This is a legacy document
This page has been deprecated and is no longer updated. The current version of the Cytoscape manual can be found at http://manual.cytoscape.org/
- Importing pre-existing, fixed-format network files.
- Importing pre-existing, unformatted text or Excel files.
- Importing data from from public databases.
- Creating an empty network and manually adding nodes and edges.
Import Fixed-Format Network Files
Network files can be specified in any of the formats described in the Supported Network Formats section. Networks are imported into Cytoscape through the File → Import → Network menu. The network file can either be located directly on the local computer, or found on a remote computer (in which case it will be referenced with a URL).
Load Networks from Local Computer
In order to load a network from a local file you can select File → Import → Network → File... or click on ![]() on the tool bar. Choose the correct file in the file chooser dialog and press Open. Some sample network files of different types have been included in the sampleData folder in Cytoscape.
on the tool bar. Choose the correct file in the file chooser dialog and press Open. Some sample network files of different types have been included in the sampleData folder in Cytoscape.
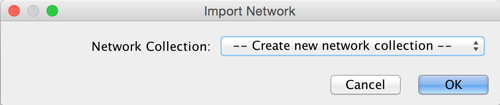
After you choose a network file, another dialog will pop up. Here, you can choose either to create a new network collection for the new network, or load the new network into an existing network collection. When you choose the latter, make sure to choose the right mapping column to map the new network to the existing network collection.
Network files in SIF, GML, and XGMML formats may also be loaded directly from the command line using the –N option.
Load Networks from a Remote Computer (URL import)
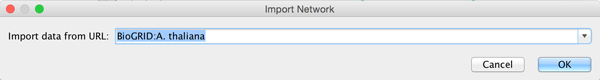
To load a network from a remote file, you can select File → Import → Network → URL.... In the import network dialog, insert the appropriate URL, either manually or using URL bookmarks. Bookmarked URLs can be accessed by clicking on the arrow to the right of the text field (see the Bookmark Manager in Preferences for more details on bookmarks). Also, you can drag and drop links from a web browser to the URL text box. Once a URL has been specified, click on the OK button to load the network.
Another issue for network import is the presence of firewalls, which can affect which files are accessible to a computer. To work around this problem, Cytoscape supports the use of proxy servers. To configure a proxy server, go to Edit → Preferences→ Proxy Settings.... This is further described in the Preferences section.
Import Networks from Unformatted Table Files
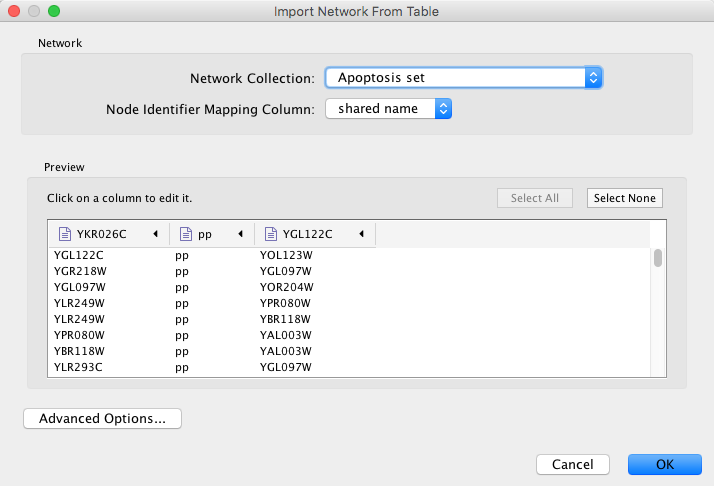
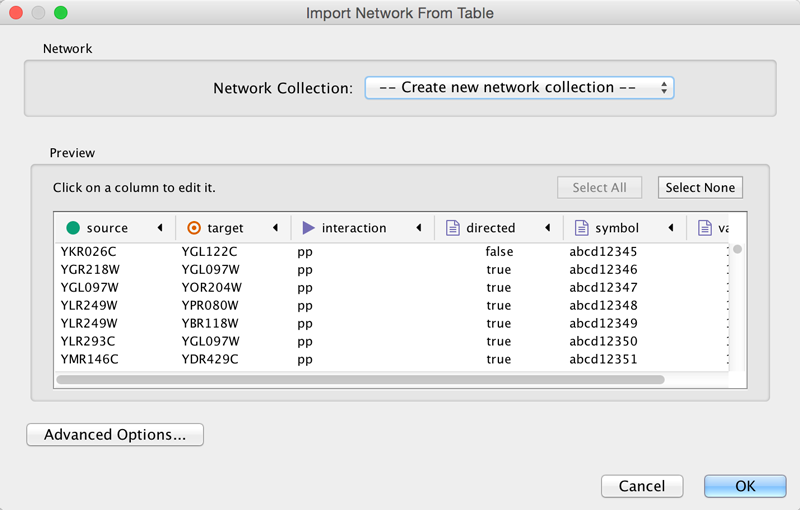
Cytoscape supports the import of networks from delimited text files and Excel workbooks using File → Import → Network → File.... An interactive GUI allows users to specify parsing options for specified files. The screen provides a preview that shows how the file will be parsed given the current configuration. As the configuration changes, the preview updates automatically. In addition to specifying how the file will be parsed, the user must also choose the columns that represent the source and target nodes as well as an optional edge interaction type.
Supported Files
The Import Network from Table function supports delimited text files and Microsoft Excel Workbooks. For Excel Workbooks with multiple sheets, one sheet can be selected for import at a time. The following is a sample table file:
source target interaction boolean data string data floating point data YJR022W YNR053C pp TRUE abcd12371 1.2344543 YER116C YDL013W pp TRUE abcd12372 1.2344543 YNL307C YAL038W pp FALSE abcd12373 1.2344543 YNL216W YCR012W pd TRUE abcd12374 1.2344543 YNL216W YGR254W pd TRUE abcd12375 1.2344543
The network table files should contain at least two columns for creating network with edges. If the file has only one column, the created network will not contain any edges. The interaction type is optional in this format. Therefore, a minimal network table looks like the following:
YJR022W YNR053C YER116C YDL013W YNL307C YAL038W YNL216W YCR012W YNL216W YGR254W
One row in a network table file represents an edge and its edge data columns. This means that a network file is considered a combination of network data and edge column data. A table may contain columns that aren't meant to be edge data. In this case, you can choose not to import those columns by clicking on the column header in the preview window. This function is useful when importing a data table like the following (1):

This data file is a tab-delimited text file and contains network data (interactions), edge data, and node data. To import network and edge data from this table, choose Unique ID A as source, Unique ID B as target, and Interactor types as interaction type. Next, turn off columns used for node data (Alternative ID A, species B, etc.). Other columns can be imported as edge data.
The network import function cannot import node table columns - only edge table columns. To import node table columns from this table, please see the Node and Edge Column Data section of this manual.
Note (1): This data is taken from the A merged human interactome datasets by Andrew Garrow, Yeyejide Adeleye and Guy Warner (Unilever, Safety and Environmental Assurance Center, 12 October 2006). Actual data files are available at http://wiki.cytoscape.org/Data_Sets/
Basic Operations
To import network from text/Excel tables, please follow these steps:
Select File → Import → Network → File... or click on
 on the tool bar.
on the tool bar. - Select a table file in the file chooser dialog.
- Define the interaction parameters by specifying which columns of data contain the Source Interaction, Target Interaction, and Interaction Type. Clicking on any column header will bring up the interface for selecting source, interaction and target:
- (Optional) Define edge table columns, if applicable. Network table files can have edge table columns in addition to network data.
- Click the OK button.
Import List of Nodes Without Edges
The table import feature supports lists of nodes without edges. If you select only a source column, it creates a network without interactions. This feature is useful with the node expansion function available from some web service clients. Please read the section Importing Networks from External Database for more detail.
Advanced Options
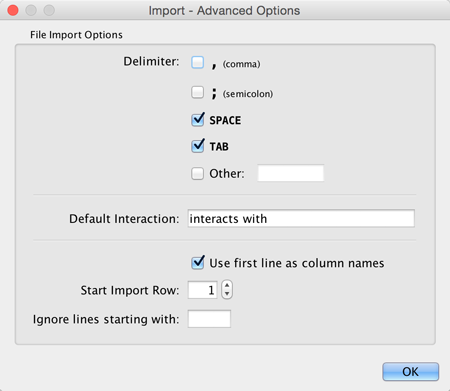
You can select several options by clicking the Advanced Options button in the main import interface.
- Delimiter: You can select multiple delimiters for text tables. By default, Tab and Space are selected as delimiters.
- Default Interaction
- Transfer first line as column names: Selecting this option will cause all edge columns to be named according to the first data entry in that column.
- Start Import Row: Set which row of the table to begin importing data from. For example, if you want to skip the first 3 rows in the file, set 4 for this option.
- Ignore lines starting with: Rows starting with this character will not be imported. This option can be used to skip comment lines in text files.
Modify Column Name/Type
In the Import Network from Table interface, you can change the name and data type of column by clicking on any column header:
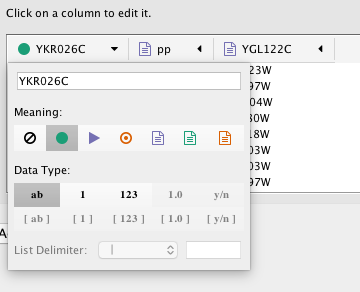
Column names and data types can be modified here.
- Modify Column Name - just enter a new column name.
- Modify Column Data Type - The following column data types are supported:
- String
- Boolean (True/False)
- Integer
- Floating Point
- List of (one of) String/Boolean/Integer/Floating Point
Cytoscape has a basic data type detection function that automatically suggests the column data type according to its entries. This can be overridden by selecting the appropriate data type from the radio buttons provided. For lists, a global delimiter must be specified (i.e., all cells in the table must use the same delimiter).
Import Networks from Public Databases
Cytoscape has a feature called Import Network from Public Databases. Users can access various kinds of databases through this function, File → Import → Network → Public Databases....
Getting Started
To get started, select File → Import → Network → Public Databases....
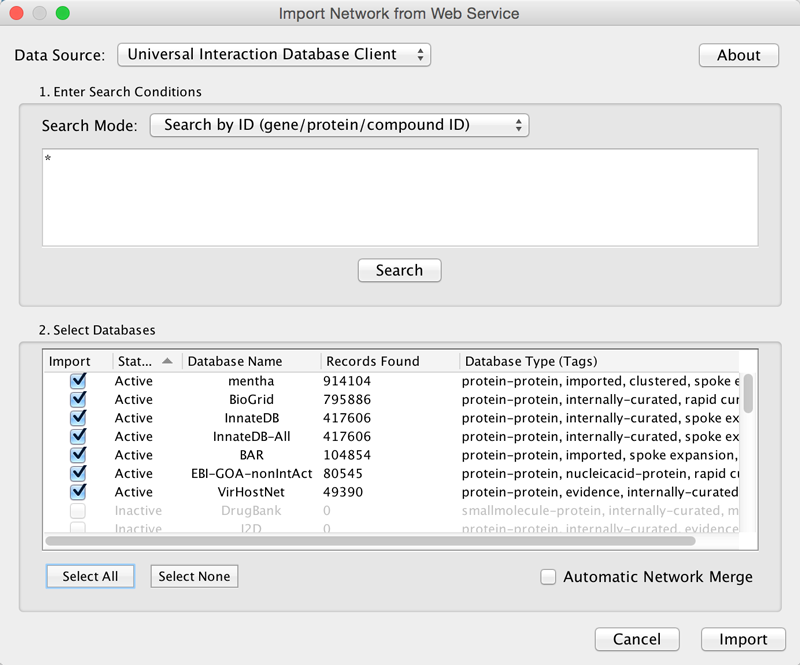
Example: Retrieving Protein-Protein Interaction Networks from Multiple Databases
Select File → Import → Network → Public Databases....
From the pull-down menu, select the Interaction databases Universal Client.
- Enter one or more search terms, such as BRCA1.
Click the Search button to start the search.
- Select databases from the hits. This selection will be saved as your default database list.
Click the Import button to import selected network data.
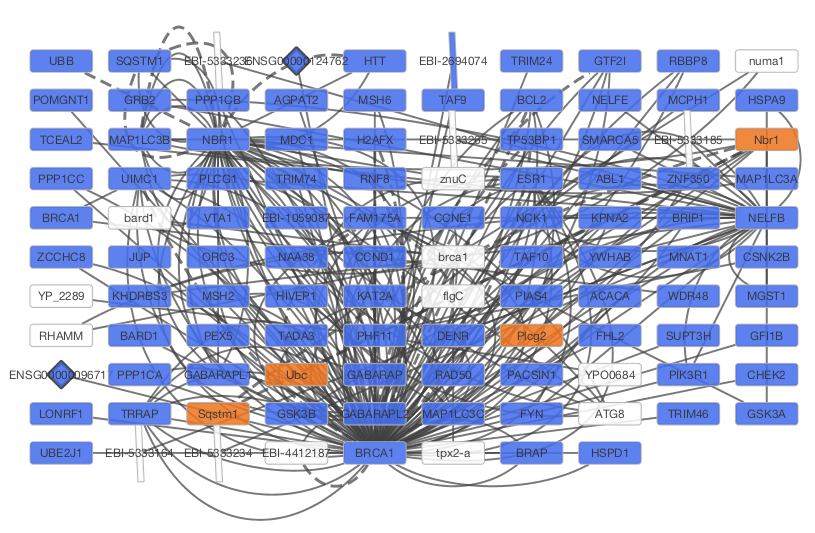
After confirming the download of interaction data, the network of BRCA1 will be imported and visualized.
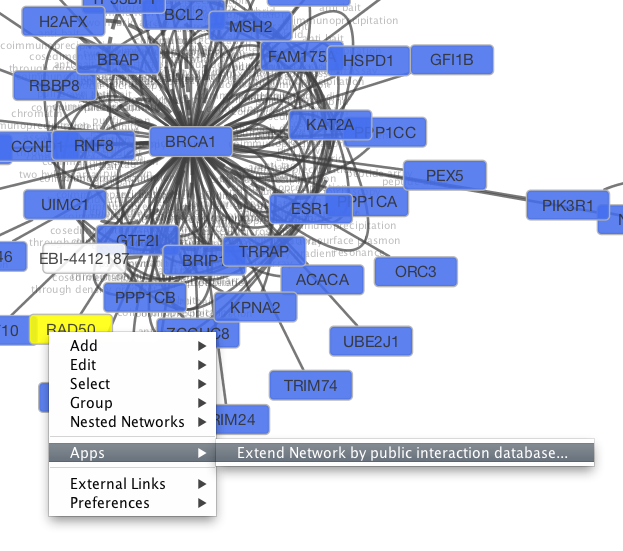
Tip: Expanding the Network: Several of the Cytoscape web services provide additional options in the node context menu. To access these options, right-click on a node and select Apps → Extend Network by public interaction database.... For example, in the screenshot, we have loaded the BRCA1 network from IntAct, and have chosen to merge this node's neighbors into the existing network.
PSICQUIC Options
PSICQUIC Web Service Client has three search modes:
- Search by ID
- Search by MIQL
- Search by Species
By default, search mode is set to Search by ID. You can search all databases by ID, such as gene symbol, Uniprot ID, or NCBI gene ID. If the search mode is set to MIQL, you can use MIQL for search. If you want to search interactions by keywords or specific functions, this is the powerful query language to filter the result. The last option is for importing all interactions for the species (i.e., interactome).
Create a New Network Manually
A new, empty network can also be created and nodes and edges manually added. To create an empty network, go to File → New → Network → Empty Network, and then manually add network components by right clicking on the network canvas or on a node.
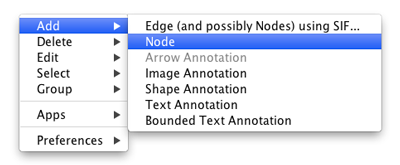
Adding a Node
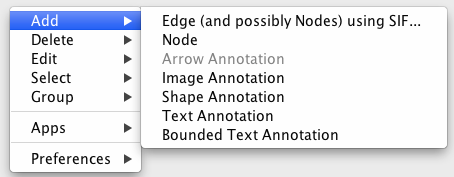
To add a new node, right-click on an empty space of the network view panel. Select Add → Node item from the pop-up menu.
Adding an Edge
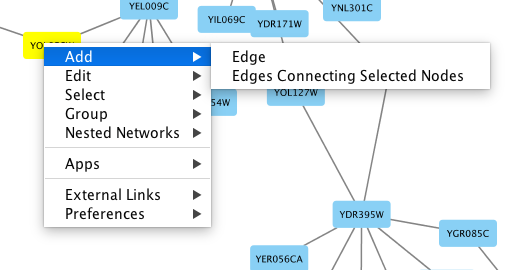
To add an edge to connect nodes, right-click on the source node. Select Edit → Add Edge from the pop-up menu. Next, click on the target node. The Images below show the two steps for drawing an edge between two nodes. You can abort the drawing of the edge by pressing Esc key. You can also select two or more nodes to connect and in the right-click menu select Add → Edges Connecting Selected Nodes to create edges connecting all selected nodes.
You can delete nodes and edges by selecting a number of nodes and edges, then selecting Edit → Cut. You can also delete selected nodes and edges from the Edit menu, under Edit → Delete Selected Nodes and Edges.... You can recover any nodes and edges deleted from a network by going to Edit → Undo.
Grouping nodes
Any number of nodes can be grouped together and displayed as either one group node or as the individual nodes. To create a group, select two or more nodes and right-click to select Group → Group Selected Nodes. You will be prompted to select a name for the group node. Once a group is created, you can use the right-click menu to collapse or expand the group. You can also quickly collapse/expand a group by double-clicking on the group node or any of its children to toggle back and forth.
Collapsed group
Expanded group
Adding Network Annotations
Annotations in the form of text, images or shapes can be added to the network canvas by right-clicking anywhere on the canvas and selecting one of the Annotation choices in the Add menu. You can add an image of your own, choose from a shapes library or add either plain or bounded text. Shapes and text are customizable and any added annotations can be edited from the right-click context menu.
What is a Web Service?
A web service is a standardized, platform-independent mechanism for computers to interact over the internet. These days, many major biological databases publish their data with a web service API:
List of Biological Web Services: http://taverna.sourceforge.net/services
Web Services at the EBI: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/webservices/
Cytoscape core developer team have developed several web service clients using this framework. Cytoscape supports many web services including:
PSICQUIC: Standard web service for biological interaction data sets. The full list of PSICQUIC-compatible databases is available here.
The following sections describe how to import network from external databases.