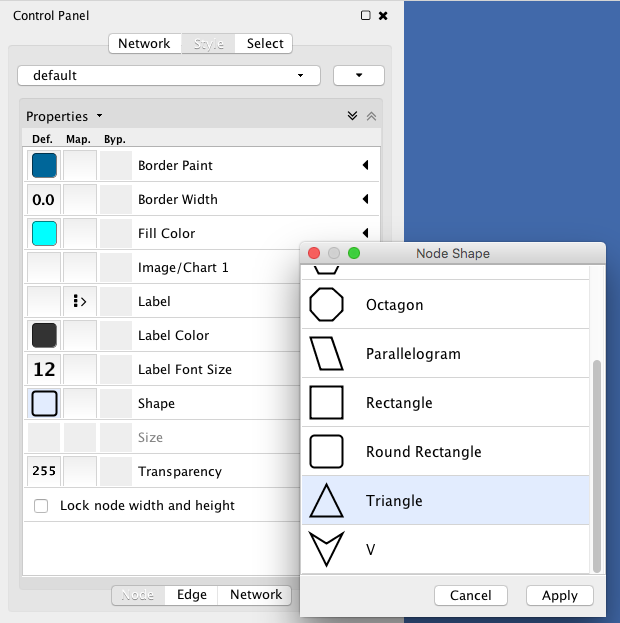
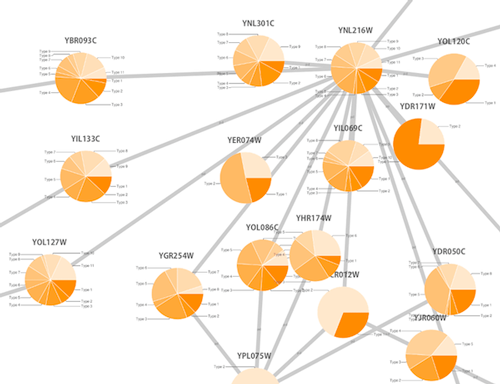
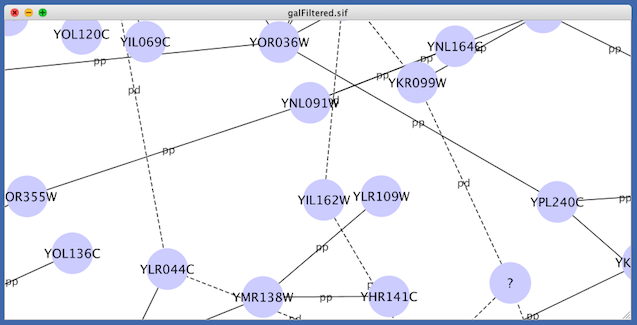
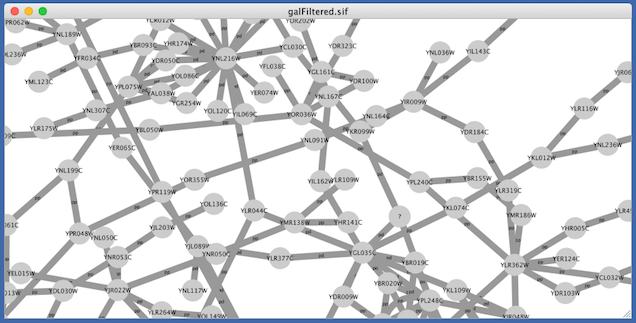



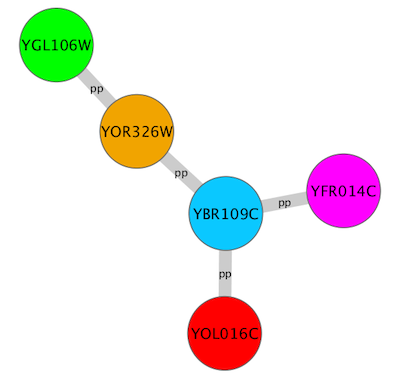
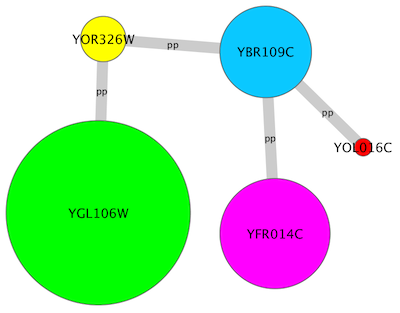
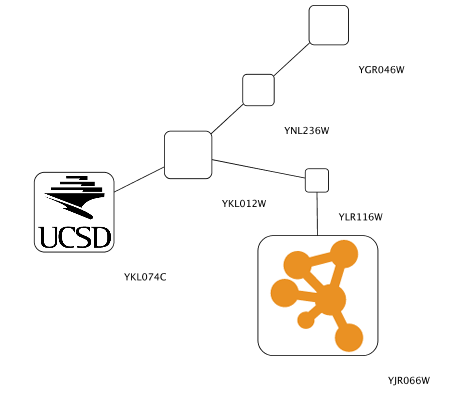
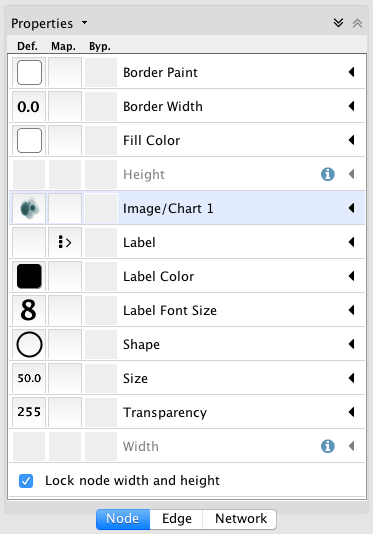
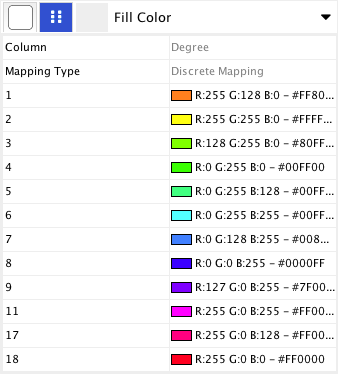
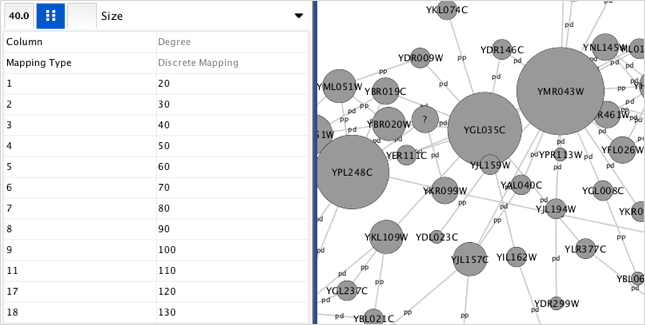
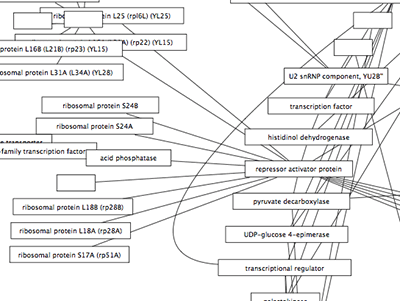

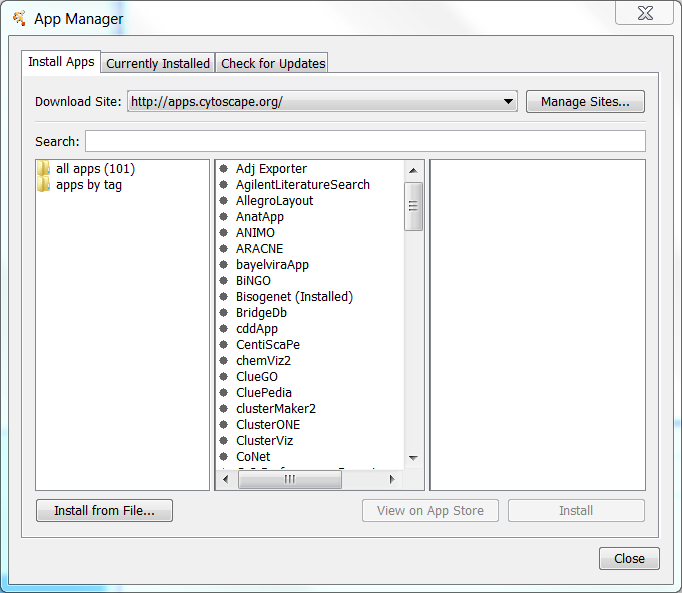
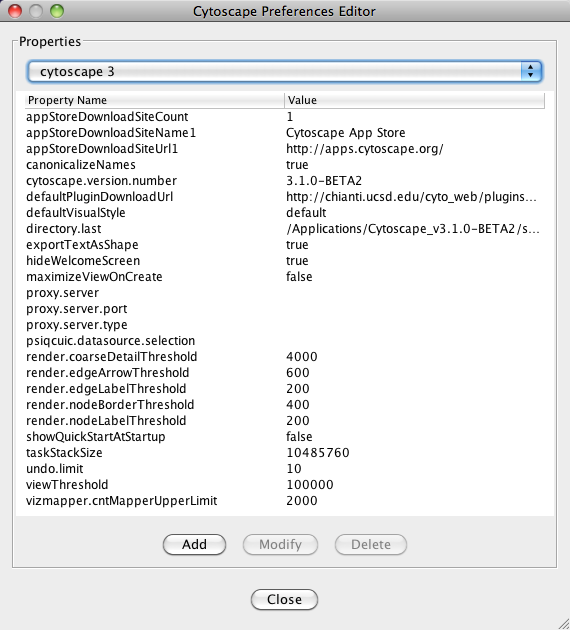
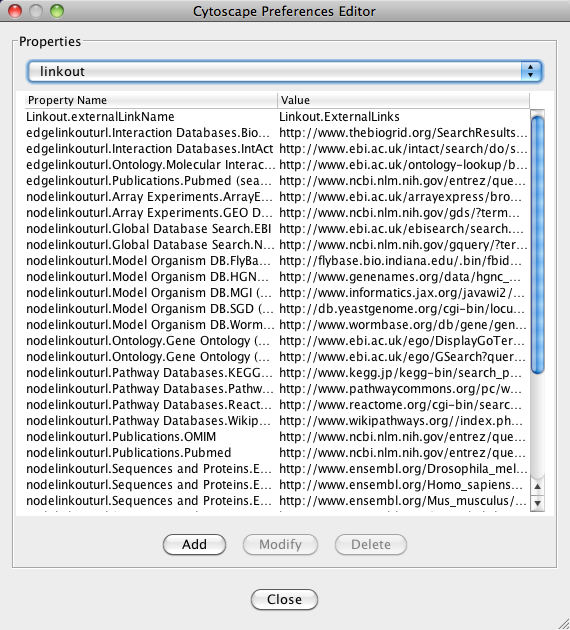
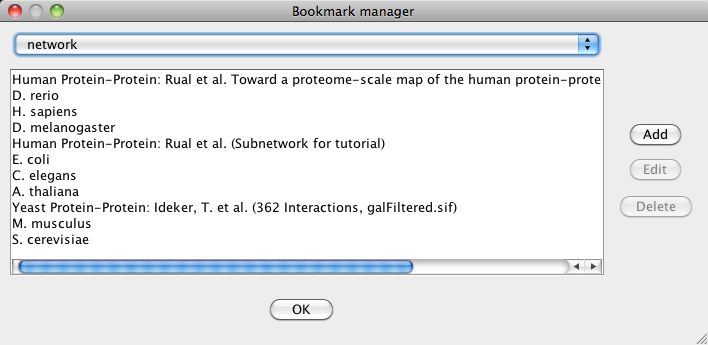
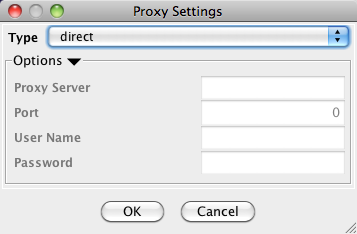
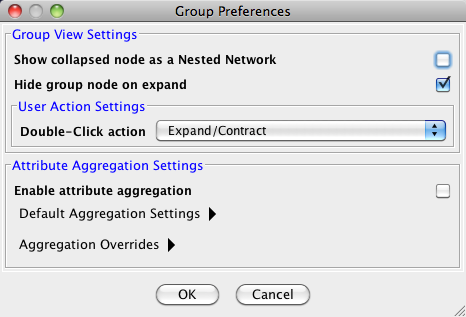

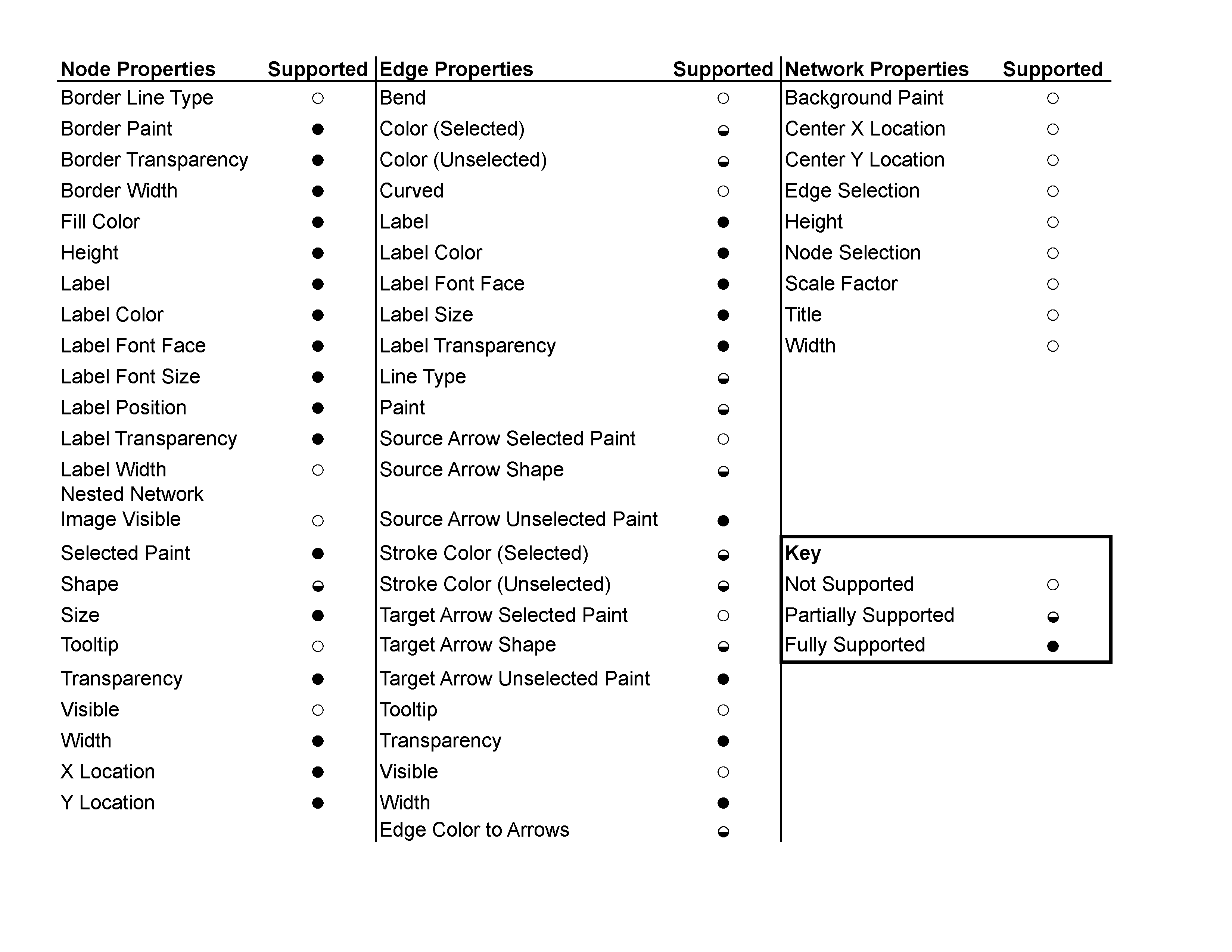
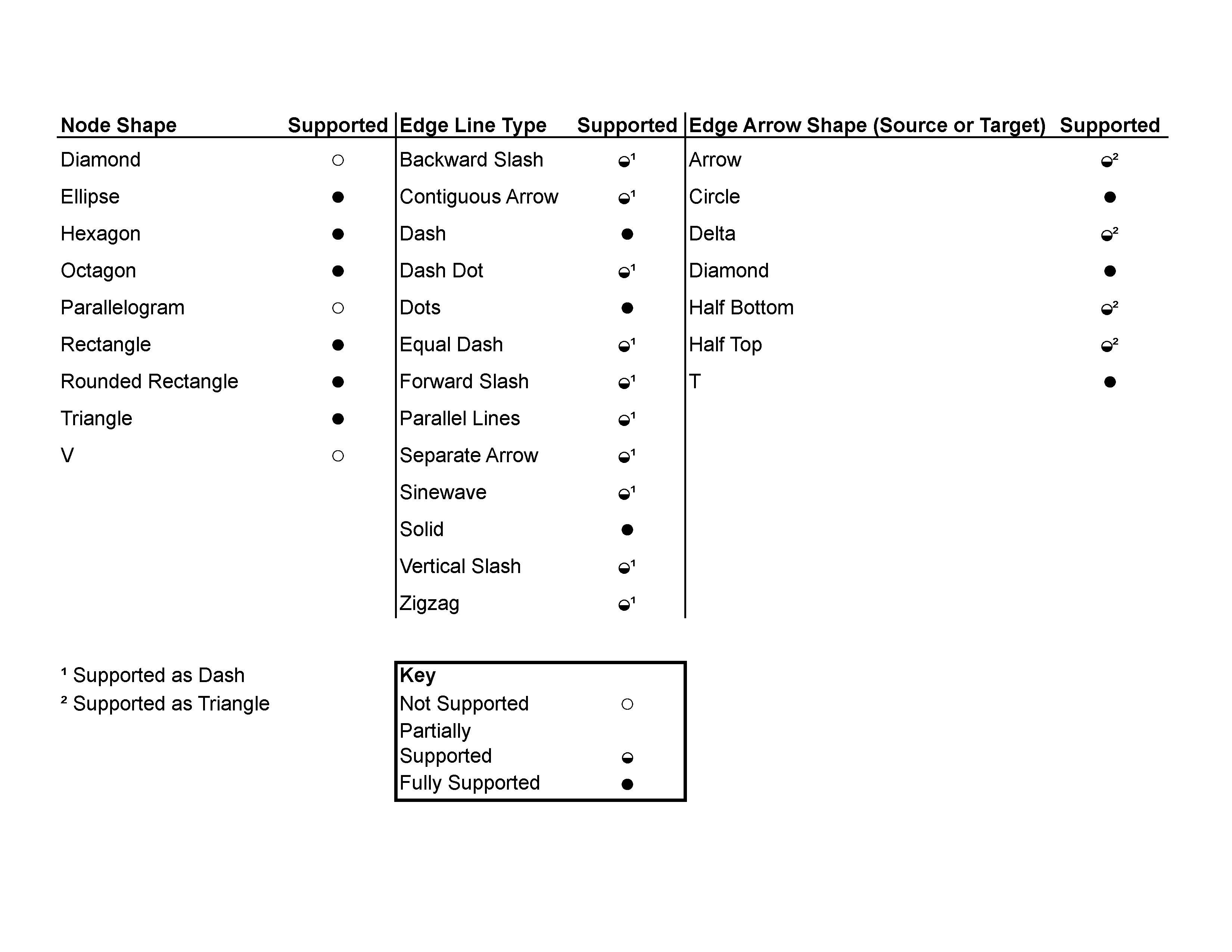
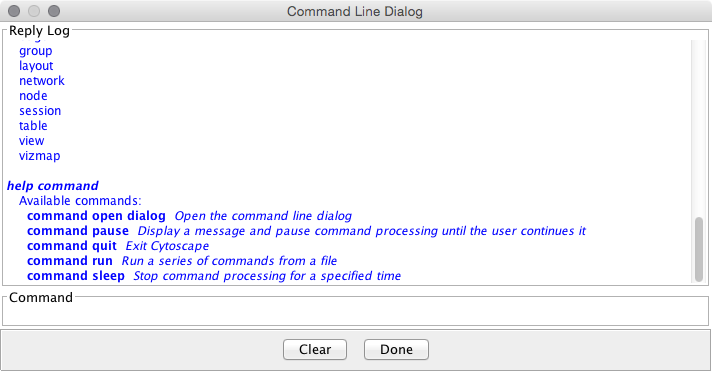
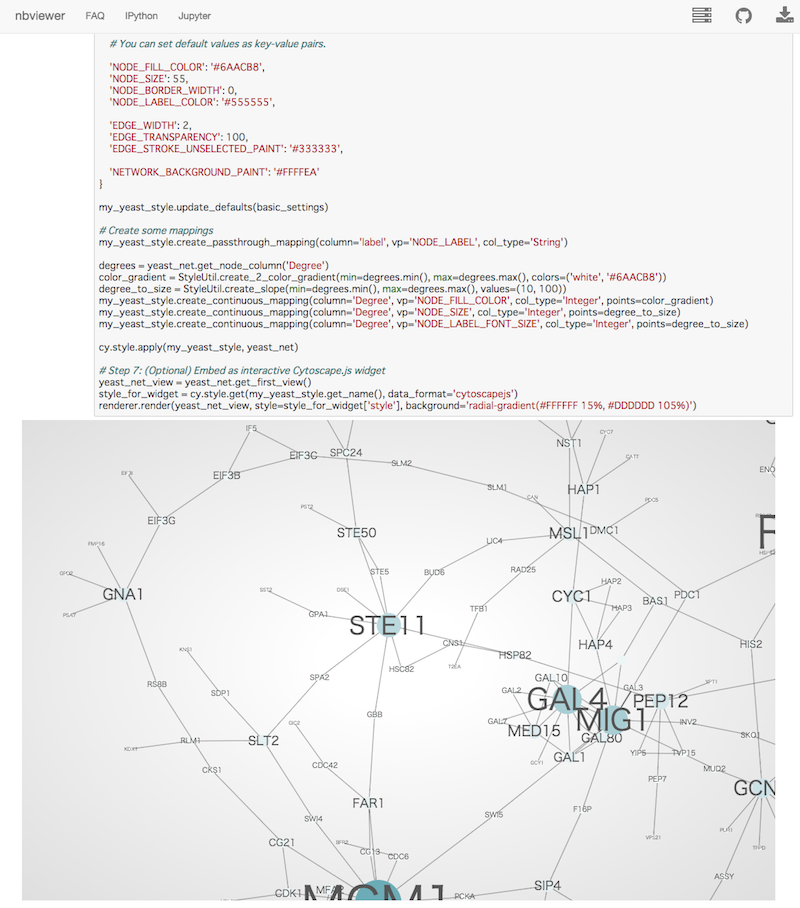
The Update Organism Preset Networks option updates the preset networks available on the Welcome screen to the latest version.