|
← Revision 16 as of 2014-01-23 00:21:42
Size: 5337
Comment:
|
← Revision 17 as of 2014-01-29 18:24:02 →
Size: 6727
Comment: Migrating Jasons changes
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
|
== Enhanced Search == Cytoscape includes a search feature, which enables you to quickly find nodes and edges. The search box is located at the right side in the icon bar and functions as a regular search box. |
== Search Bar == |
| Line 4: | Line 3: |
| {{attachment:Cy3_Enhanced_Search_Input_Field.png}} | You can search for nodes and edges by column value directly through Cytoscape's tool bar. For example, to select nodes or edges with a column value that starts with "STE", type {{{ste*}}} in the search bar. The search is case-insensitive. The {{{*}}} is a wildcard character that matches zero or more characters, while "?" matches exactly one character. So {{{ste?}}} would match "STE2" but would not match "STE12". Searching for {{{ste*}}} would match both. |
| Line 6: | Line 5: |
| For example, type in "ATRX*" in the search box and hit enter. This will find all the nodes/edges with string "ATRX" as prefix in any of the columns. Type in "taxonomy.name:homo*" will restrict the search to column named 'taxonomy.name' only. You can also use 'and', 'or' to make the complex search. The searching is actually based on Apache Lucene. Please look at [[http://lucene.apache.org/core/3_6_0/queryparsersyntax.html|this page]] for more about search syntax. | {{attachment:searchbar.png}} |
| Line 8: | Line 7: |
|
To search a specific column, you can prefix your search term with the column name followed by a {{{:}}}. For example, to select nodes and edges that have a "COMMON" column value that starts with "STE", use {{{common:ste*}}}. If you don't specify a particular column, all columns will be searched. Columns with names that contain spaces, quotes, or characters other than letters and numbers currently do not work when searching a specific column. This will be fixed in a future release. To search for column values that contain special characters you need to escape those characters using a "\". For example, to search for "GO:1232", use the query {{{GO\:1232}}}. The complete list of special characters is: {{{ + - & | ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \ }}} '''Note:''' Escaping characters only works when searching all columns. It currently does not work for column-specific searching. This will be fixed in a future release. |
|
| Line 10: | Line 20: |
|
Cytoscape allow you to quickly select multiple nodes or edges of interest by comparing node and edge column values to properties you specify. For example, you can select all the nodes whose name contains a specific pattern, or whose numeric column attribute value falls within a certain range. You can also perform complex selection by defining filters and performing the boolean operation between them. Filters are located under the '''Select''' tab in the '''Control Panel'''. The '''Select''' panel initially looks like this: |
|
| Line 13: | Line 21: |
| {{attachment:Cy3_Filter_Panel_Init.png}} | Cytoscape 3 provides a new user interface for filtering nodes and edges. These tools can be found in the '''Select''' panel: |
| Line 15: | Line 23: |
| '''1. Filter Definition''' | {{attachment:select-panel.png}} |
| Line 17: | Line 25: |
| To create a new filter, click the main drop-down menu and select '''Create New Filter'''. Enter a name for the new filter. | There are two main types of filters: narrowing filters, which can be combined into a tree; and chainable filters, which can only be combined in a linear chain. These can be found in the '''Filter''', and '''Chain''' tabs of the '''Select''' panel, respectively. |
| Line 19: | Line 27: |
| {{attachment:Cy3_Select_Filter_Option.png}} | === Narrowing Filters === |
| Line 21: | Line 29: |
| {{attachment:Cy3-New_Filter_Dialog.png}} | Narrowing filters select nodes and edges based on user-specified constraints. For example, you can use these filters to find edges with a weight between 0 and 5.5, or nodes with degree less than 3. A filter can contain an arbitrary number of sub-filters. To add one to your filter, click on the "+" button. |
| Line 23: | Line 31: |
| '''Definition of simple filter''' | ==== Interactive Filter Application Mode ==== |
| Line 25: | Line 33: |
| When a new filter is created, it is empty initially. It can be defined by choosing columns (one at a time) in the Column/Filter comboBox and clicking the Add button. Note that in the comboBox each column has a prefix, either node. or edge., denoting what type of attribute it is. After add button is clicked, a widget, depended on the item selected, will be added to the definition panel. If the column type is text-based (or String), the widget will be a indexed-text-box widget, if numeric attribute, the widget will be a range slider; clicking the slider enables specific definition of the values. | Due to the nature of narrowing filters, Cytoscape can apply them to a network efficiently and interactively. Some filters even provide slider controls to quickly explore different thresholds. This is the default behavior on smaller networks. For larger networks, Cytoscape automatically disables this interactivity. You can override this by manually checking the '''Apply Automatically''' box above the '''Apply''' button: |
| Line 27: | Line 35: |
| {{attachment:Cy3_Specify_Filter_Values.png}} | {{attachment:apply-automatically.png}} |
| Line 29: | Line 37: |
| For each widget, the name of the column it represents is on the left. A NOT checkbox gives the option to get the negation of selection for the widget. There is a trash-can icon on the right. Clicking on the trash-can icon will delete the widget. In this way, the filter definition can be modified after it is defined. | Cytoscape comes packaged with the following narrowing filters: |
| Line 31: | Line 39: |
| Note that if more than one widget is added on the filter definition panel, the relationship between them is “AND” by default. This relationship can be changed to “OR” by selecting the OR relation in Advanced Panel. | ==== Column Filter ==== |
| Line 33: | Line 41: |
| The Advanced panel can be opened by clicking on the plus (+) sign. | This filter will match nodes or edges that have particular column values. For numeric columns, sliders are provided to set thresholds in interactive mode. Otherwise, minimum and maximum values can be keyed in. |
| Line 35: | Line 43: |
| {{attachment:Cy3-Advanced_Filter_Options.png}} | From string columns, a variety of matching options are provided: |
| Line 37: | Line 45: |
| There are three rows in the advanced panel: | {{attachment:string-column.png}} |
| Line 39: | Line 47: |
| 1. The first row, labeled Save. The two checkboxes (Global and Session) will determine where the filter is saved. By default, filters are saved in individual sessions. If the Global checkbox is checked, the filter will be saved in the global properties file. Note also that the prefix of the filter name in the Current Filter dropdown list reflects where it is saved. | For example, column values can be checked if they contain or match exactly a particular string. The filter can also match against Java-style regular expressions. A checkbox controls whether the matching is done in a case-sensitive way. |
| Line 41: | Line 49: |
| 2. The second row, Relation, will determine what Boolean operation (AND or OR) will be applied to each individual widget. | ==== Degree Filter ==== |
| Line 43: | Line 51: |
| 3. Negation checkbox. If this checkbox is checked, the result of the filter will be negated. | The degree filter matches nodes with a degree that falls within the given minimum and maximum values, inclusive. You can choose whether the filter operates on the in-degree, out-degree or overall (in + out) degree. |
| Line 45: | Line 53: |
| ''Definition of complex filter'' | ==== Topology Filter ==== |
| Line 47: | Line 55: |
| In the pull-down list of Column/Filter comboBox, there are two sections, the top one is the list of columns, the bottom one is the list of previously defined filter. Those previously defined filters can also be used as components of other filters. By combinational use of AND, OR, NOT and pre-defined filters, filters with arbitrary complexity can be defined. | The topology filter matches nodes with a certain number of neighbors which are within a fixed distance away. The thresholds for the neighborhood size and distance can be set independently. |
| Line 49: | Line 57: |
| '''3. Apply the filter''' | ==== Grouping and Organizing Filters ==== |
| Line 51: | Line 59: |
| If a network is small (number of nodes or edges less than 1000), the filter will be applied dynamically when a widget is added or any value is adjusted. If the network is large, then Apply button should be clicked to apply the filter. | By default, nodes and edges need to satisfy the constraints of all your filters. You can change this so that instead, only the constraints of at least one filter needs to be met in order to match a node or edge. This behavior is controlled by the '''Match all/any''' drop-down box. This appears once your filter has more than one sub-filter. For example, suppose you wanted to match nodes with column ''COMMON'' containing {{{ste}}} or {{{cdc}}}, but you only want nodes with degree 5 or more, you'd first construct a filter that looks like this: |
| Line 53: | Line 61: |
| '''4. Other filters ''' | {{attachment:sample-group2.png}} |
| Line 55: | Line 63: |
| In the option menu pulldown, there are menu items “Create new topology filter”, “Create new NodeInteraction filter” and “Create new EdgeInteraction filter”. | This filter will match nodes where '''COMMON''' contains {{{ste}}} '''and''' {{{cdc}}}. To change this to a logical '''or''' operation, drag either of the column filters by its handle onto the other column filter to create a new group. Now change the group's matching behavior to '''Match any''': |
| Line 57: | Line 65: |
| ''Topology Filter'' | {{attachment:sample-group1.png}} |
| Line 59: | Line 67: |
| Topology filter will select nodes based on the properties of its near-by nodes (neighbors). To create a topology filter, choose the menu item “Create new topology filter” from the option menu. See below, | You can also reorder filters by dropping them in-between existing filters. |
| Line 61: | Line 69: |
| {{attachment:FilterTopo.png}} | === Chainable Filters === |
| Line 63: | Line 71: |
| ''Interaction filter'' | Chainable filters are a more general case of narrowing filters. These filters take nodes and edges, from your selection or a narrowing filter, as input. The nodes and edges in the output of the filter become the input of the next filter in the chain. The output of the last filter becomes the new selection. |
| Line 65: | Line 73: |
| Interaction filters are used to select nodes/edges based on the properties of their neighboring edges/nodes. See below for a edge interaction filter. | Chainable filters can also be reordered by dragging one by the handle and dropping it between existing filters. |
| Line 67: | Line 75: |
| {{attachment:FilterEdgeInteraction.png}} | Cytoscape currently bundles the following chainable filter: |
| Line 69: | Line 77: |
|
==== Interaction Transformer ==== This transformer will go through all the input edges and add their source nodes, target nodes, or both, to the output. This is useful for selecting nodes that are connected to edges that match a particular filter. === Working with Narrowing and Chainable Filters === The name of active filter appears in the drop-down box at the top of '''Select''' panel. Beside this is the options button which will allow you to rename, remove or export the active filter. It also lets you create a new filter, or import filters. {{attachment:select-panel-options.png}} At the bottom of the '''Select''' panel, there is an '''Apply''' button that will re-apply the active filter. On the opposite side of the progress bar is the cancel button, which will let you interrupt a long-running filter. |
|
| Line 71: | Line 90: |
| The Select → Nodes and Select → Edges menus provide several mechanisms for selecting nodes and edges. Most options are fairly straightforward; however, some need extra explanation. | The '''Select → Nodes''' and '''Select → Edges''' menus provide several mechanisms for selecting nodes and edges. Most options are fairly straightforward; however, some need extra explanation. |
| Line 73: | Line 92: |
| Select → Nodes → From ID List File... selects nodes based on node identifiers found in a specified file. The file format is simply one node id per line: | '''Select → Nodes → From ID List File...''' selects nodes based on node identifiers found in a specified file. The file format is simply one node id per line: |
Search Bar
You can search for nodes and edges by column value directly through Cytoscape's tool bar. For example, to select nodes or edges with a column value that starts with "STE", type ste* in the search bar. The search is case-insensitive. The * is a wildcard character that matches zero or more characters, while "?" matches exactly one character. So ste? would match "STE2" but would not match "STE12". Searching for ste* would match both.
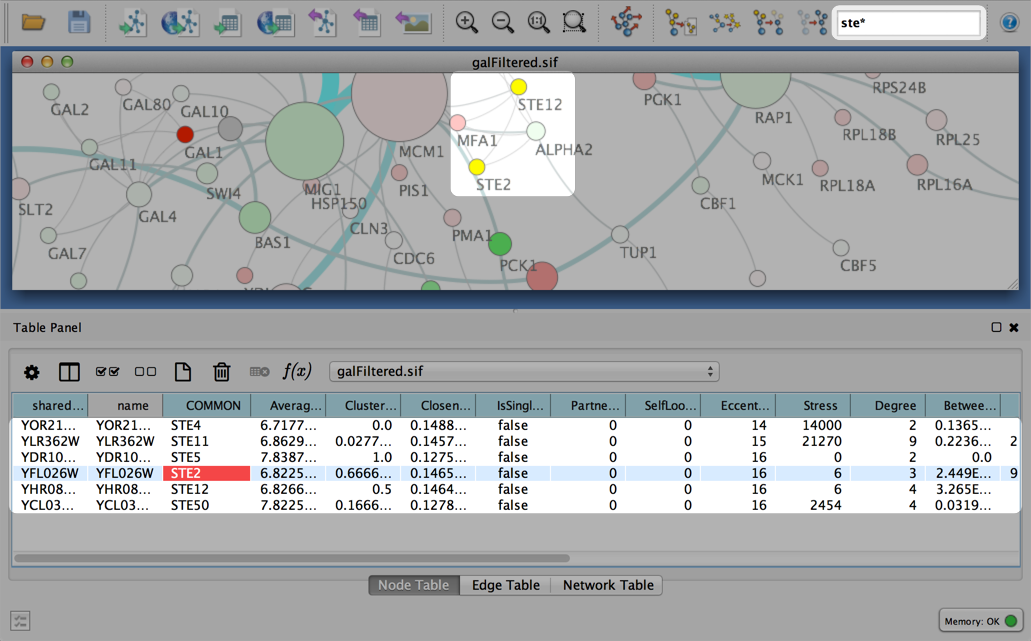
To search a specific column, you can prefix your search term with the column name followed by a :. For example, to select nodes and edges that have a "COMMON" column value that starts with "STE", use common:ste*. If you don't specify a particular column, all columns will be searched.
Columns with names that contain spaces, quotes, or characters other than letters and numbers currently do not work when searching a specific column. This will be fixed in a future release.
To search for column values that contain special characters you need to escape those characters using a "\". For example, to search for "GO:1232", use the query GO\:1232. The complete list of special characters is:
+ - & | ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \Note: Escaping characters only works when searching all columns. It currently does not work for column-specific searching. This will be fixed in a future release.
Filters
Cytoscape 3 provides a new user interface for filtering nodes and edges. These tools can be found in the Select panel:
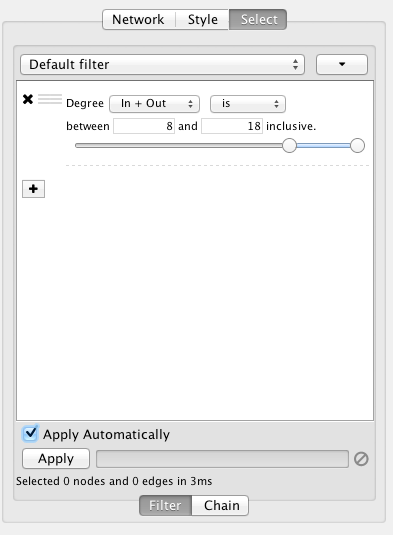
There are two main types of filters: narrowing filters, which can be combined into a tree; and chainable filters, which can only be combined in a linear chain. These can be found in the Filter, and Chain tabs of the Select panel, respectively.
Narrowing Filters
Narrowing filters select nodes and edges based on user-specified constraints. For example, you can use these filters to find edges with a weight between 0 and 5.5, or nodes with degree less than 3. A filter can contain an arbitrary number of sub-filters. To add one to your filter, click on the "+" button.
Interactive Filter Application Mode
Due to the nature of narrowing filters, Cytoscape can apply them to a network efficiently and interactively. Some filters even provide slider controls to quickly explore different thresholds. This is the default behavior on smaller networks. For larger networks, Cytoscape automatically disables this interactivity. You can override this by manually checking the Apply Automatically box above the Apply button:
Cytoscape comes packaged with the following narrowing filters:
Column Filter
This filter will match nodes or edges that have particular column values. For numeric columns, sliders are provided to set thresholds in interactive mode. Otherwise, minimum and maximum values can be keyed in.
From string columns, a variety of matching options are provided:
For example, column values can be checked if they contain or match exactly a particular string. The filter can also match against Java-style regular expressions. A checkbox controls whether the matching is done in a case-sensitive way.
Degree Filter
The degree filter matches nodes with a degree that falls within the given minimum and maximum values, inclusive. You can choose whether the filter operates on the in-degree, out-degree or overall (in + out) degree.
Topology Filter
The topology filter matches nodes with a certain number of neighbors which are within a fixed distance away. The thresholds for the neighborhood size and distance can be set independently.
Grouping and Organizing Filters
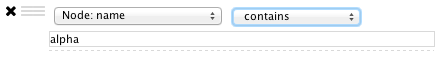
By default, nodes and edges need to satisfy the constraints of all your filters. You can change this so that instead, only the constraints of at least one filter needs to be met in order to match a node or edge. This behavior is controlled by the Match all/any drop-down box. This appears once your filter has more than one sub-filter. For example, suppose you wanted to match nodes with column COMMON containing ste or cdc, but you only want nodes with degree 5 or more, you'd first construct a filter that looks like this:
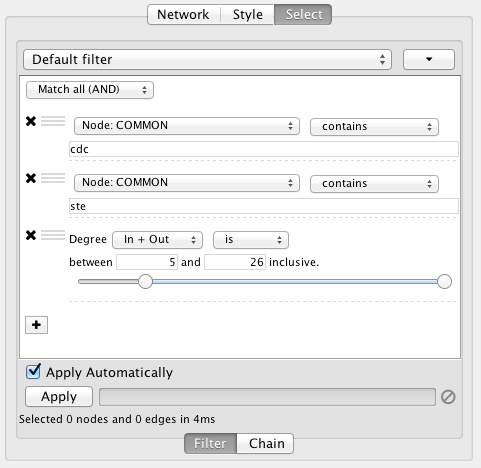
This filter will match nodes where COMMON contains ste and cdc. To change this to a logical or operation, drag either of the column filters by its handle onto the other column filter to create a new group. Now change the group's matching behavior to Match any:
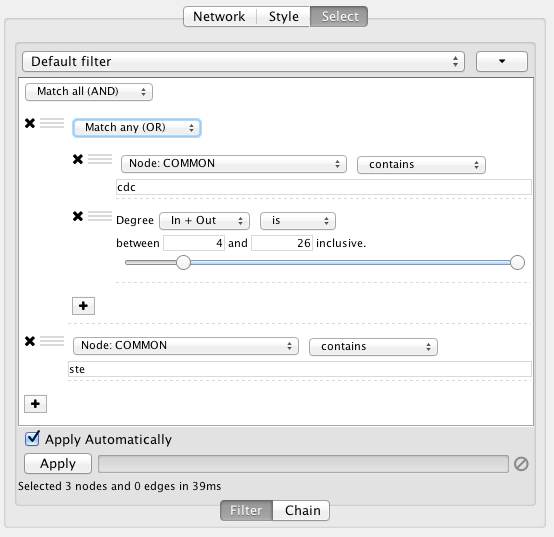
You can also reorder filters by dropping them in-between existing filters.
Chainable Filters
Chainable filters are a more general case of narrowing filters. These filters take nodes and edges, from your selection or a narrowing filter, as input. The nodes and edges in the output of the filter become the input of the next filter in the chain. The output of the last filter becomes the new selection.
Chainable filters can also be reordered by dragging one by the handle and dropping it between existing filters.
Cytoscape currently bundles the following chainable filter:
Interaction Transformer
This transformer will go through all the input edges and add their source nodes, target nodes, or both, to the output. This is useful for selecting nodes that are connected to edges that match a particular filter.
Working with Narrowing and Chainable Filters
The name of active filter appears in the drop-down box at the top of Select panel. Beside this is the options button which will allow you to rename, remove or export the active filter. It also lets you create a new filter, or import filters.
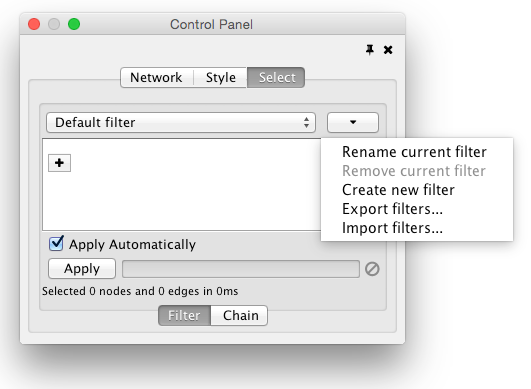
At the bottom of the Select panel, there is an Apply button that will re-apply the active filter. On the opposite side of the progress bar is the cancel button, which will let you interrupt a long-running filter.
The Select Menu
The Select → Nodes and Select → Edges menus provide several mechanisms for selecting nodes and edges. Most options are fairly straightforward; however, some need extra explanation.
Select → Nodes → From ID List File... selects nodes based on node identifiers found in a specified file. The file format is simply one node id per line:
Node1 Node2 Node3 ...