|
Size: 31219
Comment:
|
Size: 18974
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
|
Interaction networks are useful as stand-alone models. However, they are most powerful for answering scientific questions when integrated with additional information. Cytoscape allows the user to add arbitrary node, edge and network data to Cytoscape through the data table. This could include, for example, annotation data on a gene or confidence values in a protein-protein interaction. In the data table information is linked to Nodes, Edges or Networks by mapping the columns to one of their identifiers. The data can then be visualized in a user-defined way by setting up a mapping from data attributes in columns to visual attributes (colors, shapes, and so on). The section on visual styles discusses this in greater detail. Cytoscape supports several formats. The right reader will be found based on the file extension. The supported file extensions are the regular text and table formats: '''"tsv, tab, csv, net or txt"''' (comma, tab or any delimiter separated values file), '''"xls, xlsx"''' (Microsost Excel file formats). The native Cytoscape formats: '''"attrs"''' (text file in the format described below) and '''"pvals"''' (Cytoscape expression matrix). For most users the regular data table importing functionality will be sufficient. These formats are for experienced users (and to provide some backwards compatibility) == Import Data Table Files == === Basic Operation === The user interface of the "Import Attributes from Table" window is similar to that of the "Import Network from Table" window. |
Interaction networks are useful as stand-alone models. However, they are most powerful for answering scientific questions when integrated with additional information. Cytoscape allows the user to add arbitrary node, edge and network data to Cytoscape through the data table. This could include, for example, expression data of a gene or confidence values in a protein-protein interaction. In the data table, information is linked to nodes, edges or networks by mapping the columns to one of their identifiers. Through the table panel the values can be further manipulated through the use of [[Cytoscape_3/UserManual/Attribute_Formulas|attribute functions and equations]] A second type of data that can be associated with networks is ontology data: organized sets of controlled vocabulary terms. Because this type of data is mostly hierarchically organized, this requires a special importing facility, described in the second part of this section. Data associated with the network elements can be visualized in a user-defined way by setting up a mapping from data attributes in the columns to visual attributes (colors, shapes, and so on) in the network on screen. The section on [[Cytoscape_3/UserManual/Visual_Styles|visual styles]] discusses this in greater detail. == Table data == Cytoscape supports several tabular formats. The right reader will be found based on the file extension. The supported file extensions are the regular text and table formats: '''''.tsv, .tab, .csv, .net, .txt''''' (comma, tab or any delimiter separated values file), '''''.xls, .xlsx''''' (Microsoft Excel file format). Note that for Excel file formats, only the first sheet of a workbook is currently imported. The legacy native Cytoscape formats: '''''.attrs''''' and '''''.pvals''''' (Cytoscape expression matrix) are also supported (for a more thorough discussion of these formats consult the 2.x manual). For most users the regular data table importing functionality will be sufficient; in case a format is unknown, renaming the file to a '''''.txt''''' extension and toying around with delimiter and header settings will most of the times do the trick. === Importing data === ==== Basic table file ==== The basic file format consists of a table containing at least one column with identifiers (unique names) for the nodes, edges or networks, and one or (any number) more columns with data you want to associate with these network elements. '''''Sample Data Table 1''''' ||Yeast Key||Degree|| ||YER054C||85|| ||YBL079W||7|| ||YLR345W||1|| To import such a file: |
| Line 13: | Line 29: |
|
1. Select File → Import → Table → File... ( or URL... if your source data file is accessible through web) 1. Select a data file in the file chooser panel (or enter the URL in the displayed box). This file can be either a text or Excel (.xls) formats. |
1. Select File → Import → Table → File... ( or URL... if your source data file is accessible through the internet) 1. Select a data file in the file chooser panel (or enter the URL in the displayed box). This file can be in any of the accepted formats mentioned above. |
| Line 17: | Line 33: |
|
1. (Optional) If the table is not properly delimited in the preview panel, change the delimiter in the Text File Import Options panel. The default delimiter is tab. This step is not necessary for Excel Workbooks. ) 1. By default, the first column is designated as the primary key. Change the key column if necessary. |
1. (Optional) If the table is not properly delimited in the preview panel, change the delimiter in the Text File Import Options panel (the default delimiter is Tab). 1. By default, the first column is designated as the primary key. Change the key column if necessary, see below for an example. 1. The data attribute column name can be changed by right clicking on the header. A dialog appears that enables specification of the datatype and column name. 1. Left clicking selects or deselects the column for importing. |
| Line 21: | Line 39: |
|
The user interface of the "Import Table from File" window is similar to that of the "Import Network from Table" window. |
|
| Line 23: | Line 43: |
|
'''''Sample Attribute Table 1''''' ||Object Key||SGD ID|| ||AAC3||S000000289|| ||AAT2||S000004017|| ||BIK1||S000000534|| The attribute table file should contain a primary key column and at least one data attribute column. The maximum number of data columns is unlimited. Alternatively, you can specify each data attribute column name from the File → Import → Attribute from Table (text/MS Excel)... user interface. === Mapping data options === In Cytoscape 3.0 both IDs and data columns with primitive data types (string, boolean, floating point, and integer) can be selected as the Key Column using the dropdown list provided. Complex data attributes such as lists are not supported as key. === Data in complete networks === When importing a network from a table the other columns than the node ids can be imported as data also. For more detail on these options, please see the "Import Free-Format Table Files" section of the user manual in the [[Cytoscape_User_Manual/Creating_Networks|Creating Networks]] chapter. === Table Browser === |
If the data only relates to a specific network select the 'Apply to selected networks only' box and select the specific network from the list (click 'Select Networks' to show this list) {{attachment:Cy3_Import_Column_From_Table_Network_Select.png}} ===== Mapping data options ===== In Cytoscape 3.0 data columns with primitive data types (string, boolean, floating point, and integer) can be selected as the key column using the dropdown list provided. Complex data attributes such as lists are not supported as keys. {{attachment:Cy3_Import_Column_From_Table_Mapping_Options.png}} ===== Text file import options ===== When the text file import options box is checked, several additional parameters can be selected to tune the way the data file will be imported. The first line can be used to specify column header names. Another data delimiter (default is tab) can be chosen, and the comment prefix (signifying lines to be ignored) can be defined. {{attachment:Cy3_Import_Column_From_Table_Text_Import_Options.png}} ==== Import from Public Databases ==== You can import various kinds of ID sets from the !BioMart (http://www.biomart.org/index.html) public database. The !BioMart web service client is integrated into Cytoscape. {{attachment:id_mapping1.png}} 1. Select: '''File → Import → Table → Public Databases...''' 1. Select a data source. For ID mapping, select one of the ''Ensemble Genes'' data set. You need to choose the correct species for your network. 1. Select '''Attribute'''. If you want to import new ID sets matching current node IDs, select ''shared name''. 1. Select '''Data Type'''. This should be the type of ID set selected in '''Attribute''' list. For example, if you select ''shared name'' for '''Attribute''' and your network uses ''Entrez Gene ID'' for its node ID, you need to select ''!EntrezGene ID(s)'' for '''Data Type'''. 1. Select new ID sets from the list. Because there is a size limitation on the results returned by the!BioMart server, you can select only 3-5 attributes for each import. 1. Press '''Import'''. ==== Data in complete networks ==== When importing a network from a table, columns other than the node identifier can be imported as data also. For more detail on these options, please see the "Import Free-Format Table Files" section of the user manual in the [[Cytoscape_3/UserManual/Creating_Networks|Creating Networks]] chapter. === Table Panel === |
| Line 41: | Line 78: |
|
When Cytoscape is started, the Table Browser appears in the bottom !CytoPanel. This browser can be hidden and restored using the View → Show/Hide Table Browser menu option. Like other !CytoPanels, the browser can be undocked by pressing the little icon in the browser’s top right corner. To swap between displaying node, edge, and network attributes use the tabs on the bottom of the panel labeled "Node Attributes", "Edge Attributes", and "Network Attributes". In Cytoscape 3.0 there two display modes for table browser: showing only selected nodes/edges attributes or showing all attributes. This configuration can be set using button (the left most) in the figure. The attribute browser displays attributes belonging to the currently selected network. Using the three buttons (left 2nd to 4th) in the figure, it is possible to make some or all columns visible and hide others or all of them. Also, a new column can be created by pressing button the (left 5th) or mutable columns can be deleted by button (left 6th). Button f(x) is for writing equation which is explained in the section "Supported Functions". Most attribute values can be edited by double-clicking an attribute cell (only the SUID cannot be edited). Newline characters can be inserted into String attributes either by pressing ''Enter'' or by typing "\n". Once finished editing, click outside of the editing cell in the Attribute Browser or press ''Shift-Enter'' to save your edits. Pressing ''Esc'' while editing will undo any changes. Attribute rows in the browser can be sorted alphabetically by specific attribute by clicking on a column heading. A new attribute can be created using the Create New Column button (left 5th), and must be one of four types – integer, string, real number (floating point), or boolean. Attributes can be deleted using the Delete Attributes button (left 6th, trash can icon). '''NOTE: Deleting attributes removes them from Cytoscape, not just the attribute browser!''' To remove attributes from the browser without deleting them, simply unselect the attribute using the Select Column button (left 3rd). The right-click menu on the Table Browser has several functions, such as exporting attribute information to spreadsheet applications. For example, use the right-click menu to Select All and then Copy the data, and then paste it into a spreadsheet application. === Cytoscape Native Data File Formats === Node and edge attribute files are simply formatted: a node attribute file begins with the name of the attribute on the first line (note that it cannot contain spaces). Each following line contains the name of the node, followed by an equals sign and the value of that attribute. Numbers and text strings are the most common attribute types. All values for a given attribute must have the same type. For example: {{{ FunctionalCategory YAL001C = metabolism YAR002W = apoptosis YBL007C = ribosome }}} An edge attribute file has much the same structure, except that the name of the edge is the source node name, followed by the interaction type in parentheses, followed by the target node name. Directionality counts, so switching the source and target will refer to a different (or perhaps non-existent) edge. The following is an example edge attributes file: {{{ InteractionStrength YAL001C (pp) YBR043W = 0.82 YMR022W (pd) YDL112C = 0.441 YDL112C (pd) YMR022W = 0.9013 }}} Since Cytoscape treats edge attributes as directional, the second and third edge attribute values refer to two different edges (source and target are reversed, though the nodes involved are the same). Each attribute is stored in a separate file. Node and edge attribute files use the same format. Node and edge attribute file names often use the suffix ".attrs". Node and edge attributes may be loaded at the command line using the –T options or via the File → Import menu. When expression data is loaded using an expression matrix, it is automatically loaded as node attribute data unless explicitly specified otherwise. Node and edge attributes are attached to nodes and edges, and so are independent of networks. Attributes for a given node or edge will be applied to all copies of that node or edge in all loaded network files, regardless of whether the attribute file or network file is imported first. === Detailed file format (Advanced users) === Every attribute file has one header line that gives the name of the attribute, and optionally some additional meta-information about that attribute. The format is as follows: {{{ attributeName (class=JavaClassName) }}} The first field is always the attribute name: it cannot contain spaces. If present, the class field defines the name of the class of the attribute values. For example, java.lang.String or String for Strings, java.lang.Double or Double for floating point values, java.lang.Integer or Integer for integer values, etc. If the value is actually a list of values, the class should be the type of the objects in the list. If no class is specified in the header line, Cytoscape will attempt to guess the type from the first value. If the first value contains numbers in a floating point format, Cytoscape will assume java.lang.Double; if the first value contains only numbers with no decimal point, Cytoscape will assume java.lang.Integer; otherwise Cytoscape will assume java.lang.String. Note that the first value can lead Cytoscape astray: for example, {{{ floatingPointAttribute firstName = 1 secondName = 2.5 }}} In this case, the first value will make Cytoscape think the values should be integers, when in fact they should be floating point numbers. It's safest to explicitly specify the value type to prevent confusion. A better format would be: {{{ floatingPointAttribute (class=Double) firstName = 1 secondName = 2.5 }}} or {{{ floatingPointAttribute firstName = 1.0 secondName = 2.5 }}} Every line past the first line identifies the name of an object (a node in a node attribute file or an edge in a edge attribute file) along with the String representation of the attribute value. The delimiter is always an equals sign; whitespace (spaces and/or tabs) before and after the equals sign is ignored. This means that your names and values can contain whitespace, but object names cannot contain an equals sign and no guarantees are made concerning leading or trailing whitespace. Object names must be the Node ID or Edge ID as seen in the left-most column of the attribute browser if the attribute is to map to anything. These names must be reproduced exactly, including case, or they will not match. Edge names are all of the form: {{{ sourceName (edgeType) targetName }}} Specifically, that is ||sourceName space openParen edgeType closeParen space targetName|| Note that tabs are not allowed in edge names. Tabs can be used to separate the edge name from the "=" delimiter, but not within the edge name itself. Also note that this format is different from the specification of interactions in the SIF file format. To be explicit: a SIF entry for the previous interaction would look like {{{ sourceName edgeType targetName }}} or ||sourceName whiteSpace edgeType whiteSpace targetName|| To specify lists of values, use the following syntax: {{{ listAttributeName (class=java.lang.String) firstObjectName = (firstValue::secondValue::thirdValue) secondObjectName = (onlyOneValue) }}} This example shows an attribute whose value is defined as a list of text strings. The first object has three strings, and thus three elements in its list, while the second object has a list with only one element. In the case of a list every attribute value uses list syntax (i.e. parentheses), and each element is of the same class. Again, the class will be inferred if it is not specified in the header line. Lists are not supported by the visual mapper and so can’t be mapped to visual attributes. ==== Newline Feature ==== Sometimes it is desirable to for attributes to include linebreaks, such as node labels that extend over two lines. You can acomplish by inserting {{{\n}}} into the attribute value. For example: {{{ newlineAttr YJL157C = This is a long\nline for a label. }}} === Gene Expression (Attribute Matrix) Data format === In addition to normal node and edge attribute data, Cytoscape also supports importing gene expression data. Gene expression data are imported using a different file format than normal attributes (File extension is '.pvals'); however, the resulting attributes are not treated differently by Cytoscape. ==== Data File Format ==== Gene expression ratios or values are specified over one or more experiments using a text file. Ratios result from a comparison of two expression measurements (experiment vs. control). Some expression platforms, such as Affymetrix, directly measure expression values, without a comparison. The file consists of a header and a number of space- or tab-delimited fields, one line per gene, with the following format: {{{ Identifier [CommonName] value1 value2 ... valueN [pval1 pval2 ... pvalN] }}} Brackets [ ] indicate fields that are optional. The first field identifies which Cytoscape node the data refers to. In the simplest case, this is the gene name - exactly as it appears on the network generated by Cytoscape (case sensitive!). Alternatively, this can be some node attribute that identifies the node uniquely, such as a probeset identifier for commercial microarrays. The next field is an optional common name. It is not used by Cytoscape, and is provided strictly for the user's convenience. With this common name field, the input format is the same as for commonly-used expression data anaysis packages such as SAM (http://www-stat.stanford.edu/~tibs/SAM/). The next set of columns represent expression values, one per experiment. These can be either absolute expression values or fold change ratios. Each experiment is identified by its experiment name, given in the first line. Optionally, significance measures such as P values may be provided. These values, generated by many microarray data analysis packages, indicate where the level of gene expression or the fold change appears to be greater than random chance. If you are using significance measures, then your expression file should contain them in a second set of columns after the expression values. The column names for the expression significance measures need to match those of the expression values '''exactly'''. For example, here is an excerpt from the file galExpData.pvals in the Cytoscape sampleData directory: {{{ GENE COMMON gal1RG gal4RG gal80R gal1RG gal4RG gal80R YHR051W COX6 -0.034 0.111 -0.304 3.75720e-01 1.56240e-02 7.91340e-06 YHR124W NDT80 -0.090 0.007 -0.348 2.71460e-01 9.64330e-01 3.44760e-01 YKL181W PRS1 -0.167 -0.233 0.112 6.27120e-03 7.89400e-04 1.44060e-01 YGR072W UPF3 0.245 -0.471 0.787 4.10450e-04 7.51780e-04 1.37130e-05 }}} This indicates that there is data for three experiments: gal1RG, gal4RG, and gal80R. These names appear two times in the header line: the first time gives the expression values, and the second gives the significance measures. For instance, the second line tells us that in Experiment gal1RG, the gene YHR051W has an expression value of -0.034 with significance measure 3.75720e-01. Some variations on this basic format are recognized; see the formal file format specification below for more information. Expression data files commonly have the file extension ".pvals", and this file extension is recognized by Cytoscape when browsing for data files (File → Import → Table → File...). ==== General Procedure ==== Load an expression attribute matrix file using File → Import → Table → File... to bring up the import window, or by specifying the filename using the -m option at the command line. ===== Worked Example ===== For the sample network file {{{sampleData/galFiltered.sif}}}: Load a sample gene expression data set by going to File → Import → Table → File.... In the resulting window, select the file {{{sampleData/galExpData.pvals}}}. In the combobox 'Import Data to', make sure the selected item is 'Node Attributes'. The identifiers used in this file are the same ones used in the network file {{{sampleData/galFiltered.sif}}}, so the attributes will be mapped to the nodes automatically. A few lines of this file are shown below: {{{ GENE COMMON gal1RG gal4RG gal80R gal1RG gal4RG gal80R YHR051W COX6 -0.034 0.111 -0.304 3.75720e-01 1.56240e-02 7.91340e-06 YHR124W NDT80 -0.090 0.007 -0.348 2.71460e-01 9.64330e-01 3.44760e-01 YKL181W PRS1 -0.167 -0.233 0.112 6.27120e-03 7.89400e-04 1.44060e-01 }}} ===== Detailed file format (Advanced users) ===== Expression data files must have extension '.pvals'. In all expression data files, any whitespace (spaces and/or tabs) is considered a delimiter between adjacent fields. Every line of text is either the header line or contains all the measurements for a particular gene. No name conversion is applied to expression data files. The names given in the first column of the expression data file should match exactly the names used elsewhere (i.e. in SIF or GML files). The first line is a header line with one of the following three header formats: {{{ <text> <text> cond1 cond2 ... cond1 cond2 ... [NumSigConds] <text> <text> cond1 cond2 ... <tab><tab>RATIOS<tab><tab>...LAMBDAS }}} The first format specifies that both expression ratios and significance values are included in the file. The first two text tokens (in angled brackets) contain names for each gene, such as the formal and common gene names. The {{{condX}}} token set specifies the names of the experimental conditions; these columns will contain ratio values. This list of condition names must then be duplicated exactly, each spelled the same way and in the same order. Optionally, a final column with the title !NumSigConds may be present. If present, this column will contain integer values indicating the number of conditions in which each gene had a statistically significant change according to some threshold. The second format is similar to the first except that the duplicate column names are omitted, and there is no !NumSigConds field. This format specifies data with ratios but no significance values. The third format specifies an MTX header, which is a commonly used format. Two tab characters precede the RATIOS token. This token is followed by a number of tabs equal to the number of conditions, followed by the LAMBDAS token. This format specifies both ratios and significance values. Each line after the first is a data line with the following format: {{{ FormalGeneName CommonGeneName ratio1 ratio2 ... [lambda1 lambda2 ...] [numSigConds] }}} The first two tokens are gene names. The names in the first column are the keys used for node name lookup; these names should be the same as the names used elsewhere in Cytoscape (i.e. in the SIF, GML, or XGMML files). Traditionally in the gene expression microarray community, who defined these file formats, the first token is expected to be the formal name of the gene (in systems where there is a formal naming scheme for genes), while the second is expected to be a synonym for the gene commonly used by biologists, although Cytoscape does not make use of the common name column. The next columns contain floating point values for the ratios, followed by columns with the significance values if specified by the header line. The final column, if specified by the header line, should contain an integer giving the number of significant conditions for that gene. Missing values are not allowed and will confuse the parser. For example, using two consecutive tabs to indicate a missing value will not work; the parser will regard both tabs as a single delimiter and be unable to parse the line correctly. Optionally, the last line of the file may be a special footer line with the following format: {{{ NumSigGenes int1 int2 ... }}} This line specified the number of genes that were significantly differentially expressed in each condition. The first text token must be spelled exactly as shown; the rest of the line should contain one integer value for each experimental condition. == Annotations == Annotations in Cytoscape are stored as a set of ontologies (e.g. the Gene Ontology, or GO). An ontology consists of a set of controlled vocabulary terms that annotate the objects. For example, using the Gene Ontology, the Saccharomyces Cerevisiae '''CDC55''' gene has a biological process described as “protein biosynthesis”, to which GO has assigned the number 6412 (a GO ID). |
When Cytoscape is started, the Table Panel appears in the bottom !CytoPanel. This panel can be hidden and restored using the View → Show/Hide Table Panel menu option. Like other !CytoPanels, the panel can be undocked by pressing the little icon in the panel’s top right corner. To swap between displaying node, edge, and network tables use the tabs on the bottom of the panel labeled "Node Table", "Edge Table", and "Network Table". In Cytoscape 3.0 there are two display modes for the table: show selected nodes/edges only and show all rows. This configuration can be set using button (the left most) in the figure. The Table Panel displays data belonging to the currently selected network. Using the three buttons (left 2nd to 4th) in the figure, it is possible to make some or all columns visible and hide others or all of them. Also, a new column can be created by pressing button the (left 5th) or mutable columns can be deleted by button (left 6th). Button f(x) is for writing equations to manipulate the data which is further explained in the section [[Cytoscape_3/UserManual/Attribute_Formulas|attribute functions and equations]]. Most data values can be edited by double-clicking on their table cell (only the SUID cannot be edited). Newline characters can be inserted into String attributes either by pressing ''Enter'' or by typing "\n". Once finished editing, click outside of the editing cell in the Table Panel or press ''Shift-Enter'' to save your edits. Pressing ''Esc'' while editing will undo any changes. Table rows in the browser can be sorted by a specific column by clicking on a column heading. A new column can be created using the Create New Column button (left 5th), and must be one of four types – integer, string, real number (floating point), or boolean. Attributes can be deleted using the Delete Attributes button (left 6th, trash can icon). '''NOTE: Deleting attributes removes them from Cytoscape, not just the attribute browser!''' To remove attributes from the browser without deleting them, simply unselect the attribute using the Select Column button (left 3rd). The right-click menu on the Table Panel has several functions, such as exporting attribute information to spreadsheet applications. For example, use the right-click menu to select the data and copy for use in a spreadsheet application. == Ontologies == Another type of data that can be associated with network elements are ontologies. An ontology consists of an organized set of controlled vocabulary terms that annotate the objects. Most ontologies in science are organized in a hierarchical way. In biology for example, using the Gene Ontology, the Saccharomyces Cerevisiae '''CDC55''' gene has a biological process described as “protein biosynthesis”, to which GO has assigned the number 6412 (a GO ID). |
| Line 260: | Line 108: |
|
Cytoscape can use this ontology DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) to annotate objects in networks. The Ontology Server is a Cytoscape feature which allows you to load, navigate, and assign annotation terms to nodes and edges in a network. Cytoscape has an GUI for loading ontology and associated annotation, enabling you to load both local and remote files. === Ontology and Annotation File Format === |
Cytoscape can use this ontology DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) to annotate objects in networks. The Ontology Server is a Cytoscape feature which allows you to load, navigate, and associate ontology terms to nodes and edges in a network. Cytoscape has an GUI for loading ontology and associating it with the network elements, enabling you to load both local and remote files. === Ontology and Association File Format === |
| Line 267: | Line 115: |
| * Current Annotations: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.current.annotations.shtml | * Current Associtations: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.current.annotations.shtml |
| Line 307: | Line 155: |
| Cytoscape provides a list of ontologies available in OBO format. If an Internet connection is available, Cytoscape will import ontology and annotation files directly from the remote source. The table below lists the included ontologies. | Cytoscape provides a list of ontologies available in OBO format. If an Internet connection is available, Cytoscape will import ontology and associatation files directly from the remote source. The table below lists the included ontologies. |
| Line 321: | Line 169: |
| Although Cytoscape can import all kinds of ontologies in OBO format, annotation files are associated with specific ontologies. Therefore, you need to provide the correct ontology-specific annotation file to annotate nodes/edges/networks in Cytoscape. For example, while you can annotate human network data using the GO Full ontology with human Gene Association files, you cannot use a combination of the human Disease Ontology file and human Gene Association files, because the Gene Association file is only compatible with GO. | Although Cytoscape can import all kinds of ontologies in OBO format, association files are associated with specific ontologies. Therefore, you need to provide the correct ontology-specific association file to annotate nodes/edges/networks in Cytoscape. For example, while you can annotate human network data using the GO Full ontology with human Gene Association files, you cannot use a combination of the human Disease Ontology file and human Gene Association files, because the Gene Association file is only compatible with GO. |
| Line 337: | Line 185: |
|
The Gene Association (GA) file provides annotation only for the Gene Ontology. It is a species-specific annotation file for GO terms. '''Gene Association files will only work with Gene Ontologies and NOT others!''' Sample Gene Association File ([[http://viewvc.geneontology.org/viewvc/GO-SVN/trunk/gene-associations/gene_association.sgd.gz?rev=HEAD|gene_association.sgd]] - annotation file for yeast): |
The Gene Association (GA) file provides annotation only for the Gene Ontology. It is a species-specific association file for GO terms. '''Gene Association files will only work with Gene Ontologies and NOT others!''' Sample Gene Association File ([[http://viewvc.geneontology.org/viewvc/GO-SVN/trunk/gene-associations/gene_association.sgd.gz?rev=HEAD|gene_association.sgd]] - association file for yeast): |
| Line 346: | Line 194: |
|
=== Node Name Mapping === If you have a network file and an attribute file, they should have a common key to map attributes onto network data. If those two do not have a common key, you need to do an extra step to add a shared key. The following is a quick tutorial to learn how to use Gene Name Mapping files. ==== Import New ID Sets from BioMart ==== You can import various kinds of ID sets from !BioMart (http://www.biomart.org/index.html). !BioMart web service client is integrated into Cytoscape. {{attachment:id_mapping1.png}} 1. Select: '''File → Import → Table → Public Databases...''' 1. Select a data source. For ID mapping, select one of the ''Ensemble Genes'' data set. You need to choose correct species for your network. 1. Select '''Attribute'''. If you want to import new ID sets matching current node IDs, select ''name''. 1. Select '''Data Type'''. This should be the type of ID set selected in '''Attribute''' list. For example, if you select ''name'' for '''Attribute''' and your network uses ''Entrez Gene ID'' for its node ID, you need to select ''!EntrezGene ID(s)'' for '''Data Type'''. 1. Select new ID sets from the list. Because !BioMart server does not accept query to import lots of annotations at once, you can select only 3-5 attributes for each import. 1. Press '''Import'''. ==== Import Gene Ontology and Gene Association Files ==== |
If you have a network file and an association file, they should have a common key to map attributes onto network data. If those two do not have a common key, you need to do an extra step to add a shared key by mapping the current key to a common key as described above (Node Name Mapping). === Import Gene Ontology and Gene Association Files === |
| Line 373: | Line 207: |
Interaction networks are useful as stand-alone models. However, they are most powerful for answering scientific questions when integrated with additional information.
Cytoscape allows the user to add arbitrary node, edge and network data to Cytoscape through the data table. This could include, for example, expression data of a gene or confidence values in a protein-protein interaction. In the data table, information is linked to nodes, edges or networks by mapping the columns to one of their identifiers. Through the table panel the values can be further manipulated through the use of attribute functions and equations
A second type of data that can be associated with networks is ontology data: organized sets of controlled vocabulary terms. Because this type of data is mostly hierarchically organized, this requires a special importing facility, described in the second part of this section.
Data associated with the network elements can be visualized in a user-defined way by setting up a mapping from data attributes in the columns to visual attributes (colors, shapes, and so on) in the network on screen. The section on visual styles discusses this in greater detail.
Table data
Cytoscape supports several tabular formats. The right reader will be found based on the file extension. The supported file extensions are the regular text and table formats: .tsv, .tab, .csv, .net, .txt (comma, tab or any delimiter separated values file), .xls, .xlsx (Microsoft Excel file format). Note that for Excel file formats, only the first sheet of a workbook is currently imported. The legacy native Cytoscape formats: .attrs and .pvals (Cytoscape expression matrix) are also supported (for a more thorough discussion of these formats consult the 2.x manual). For most users the regular data table importing functionality will be sufficient; in case a format is unknown, renaming the file to a .txt extension and toying around with delimiter and header settings will most of the times do the trick.
Importing data
Basic table file
The basic file format consists of a table containing at least one column with identifiers (unique names) for the nodes, edges or networks, and one or (any number) more columns with data you want to associate with these network elements.
Sample Data Table 1
Yeast Key |
Degree |
YER054C |
85 |
YBL079W |
7 |
YLR345W |
1 |
To import such a file:
Select File → Import → Table → File... ( or URL... if your source data file is accessible through the internet)
- Select a data file in the file chooser panel (or enter the URL in the displayed box). This file can be in any of the accepted formats mentioned above.
- In the "Import Attribute from File" panel, select one of the attribute types. Cytoscape can import node, edge, and network attributes.
- (Optional) Choose if you would like to import the file for all of the available networks or only selected networks using the check box in the expandable "Network Options" panel (this panel is collapsed by default). Select networks from the list.
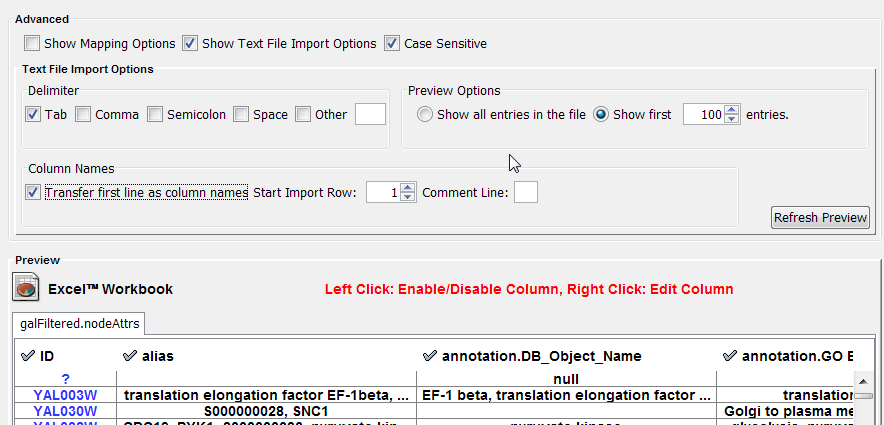
- (Optional) If the table is not properly delimited in the preview panel, change the delimiter in the Text File Import Options panel (the default delimiter is Tab).
- By default, the first column is designated as the primary key. Change the key column if necessary, see below for an example.
- The data attribute column name can be changed by right clicking on the header. A dialog appears that enables specification of the datatype and column name.
- Left clicking selects or deselects the column for importing.
- Click the Import button.
The user interface of the "Import Table from File" window is similar to that of the "Import Network from Table" window.
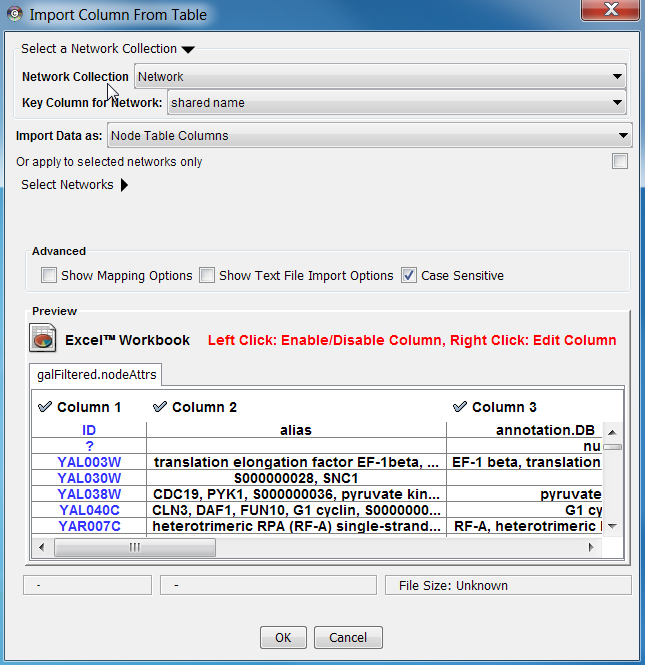
If the data only relates to a specific network select the 'Apply to selected networks only' box and select the specific network from the list (click 'Select Networks' to show this list)
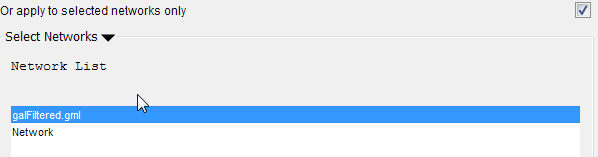
Mapping data options
In Cytoscape 3.0 data columns with primitive data types (string, boolean, floating point, and integer) can be selected as the key column using the dropdown list provided. Complex data attributes such as lists are not supported as keys.
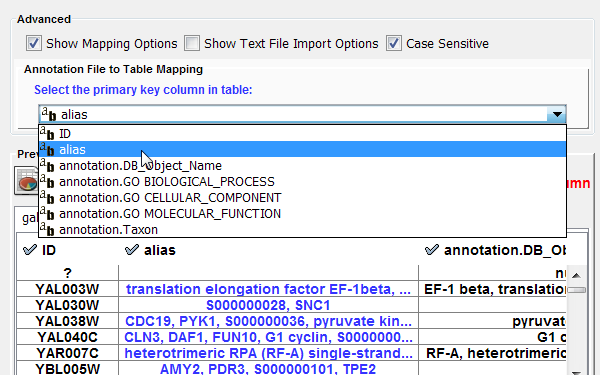
Text file import options
When the text file import options box is checked, several additional parameters can be selected to tune the way the data file will be imported. The first line can be used to specify column header names. Another data delimiter (default is tab) can be chosen, and the comment prefix (signifying lines to be ignored) can be defined.
Import from Public Databases
You can import various kinds of ID sets from the BioMart (http://www.biomart.org/index.html) public database. The BioMart web service client is integrated into Cytoscape.
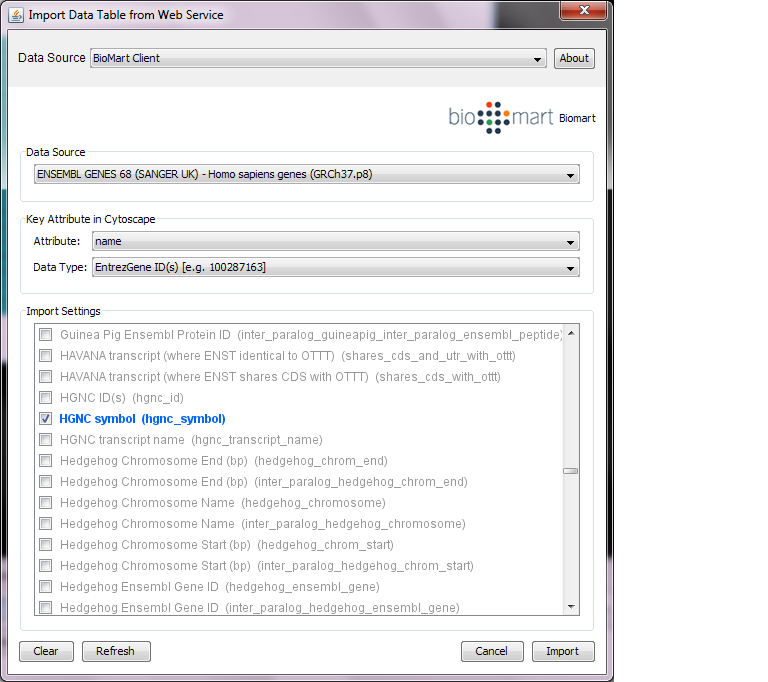
Select: File → Import → Table → Public Databases...
Select a data source. For ID mapping, select one of the Ensemble Genes data set. You need to choose the correct species for your network.
Select Attribute. If you want to import new ID sets matching current node IDs, select shared name.
Select Data Type. This should be the type of ID set selected in Attribute list. For example, if you select shared name for Attribute and your network uses Entrez Gene ID for its node ID, you need to select EntrezGene ID(s) for Data Type.
Select new ID sets from the list. Because there is a size limitation on the results returned by the!BioMart server, you can select only 3-5 attributes for each import.
Press Import.
Data in complete networks
When importing a network from a table, columns other than the node identifier can be imported as data also. For more detail on these options, please see the "Import Free-Format Table Files" section of the user manual in the Creating Networks chapter.
Table Panel
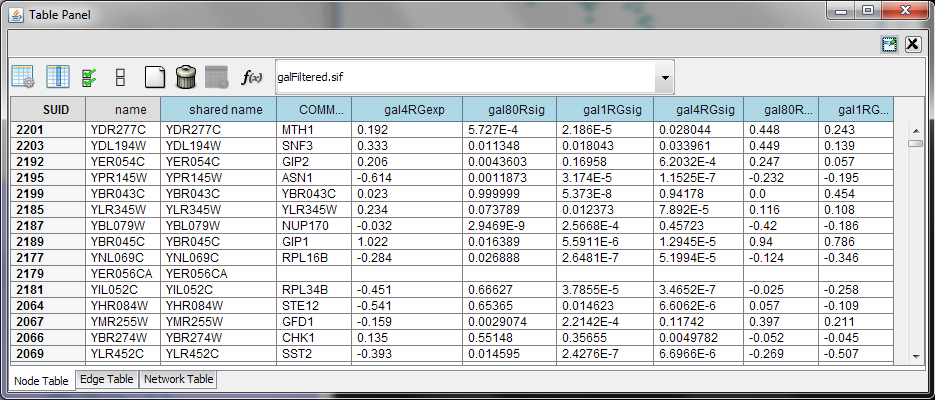
When Cytoscape is started, the Table Panel appears in the bottom CytoPanel. This panel can be hidden and restored using the View → Show/Hide Table Panel menu option. Like other CytoPanels, the panel can be undocked by pressing the little icon in the panel’s top right corner.
To swap between displaying node, edge, and network tables use the tabs on the bottom of the panel labeled "Node Table", "Edge Table", and "Network Table".
In Cytoscape 3.0 there are two display modes for the table: show selected nodes/edges only and show all rows. This configuration can be set using button (the left most) in the figure. The Table Panel displays data belonging to the currently selected network.
Using the three buttons (left 2nd to 4th) in the figure, it is possible to make some or all columns visible and hide others or all of them. Also, a new column can be created by pressing button the (left 5th) or mutable columns can be deleted by button (left 6th). Button f(x) is for writing equations to manipulate the data which is further explained in the section attribute functions and equations.
Most data values can be edited by double-clicking on their table cell (only the SUID cannot be edited). Newline characters can be inserted into String attributes either by pressing Enter or by typing "\n". Once finished editing, click outside of the editing cell in the Table Panel or press Shift-Enter to save your edits. Pressing Esc while editing will undo any changes.
Table rows in the browser can be sorted by a specific column by clicking on a column heading. A new column can be created using the Create New Column button (left 5th), and must be one of four types – integer, string, real number (floating point), or boolean. Attributes can be deleted using the Delete Attributes button (left 6th, trash can icon). NOTE: Deleting attributes removes them from Cytoscape, not just the attribute browser! To remove attributes from the browser without deleting them, simply unselect the attribute using the Select Column button (left 3rd).
The right-click menu on the Table Panel has several functions, such as exporting attribute information to spreadsheet applications. For example, use the right-click menu to select the data and copy for use in a spreadsheet application.
Ontologies
Another type of data that can be associated with network elements are ontologies. An ontology consists of an organized set of controlled vocabulary terms that annotate the objects. Most ontologies in science are organized in a hierarchical way. In biology for example, using the Gene Ontology, the Saccharomyces Cerevisiae CDC55 gene has a biological process described as “protein biosynthesis”, to which GO has assigned the number 6412 (a GO ID).
GO 8150 biological_process
GO 7582 physiological processes
GO 8152 metabolism
GO 44238 primary metabolism
GO 19538 protein metabolism
GO 6412 protein biosynthesisGraphical View of GO Term 6412: protein biosynthesis
Cytoscape can use this ontology DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) to annotate objects in networks. The Ontology Server is a Cytoscape feature which allows you to load, navigate, and associate ontology terms to nodes and edges in a network. Cytoscape has an GUI for loading ontology and associating it with the network elements, enabling you to load both local and remote files.
Ontology and Association File Format
The standard file formats used in Cytoscape Ontology Server are OBO and Gene Association. The GO website details these file formats:
Ontologies and Definitions: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.downloads.shtml#ont
Current Associtations: http://www.geneontology.org/GO.current.annotations.shtml
OBO File
An OBO file is the ontology DAG itself. This file defines the relationships between ontology terms. Cytoscape can load all ontology files written in OBO format. The full listing of ontology files are available from the Open Biomedical Ontologies (OBO) website:
OBO Ontology Browser: http://obo.sourceforge.net/browse.html
Sample OBO File - gene_ontology.obo: http://www.geneontology.org/ontology/gene_ontology_edit.obo
format-version: 1.2 date: 27:11:2006 17:12 saved-by: midori auto-generated-by: OBO-Edit 1.002 subsetdef: goslim_generic "Generic GO slim" subsetdef: goslim_goa "GOA and proteome slim" subsetdef: goslim_plant "Plant GO slim" subsetdef: goslim_yeast "Yeast GO slim" subsetdef: gosubset_prok "Prokaryotic GO subset" default-namespace: gene_ontology remark: cvs version: $Revision: 5.49 $ [Term] id: GO:0000001 name: mitochondrion inheritance namespace: biological_process def: "The distribution of mitochondria, including the mitochondrial genome, into daughter cells after mitosis or meiosis, mediated by interactions between mitochondria and the cytoskeleton." [GOC:mcc, PMID:10873824, PMID:11389764] synonym: "mitochondrial inheritance" EXACT [] is_a: GO:0048308 ! organelle inheritance is_a: GO:0048311 ! mitochondrion distribution [Term] id: GO:0000002 name: mitochondrial genome maintenance namespace: biological_process def: "The maintenance of the structure and integrity of the mitochondrial genome." [GOC:ai] is_a: GO:0007005 ! mitochondrion organization and biogenesis
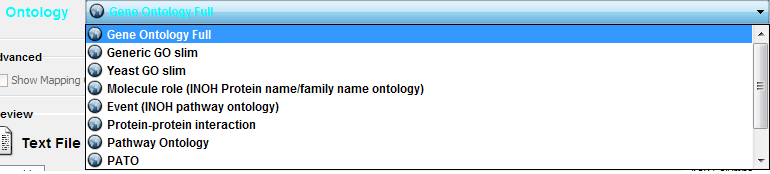
Default List of Ontologies
Cytoscape provides a list of ontologies available in OBO format. If an Internet connection is available, Cytoscape will import ontology and associatation files directly from the remote source. The table below lists the included ontologies.
Ontology Name |
Description |
Gene Ontology Full |
This data source contains a full-size GO DAG, which contains all GO terms. This OBO file is written in version 1.2 format. |
Generic GO slim |
A subset of general GO Terms, including higer-level terms only. |
Yeast GO slim |
A subset of GO Terms for annotating Yeast data sets maintained by SGD. |
Molecule role (INOH Protein name/family name ontology) |
A structured controlled vocabulary of concrete and abstract (generic) protein names. This ontology is a INOH pathway annotation ontology, one of a set of ontologies intended to be used in pathway data annotation to ease data integration. This ontology is used to annotate protein names, protein family names, and generic/concrete protein names in the INOH pathway data. INOH is part of the BioPAX working group. |
Event (INOH pathway ontology) |
A structured controlled vocabulary of pathway-centric biological processes. This ontology is a INOH pathway annotation ontology, one of a set of ontologies intended to be used in pathway data annotation to ease data integration. This ontology is used to annotate biological processes, pathways, and sub-pathways in the INOH pathway data. INOH is part of the BioPAX working group. |
Protein-protein interaction |
A structured controlled vocabulary for the annotation of experiments concerned with protein-protein interactions. |
Pathway Ontology |
The Pathway Ontology is a controlled vocabulary for pathways that provides standard terms for the annotation of gene products. |
PATO |
PATO is an ontology of phenotypic qualities, intended for use in a number of applications, primarily phenotype annotation. For more information, please visit the PATO wiki (http://www.bioontology.org/wiki/index.php/PATO:Main_Page). |
Mouse pathology |
The Mouse Pathology Ontology (MPATH) is an ontology for mutant mouse pathology. This is Version 1. |
Human disease |
This ontology is a comprehensive hierarchical controlled vocabulary for human disease representation. For more information, please visit the Disease Ontology website (http://diseaseontology.sourceforge.net/). |
Although Cytoscape can import all kinds of ontologies in OBO format, association files are associated with specific ontologies. Therefore, you need to provide the correct ontology-specific association file to annotate nodes/edges/networks in Cytoscape. For example, while you can annotate human network data using the GO Full ontology with human Gene Association files, you cannot use a combination of the human Disease Ontology file and human Gene Association files, because the Gene Association file is only compatible with GO.
Visualize and Browse Ontology DAG (for Advanced Users)
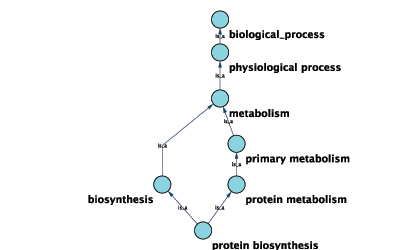
Relationships between ontology terms are usually represented as Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). This is a special case of a network (or graph), where nodes are ontology terms and edges are relationships between terms. Ontology data is stored in the same data structure as normal networks. This enables users and App writers to visualize, browse and manipulate ontology DAGs just like other networks. The following is an example of visualization of an ontology DAG (Generic GO Slim):
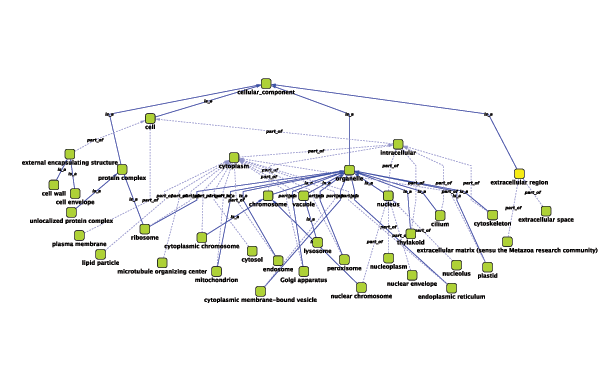
Every ontology term and relationship can have attributes. In the OBO files, ontology terms have optional fields such as definition, synonyms, comments, or cross-references. These fields will be imported as node attributes. To browse those attributes, please use the attribute browser (see the example below):
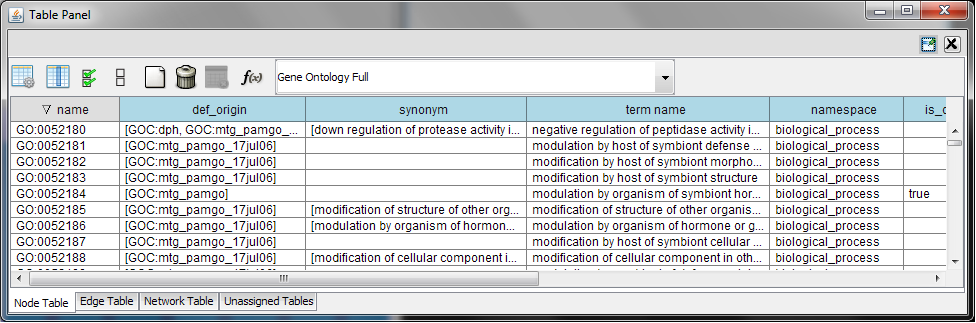
- Note 1: Some ontologies have a lot of terms. For example, the full Gene Ontology contains more than 20,000 terms. If you need to save memory, you can remove this ontology DAG from Network Panel (right-click on the ontology name at the left-hand side of the screen and select Destroy Network).
- Note 2: All ontology DAGs will be saved in the session file. To minimize the session file size, you can delete the Ontology DAG before saving session.
Gene Association File
The Gene Association (GA) file provides annotation only for the Gene Ontology. It is a species-specific association file for GO terms. Gene Association files will only work with Gene Ontologies and NOT others!
Sample Gene Association File (gene_association.sgd - association file for yeast):
SGD S000003916 AAD10 GO:0006081 SGD_REF:S000042151|PMID:10572264 ISS P aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase (putative) YJR155W gene taxon:4932 20020902 SGD SGD S000005275 AAD14 GO:0008372 SGD_REF:S000069584 ND C aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase (putative) YNL331C gene taxon:4932 20010119 SGD
If you have a network file and an association file, they should have a common key to map attributes onto network data. If those two do not have a common key, you need to do an extra step to add a shared key by mapping the current key to a common key as described above (Node Name Mapping).
Import Gene Ontology and Gene Association Files
For convenience, Cytoscape has a list of URLs for commonly used ontology data and a complete set of Gene Association files. To import Gene Ontology and Gene Association files for the loaded networks, please follow these steps:
Important: All data sources in the preset list are remote URLs, meaning a network connection is required!
Step 1. Select an Annotation File
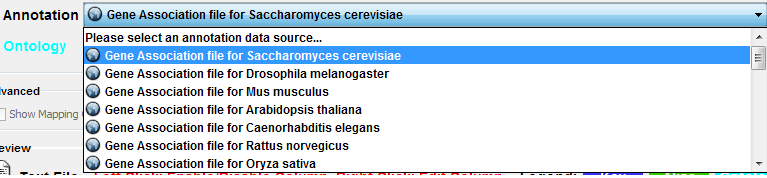
Select File → Import → Ontology and Annotation... to open the "Import Ontology and Annotation" window. From the Annotation dropdown list, select a gene association file for your network. For example, if you want to annotate the yeast network, select "Gene Association file for Saccharomyces cerevisiae".
Step 2. Select an Ontology File
- Select an Ontology data (OBO file) from the Ontology dropdown list. If the file is not loaded yet, it will be shown in red. The first three files are Gene Ontology files. You can load other ontologies, but you need your own annotation file to annotate networks.
Step 3. Import the files
- Once you click the Import button, Cytoscape will start loading OBO and Gene Association files from the remote sources. If you choose GO Full it may take a while since it is a large data file.