|
Size: 44015
Comment:
|
Size: 43142
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 47: | Line 47: |
|
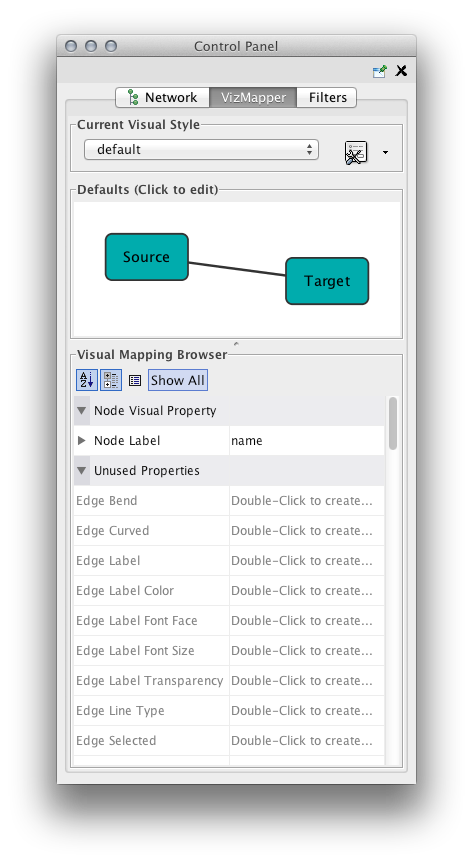
. {{attachment:VizMapperMainPanel.png}} * This panel allows you to create/delete/view/switch between different visual styles using the Current Visual Style options. The Visual Mapping Browser at the bottom displays the mapping details for a given visual style and is used to edit these details as well. 1. Default Appearance Editor . {{attachment:DefaultEditorPanel.png}} * Clicking on the section labelled "Defaults" on the Main Panel will bring up the Default Appearance Editor, which allows you to visually edit the default appearance of nodes and edges for the selected visual style. These editors will be discussed in further detail below. |
. {{attachment:VisualStyles_31.png}} This panel allows you to create/delete/view/switch between different visual styles using the Current Visual Style options. The panel displays the mapping details for a given visual style and is used to edit these details as well. |
| Line 65: | Line 58: |
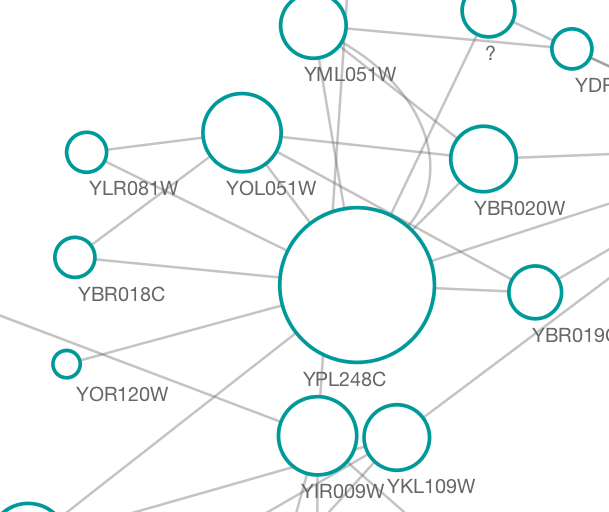
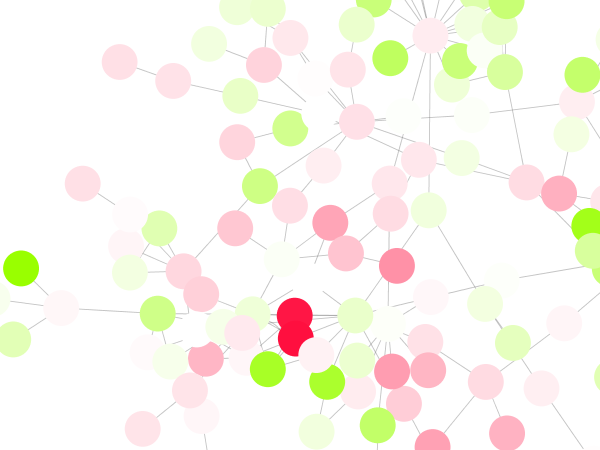
| * The session file includes a network, some annotations, and sample visual styles. By default, the '''galFiltered Style''' is selected. Gene expression values for each node are colored along a color gradient between red and green (where red represents a low expression ratio and green represents a high expression ratio, using thresholds set for the gal4RGexp experiment bundled with Cytoscape in the ''sampleData/galExpData.pvals'' file). Also, node size is mapped to the degree of the node (number of edges connected to the node) and you can see the hubs of the network as larger nodes. See the sample screenshot below: {{attachment:galFilteredSessionDefault.png}} |
* The session file includes a network, some annotations, and sample visual styles. By default, the '''Sample for galFiltered''' style is selected. Gene expression values for each node are colored along a color gradient between red and green (where red represents a low expression ratio and green represents a high expression ratio, using thresholds set for the gal4RGexp experiment bundled with Cytoscape in the ''sampleData/galExpData.csv'' file). Also, node size is mapped to the degree of the node (number of edges connected to the node) and you can see the hubs of the network as larger nodes. See the sample screenshot below: . {{attachment:galFilteredSessionDefault.png}} |
| Line 71: | Line 66: |
| For example, if you select '''Sample1''', a new visual style will be applied to your network, and you will see a white background and round blue nodes. If you zoom in closer, you can see that protein-DNA interactions (specified with the label "pd") are drawn with dashed red edges, whereas protein-protein interactions (specified with the label "pp") are drawn with a solid light blue edge (see sample screenshot below). | For example, if you select '''Sample1''', a new visual style will be applied to your network, and you will see a white background and round blue nodes. If you zoom in closer, you can see that protein-DNA interactions (specified with the label "pd") are drawn with dashed edges, whereas protein-protein interactions (specified with the label "pp") are drawn with solid edges (see sample screenshot below). |
| Line 79: | Line 74: |
|
This Visual Style does not have mappings except node/edge labels, but you can modify the network graphics by editing ''Default View''. Additional sample styles are available in the ''sampleStyles.props'' file in the ''SampleData'' directory. You can import the sample file from '''''File → Import → Vizmap Property File'''''. |
This Visual Style does not have mappings except node/edge labels, but you can modify the network graphics by editing the ''Default Value'' for any visual property. Additional sample styles are available in the {{{sampleStyles.xml}}} file in the ''sampleData'' directory. You can import the sample file from '''''File → Import → Vizmap File...''''' |
| Line 94: | Line 89: |
| ||''Node Selected Paint'' ||The color of the node when selected. || | ||''Node Selection'' ||The color of the node when selected. || |
| Line 98: | Line 93: |
| ||''Node Border Line Type'' ||Ostensibly the type of line used for the border of the node. '''This is not currently functional!''' || | ||''Node Border Line Type'' ||The type of line used for the border of the node. || |
| Line 108: | Line 103: |
|
||''Node Size'' ||The size of the node. Width and height will be equal. This visual property is mutually exclusive of Node Height and Node Width. || ||''Node Height'' ||The height of the node. Height will be independent of width. This visual property is mutually exclusive of Node Size. || ||''Node Width'' ||The width of the node. Width will be independent of height. This visual property is mutually exclusive of Node Size. || ||''Node Custom Graphics 1 - 9'' ||Custom Graphics objects on the node. These are selected from the ''Custom Graphics Manager'' || ||''Node Custom Graphics Position 1 - 9'' ||Position of Custom Graphics relative to the node. By default, this value is set to center. || |
||''Node Size'' ||The size of the node. Width and height will be equal. This visual property is mutually exclusive of ''Node Height'' and ''Node Width''. || ||''Node Height'' ||The height of the node. Height will be independent of width. This visual property is mutually exclusive of ''Node Size''. || ||''Node Width'' ||The width of the node. Width will be independent of height. This visual property is mutually exclusive of ''Node Size''. || |
| Line 115: | Line 108: |
| ||''Node Visible'' ||Node is visible or not. By default, this value is set to true. || | ||''Node Visible'' ||Node is visible or not. By default, this value is set to ''true''. || |
| Line 120: | Line 113: |
|
||''Edge Stroke Color (Selected)'' ||The color of edge. || ||''Edge Stroke Color (Unselected)'' ||The color of selected edge. || |
||''Edge Stroke Color (Unselected)'' ||The color of the edge. || ||''Edge Stroke Color (Selected)'' ||The color of the edge when selected. || |
| Line 138: | Line 131: |
|
||''Edge Curved'' ||If Egde Bend is defined, edge will be rendered as straight or curved lines. If this value is set to True, edges will be drawn as curved line. || ||''Edge Visible'' ||Edge is visible or not. By default, this value is set to true. || |
||''Edge Curved'' ||If ''Egde Bend'' is defined, edges will be rendered as straight or curved lines. If this value is set to ''true'', edges will be drawn as curved lines. || ||''Edge Visible'' ||Edge is visible or not. By default, this value is set to ''true''. || |
| Line 143: | Line 136: |
|
||''Network Background Paint'' ||The background color of the network. || ||''Network Title'' ||The title of the network. || |
||''Network Background Paint'' ||The background color of the network view. || ||''Network Title'' ||The title of the network view. || |
| Line 147: | Line 140: |
| ||''Network Scale Factor'' ||The zoom level of network view. || | ||''Network Scale Factor'' ||The zoom level of the network view. || |
| Line 150: | Line 143: |
|
||''Network Edge Selection'' ||Edges are selectable or not. If this is false, users cannot select edges.|| ||''Network Node Selection'' ||Nodes are selectable or not. If this is false, users cannot select nodes.|| |
||''Network Edge Selection'' ||Edges are selectable or not. If this is ''false'', users cannot select edges.|| ||''Network Node Selection'' ||Nodes are selectable or not. If this is ''false'', users cannot select nodes.|| |
| Line 155: | Line 148: |
|
||''Node Shapes'' || {{attachment:NewVizMapperNodeShape.png}} || ||''Edge Line Styles'' || {{attachment:NewVizMapperLineType.png}} || ||''Arrow Types'' || {{attachment:NewVizMapperArrowType.png}} || |
||''Node Shapes'' || {{attachment:NodeShapeOptions.png}} || ||''Edge Line Types'' || {{attachment:BorderLineOptions.png}} || ||''Arrow Shapes'' || {{attachment:ArrowShapeOptions.png}} || |
| Line 189: | Line 180: |
| ||''Node Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || | ||''Node Transparency'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || |
| Line 191: | Line 182: |
| ||''Node Border Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || | ||''Node Border Transparency'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || |
| Line 193: | Line 184: |
| ||''Node Label Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || | ||''Node Label Transparency'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || |
| Line 198: | Line 189: |
| ||<style="text-align: center;" |7>Other ||''Node Border Type'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || | ||<style="text-align: center;" |7>Other ||''Node Border Line Type'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || |
| Line 211: | Line 202: |
|
||<style="text-align: center;" |8>Color ||''Edge Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Target Arrow Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Source Arrow Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Target Arrow Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Source Arrow Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Label Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Label Opacity'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || |
||<style="text-align: center;" |6>Color ||''Edge Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Transparency'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Target Arrow Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Source Arrow Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Label Color'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || ||''Edge Label Transparency'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">+ || |
| Line 222: | Line 211: |
|
||<style="text-align: center;" |6>Other ||''Edge Line Type'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || ||''Edge Source Arrow Shape'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || ||''Edge Target Arrow Shape'' ||<style="text-align: center;">- ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || |
||<style="text-align: center;" |6>Other ||''Edge Line Type'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || ||''Edge Source Arrow Shape'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || ||''Edge Target Arrow Shape'' ||<style="text-align: center;">o ||<style="text-align: center;">+ ||<style="text-align: center;">o || |
| Line 274: | Line 263: |
| '''Custom Graphics''' is a new type of Visual Property and you can use them from the standard VizMap user interface. There are nine Custom Graphics Visual Properties ('''Node Custom Graphics 1 - 9''') and they will be displayed in the standard VizMap Default View Editor or Mapping Editors. | '''Custom Graphics''' is a new type of Visual Property and you can use them from the standard !VizMapper user interface. There are nine Custom Graphics Visual Properties ('''Node Custom Graphics 1 - 9''') and they will be displayed in the standard !VizMapper Default View Editor or Mapping Editors. |
| Line 290: | Line 279: |
| To select an Custom Graphics, just click one of them and press '''Apply'''. To remove a value from mappings/defaults, select '''Empty''' Custom Graphics. | To select a Custom Graphics, just click one of them and press '''Apply'''. To remove a value from mappings/defaults, select the '''Remove Graphics''' option from the Custom Graphics list. |
| Line 299: | Line 288: |
| . When you select '''File-->Quit''', all of Custom Graphics in the Manager will be saved automatically to your Cytoscape setting directory. Usually, it's {{{YOUR_HOME_DIRECTORY/CytoscapeConfiguration/images3}}}. | . When you select '''''File → Quit''''', all of Custom Graphics in the Manager will be saved automatically to your Cytoscape setting directory. Usually, it's {{{YOUR_HOME_DIRECTORY/CytoscapeConfiguration/images3}}}. |
| Line 309: | Line 298: |
|
'''Step 0. Load a sample network.''' From the main menu, select File → Import → Network (Multiple file types), and select {{{sampleData/galFiltered.sif}}}. '''Step 1. Create some node/edge statistics by Network Analyzer.''' Network Analyzer calculates some basic statistics for nodes and edges. From the main menu, select Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysys, and click OK. Once result is displayed, simply close the window. All statistics are stored as a regular table data. '''Step 2. Open the !VizMapper.''' Select the !VizMapper tab in the Control Panel at the left of the screen. You will now see a !VizMapper Main Panel, as shown below. |
'''Step 1. Load a sample network.''' From the main menu, select ''File → Import → Network → File...'', and select {{{sampleData/galFiltered.sif}}}. '''Step 2. Create some node/edge statistics by Network Analyzer.''' Network Analyzer calculates some basic statistics for nodes and edges. From the main menu, select ''Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network'', and click ''OK''. Once the result is displayed, simply close the window. All statistics are stored as a regular table data. '''Step 3. Open the !VizMapper.''' Select the ''!VizMapper'' tab in the Control Panel at the left of the screen. You will now see the !VizMapper main panel, as shown below. |
| Line 317: | Line 306: |
| '''Step 3. Create a new visual style.''' Click the Options {{attachment:VizMapOptionIcon.png}} button, and select ''Create new visual style...'' Then enter a name for your new visual style when prompted. You will see an empty visual style in the !VizMapper Main Panel, as shown below. | '''Step 4. Create a new visual style.''' Click the Options {{attachment:VizMapOptionIcon.png}} button, and select ''Create New Visual Style''. Then enter a name for your new visual style when prompted. You will see an empty visual style in the !VizMapper Main Panel, as shown below. |
| Line 321: | Line 310: |
|
Since no mappings are set up yet, all visual attributes are listed in the Unused Properties category. From this panel, you can create node/edge mappings for all visual properties. '''Step 4. Edit default values.''' Open the Default Appearance Editor by clicking on the Defaults graphics window (shown below) in the !VizMapper Main Panel. |
Since no mappings are set up yet, all visual attributes are listed in the ''Unused Properties'' category. From this panel, you can create node/edge mappings for all visual properties. '''Step 5. Edit default values.''' Open the Default Appearance Editor by clicking on the ''Defaults'' graphics window (shown below) in the ''!VizMapper'' Main Panel. |
| Line 327: | Line 316: |
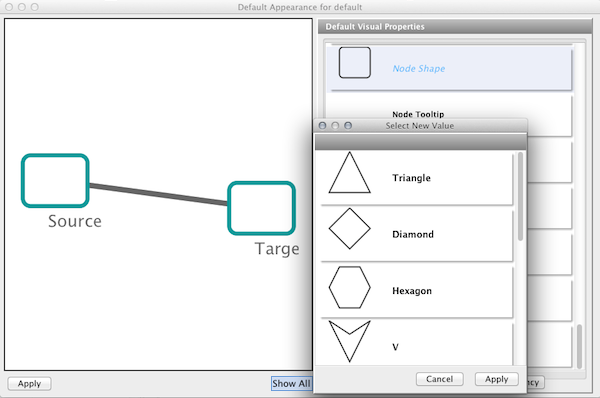
| '''Step 5. Change the default node color and shape.''' To set the default node shape to triangles, click "Node Shape" in the Default Visual Properties list. A list of available node shapes will be shown. Click on the Triangle icon and then click the Apply button. The Default Appearance Editor will be automatically updated. You can edit other default values by clicking on visual attribute names on the list. In the example shown below, the node shape is set to Round Rectangle, while the node color is set to white. | '''Step 6. Change the default node color and shape.''' To set the default node shape to triangles, click '''''Node Shape''''' in the Default Visual Properties list. A list of available node shapes will be shown. Click on the ''Triangle'' icon and then click the ''Apply'' button. The Default Appearance Editor will be automatically updated. You can edit other default values by clicking on visual attribute names on the list. In the example shown below, the node shape is set to ''Round Rectangle'', while the '''''Node Fill Color''''' is set to white. |
| Line 331: | Line 320: |
| '''Step 6. Apply your settings.''' When you finish editing, click the Apply button at the bottom of the editor. Your new Visual Style will be applied to the current network, as shown below. | '''Step 7. Apply your settings.''' When you finish editing, click the ''Apply'' button at the bottom of the editor. Your new Visual Style will be applied to the current network, as shown below. |
| Line 338: | Line 327: |
|
'''Step 1. Choose a visual attribute.''' Double click the '''''Edge Stroke Color (Unselected)''''' entry listed in Unused Properties. It will now appear at the top of the list, under the Edge Visual Mapping category (as shown below). '''Step 2. Choose an edge column.''' Click on the cell to the right of the Edge Color entry and select "interaction" from the dropdown list that appears. '''Step 3. Choose a mapping type.''' Set the Discrete Mapper option as the Mapping Type. All available attribute values for "interaction" will be displayed, as shown below. |
'''Step 1. Choose a visual attribute.''' Double click the '''''Edge Stroke Color (Unselected)''''' entry listed in ''Unused Properties''. It will now appear at the top of the list, under the ''Edge Visual Property'' category (as shown below). '''Step 2. Choose an edge column.''' Click on the cell to the right of the ''Edge Stroke Color'' entry and select "interaction" from the dropdown list that appears. '''Step 3. Choose a mapping type.''' Set the "Discrete Mapping" option as the ''Mapping Type''. All available attribute values for "interaction" will be displayed, as shown below. |
| Line 350: | Line 339: |
| Repeat step 4 for "pp" (protein-protein interactions), but select darker color as its edge color. Then repeat steps 3 through 4 for the Edge Line Type attribute. You can select the correct line style (dashed or solid) from the dropdown list. | Repeat step 4 for "pp" (protein-protein interactions), but select a darker color as edge stroke color. Then repeat steps 3 through 4 for the ''Edge Line Type'' attribute. You can select the correct line style ("Dash" or "Solid") from the list. |
| Line 361: | Line 350: |
|
'''Step 1. Choose a visual attribute.''' Double click the Node Fill Color entry listed in Unused Properties. Node Fill Color will now appear at the top of the list, under the Node Visual Mapping category. '''Step 2. Choose a node table column.''' Click on the cell to the right of the Node Fill Color entry and select "deg" from the dropdown list that appears. '''Step 3. Choose a mapping type.''' Set the Continuous Mapping option as the Mapping Type. This automatically creates a default mapping |
'''Step 1. Choose a visual attribute.''' Double click the ''''Node Fill Color'''' entry listed in ''Unused Properties''. Node Fill Color will now appear at the top of the list, under the ''Node Visual Property'' category. '''Step 2. Choose a node table column.''' Click on the cell to the right of the ''Node Fill Color'' entry and select "Degree" from the dropdown list that appears. '''Step 3. Choose a mapping type.''' Set the "Continuous Mapping" option as the ''Mapping Type''. This automatically creates a default mapping |
| Line 381: | Line 370: |
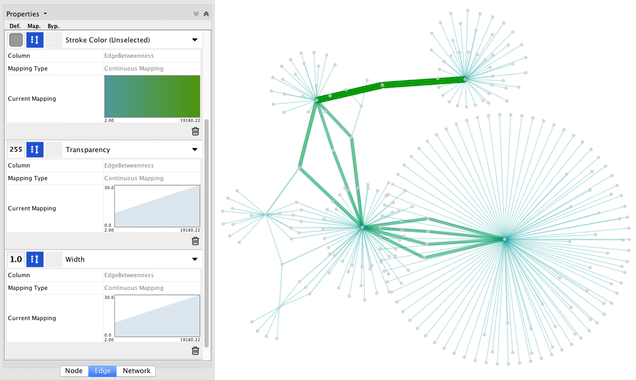
| '''Step 6. Repeat for other Visual Properties.''' You can create some more mappings for other number table data. For example, edge data table column ''ebt'' is a number, so you can use it for continuous mapping. The following is an example visualization by mapping Edge Width to ebt. | '''Step 6. Repeat for other Visual Properties.''' You can create some more mappings for other numeric table data. For example, edge data table column "!EdgeBetweenness" is a number, so you can use it for continuous mapping. The following is an example visualization by mapping ''Edge Width'' to "!EdgeBetweenness". |
| Line 390: | Line 379: |
|
1. Cretate a '''Discrete Node Color Mapping'''. Select ''spl'' (Shortest Path Length generated by Network Analyzer) as controlling attribute. 1. Click '''Node Fill Color''' cell, then right click to show popup menu. Select __Mapping Value Generators → Rainbow__. It generates different colors for different table values as shown below: |
1. Cretate a '''Discrete Node Color Mapping'''. Select "!AverageShortestPathLength" (generated by Network Analyzer) as controlling attribute. 1. Click the '''Node Fill Color''' cell, then right-click it to show the popup menu. Select ''Mapping Value Generators → Rainbow''. It generates different colors for different table values as shown below: |
| Line 393: | Line 382: |
|
1. Cretate a '''Discrete Node Label Font Size Mapping'''. Select ''spl'' as controlling attribute. 1. Click '''Node Label Font Size''' and right click to show popup menu. Select __Mapping Value Generators → Number Series__. Type ''3'' for the first value and click OK. Enter ''3'' for increment. 1. Apply yFiles → Organic layout. The final view is shown below: |
1. Create a '''Discrete Node Label Font Size Mapping'''. Select "!AverageShortestPathLength" as controlling attribute. 1. Click the '''Node Label Font Size''' cell, then right-click it to show the popup menu. Select ''Mapping Value Generators → Number Series''. Type ''3'' for the first value and click OK. Enter ''3'' for increment. 1. Apply ''Layout → yFiles Layouts → Organic''. The final view is shown below: |
| Line 405: | Line 394: |
|
1. Prepare images. These can be any type of bitmap graphics. In this tutorial, we are going to use theCrystal Project's PNG icons. You can download it from [[http://everaldo.com/crystal/crystal_project_256x256.zip|here]]. 1. Start Cytoscape and select __View → Open Custom Graphics Manager__. Cytoscape 3 has some preset images and in this example, we use these presets. You can close the Custom Graphics Manager window for now. |
1. Prepare images. These can be any type of bitmap graphics. In this tutorial, we are going to use the Crystal Project's PNG icons. You can download it from [[http://everaldo.com/crystal/crystal_project_256x256.zip|here]]. 1. Start Cytoscape and select ''View → Open Custom Graphics Manager''. Cytoscape 3 has some preset images and in this example, we use these presets. You can close the Custom Graphics Manager window for now. |
| Line 408: | Line 397: |
|
1. Load a network and run Network Analyzer. This creates several new table columns (statistics for nodes and edges). 1. Click ''VizMapper'' tab in the Control Panel, and select ''Solid'' style. 1. Click default view to open Default Appearance Editor. 1. Click '''Node Custom Graphics 1''' and select any of a custom graphics from the list. Click '''Node Transparency''' and set the value to zero. |
1. Load a network and run the Network Analyzer (''Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network''). This creates several new table columns (statistics for nodes and edges). 1. Click the ''!VizMapper'' tab in the ''Control Panel'', and select the ''Solid'' style. 1. Click the ''Defaults'' section to open the ''Default Appearance Editor''. 1. Click '''Node Custom Graphics 1''' and select any of the custom graphics from the list. Click '''Node Transparency''' and set the value to zero. |
| Line 417: | Line 406: |
| 1. Open Custom Graphics Manager again. Drag and Drop this {{attachment:sampleImage.png}} icon to the image list. It automatically adds it to the manager. | 1. Open the Custom Graphics Manager again. Drag and Drop this {{attachment:sampleImage.png}} icon to the image list. It automatically adds it to the manager. |
| Line 419: | Line 408: |
| 1. Create Continuous Mapping for Node Custom Graphics 2. Select ''nbt'' as controlling column and move the handle to 0.2. Double click the region over 0.2 and set the new icon you have just added in the last step. | 1. Create a ''Continuous Mapping'' for '''Node Custom Graphics 2'''. Select "!BetweennessCentrality" as controlling column and move the handle to ''0.2''. Double click the region over ''0.2'' and set the new icon you have just added in the last step. |
| Line 421: | Line 410: |
| 1. Press Apply and now open the Default Editor again. Click Custom Graphics Position 2 and move the position of the graphics to upper left. | 1. Press ''Apply'' and now open the ''Default Appearance Editor'' again. Click '''Node Custom Graphics Position 2''' and move the position of the graphics to upper left. |
| Line 423: | Line 412: |
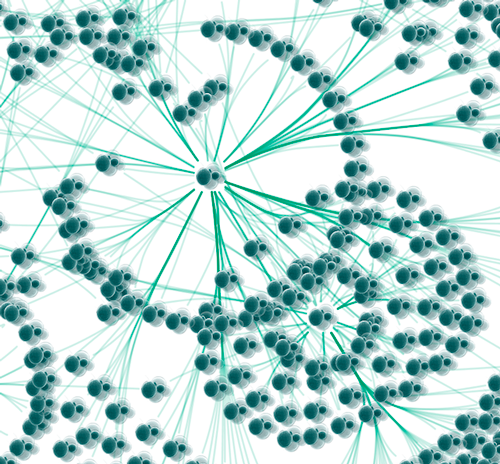
| 1. Press Apply. Now the important nodes in the network (nodes with high [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betweenness_centrality|betweenness centrality]]) is annotated with the icon. | 1. Press ''Apply''. Now the important nodes in the network (nodes with high [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betweenness_centrality|betweenness centrality]]) is annotated with the icon. |
| Line 433: | Line 422: |
|
* '''''Generate Discrete Values''''' - Functions in this menu category are value generators for discrete mappings. Users can set values for discrete mappings automatically by these functions. * '''Rainbow 1''' and '''Rainbow 2''' - These functions try to assign as diverse a set colors as possible for each data value. |
* '''''Mapping Value Generators''''' - Functions in this menu category are value generators for discrete mappings. Users can set values for discrete mappings automatically by these functions. * '''Rainbow''' and '''Rainbow OSC''' - These functions try to assign as diverse a set of colors as possible for each data value. |
| Line 437: | Line 426: |
|
* '''Randomize''' - Randomize colors and numbers. If you use this function for numerical values (node size, opacity, etc.) you need to specify a range. For example, if you want to set values from 1 to 100, you need to type ''1-100'' in the dialog. * '''Series''' - Set a series of numbers to the specified mapping. |
* '''Random Numbers''' and '''Random Colors''' - Randomize numbers and colors. If you use this function for numerical values (node size, opacity, etc.) you need to specify a range. For example, if you want to set values from 1 to 100, you need to type ''1-100'' in the dialog. * '''Number Series''' - Set a series of numbers to the specified mapping. |
| Line 441: | Line 431: |
| * '''Fit node size to label''' - This function is only for node width and height. When the node size is ''unlocked'' AND ''Node Width/Height'' discrete mappings are available, you can fit the size of each node to its label automatically by selecting this function. See the example below: | * '''Fit label width''' - This function is only for node width and height. When the node size is ''unlocked'' AND ''Node Width/Height'' discrete mappings are available, you can fit the size of each node to its label automatically by selecting this function. See the example below: |
| Line 443: | Line 433: |
|
* '''''Modify Discrete Values''''' - Currently, this is only for colors. You can change overall brightness for discrete color mappings. |
|
| Line 471: | Line 459: |
| 1. '''Handle Value Box''' - This box displays current value for selected slider handle. Also you can directly type value in this box to move the slider to an exact location. | 1. '''Handle Value Box''' - This box displays the current value for the selected slider handle. Also you can directly type the value in this box to move the slider to an exact location. |
| Line 474: | Line 462: |
| 1. '''Delete Handle Button''' - Delete selected handle from the slider widget. | 1. '''Delete Handle Button''' - Delete the selected handle from the slider widget. |
| Line 481: | Line 469: |
| ||1 Slider (No Graient) ||2 Sliders || | ||1 handle (no gradient) ||2 handles || |
| Line 498: | Line 486: |
| All Cytoscape Visual Style settings are initially loaded from a a default file called {{{vizmap.props}}} that cannot be altered by users. When users make changes to the visual properties, a {{{vizmap.props}}} file is saved in the session file. This means that if you save your session, you will not lose your visual properties. No other {{{vizmap.props}}} files are saved during normal operation. | All Cytoscape Visual Style settings are initially loaded from a default file that cannot be altered by users. When users make changes to the visual properties, a {{{session_vizmap.xml}}} file is saved in the session file. This means that if you save your session, you will not lose your visual properties. No other vizmap files are saved during normal operation. |
| Line 501: | Line 489: |
| Visual styles are automatically saved with the session they were created in. Before Cytoscape exits, you will be prompted to make sure you save the session before quitting. It is also possible to save your visual styles in a file separate from the session file. To do this, navigate to the File → Export → Vizmap Property File menu option and save the properties as a file. This feature can be used to share visual styles with other users. | Visual styles are automatically saved with the session they were created in. Before Cytoscape exits, you will be prompted to make sure you save the session before quitting. It is also possible to save your visual styles in a file separate from the session file. To do this, navigate to the ''File → Export → Vizmap...'' menu option and save the properties as an XML file. This feature can be used to share visual styles with other users. |
| Line 504: | Line 492: |
|
To import existing visual styles, navigate to the File → Import → Vizmap Property File menu option and select a {{{vizmap.props}}} file. Imported properties will supplement existing properties or override existing properties if the properties have the same name. You can also specify a visual properties file using the -V command line option ({{{cytoscape.sh -V myVizmap.props}}}). Visual properties loaded from the command line will override any default properties. === Default Visual Styles === It is possible to change the default visual properties for all sessions of Cytoscape. To do this, navigate to the Edit → Preferences → Properties... menu option, check the "Make Current Visual Styles Default" box in the Default Visual Styles section, and click the OK button. This will save the current visual styles as a {{{vizmap.props}}} file to your {{{CytoscapeConfiguration}}} directory (found in your home directory). These visual styles will then be loaded each time Cytoscape is started. |
To import existing visual styles, navigate to the ''File → Import → Vizmap File...'' menu option and select a {{{vizmap.props}}} (Cytoscape 2 format) or {{{vizmap.xml}}} (Cytoscape 3 format) file. Imported properties will supplement existing properties or override existing properties if the properties have the same name. You can also specify a visual properties file using the -V command line option ({{{cytoscape.sh -V myVizmap.props}}}). Visual properties loaded from the command line will override any default properties. |
| Line 510: | Line 495: |
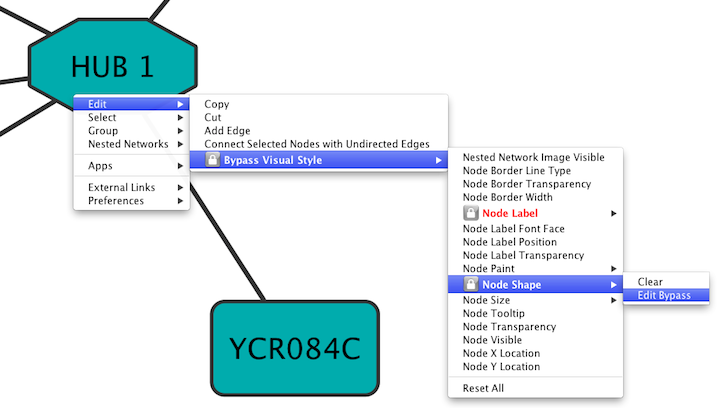
| Cytoscape has a feature that allows users to override visualizations created by the !VizMapper for individual nodes and edges. This feature is available by right-clicking on a node or edge and then clicking on the '''Bypass Visual Style''' menu. | Cytoscape has a feature that allows users to override visualizations created by the !VizMapper for individual nodes and edges. This feature is available by right-clicking on a node or edge and then clicking on ''Edit → Bypass Visual Style''. |
| Line 514: | Line 499: |
| Each visual property of the node or edge is displayed. When a property is overridden, a lock icon {{attachment:LockIcon.png}} appears next to the property and '''Clear'''/ '''Edit Bypass''' menu options appear. By clicking this Clear option, the bypass will be removed and the attribute will be displayed as defined by the !VizMapper. At the bottom of the menu a '''Reset All''' option appears. When clicked, this will remove all bypasses for the specified node or edge. In the example above, you can see the selected node size, color, and shape have been overridden. This is apparent in the appearance of the node itself and by the check marks in the popup menu. | Each visual property of the node or edge is displayed. When a property is overridden, a lock icon {{attachment:LockIcon.png}} appears next to the property and ''Clear'' / ''Edit Bypass'' menu options appear. By clicking the ''Clear'' option, the bypass will be removed and the attribute will be displayed as defined by the !VizMapper. At the bottom of the menu a ''Reset All'' option appears. When clicked, this will remove all bypasses for the specified node or edge. In the example above, you can see the selected node size, color, and shape have been overridden. This is apparent in the appearance of the node itself and by the check marks in the popup menu. |
| Line 518: | Line 503: |
|
Bypass is accomplished using special attributes with names like {{{node.fillColor}}} and {{{node.shape}}}. These are normal Cytoscape attributes and can be seen and edited in the Data Panel. The value of the attribute is a string representation of a property. For example, color is represented by 3 integers representing the RGB (red, green, blue) value of the color. Different types of properties have different string representations. When in doubt, just use the right click menu to create valid attribute values. Because bypass values are specified using normal attributes, these attributes will persist between sessions only as long as you save your session. If you don't save your session, you will lose whatever bypass values you set. |
The bypass values will persist between sessions only as long as you save your session. If you don't save your session, you will lose whatever bypass values you set. == Visual Property Dependencies == In some cases, you want to use the same value for multiple Visual Properties. For example, if you want to use the same value for ''Node Width'' and ''Node Height'', you have to use the '''''Visual Property Dependency''''' feature in !VizMapper. Currently, Cytoscape supports the following Visual Property Dependencies: * '''Edge color to arrows''' - Assign same color for edge and arrows. * '''Fit Custom Graphics to node''' - Adjust the size of Custom Graphics based on ''Node Size''. * '''Lock node width and height''' - Assign the same value to node width and height. ==== Example: Unlocked ==== {{attachment:Unlocked.png}} ==== Example: Locked ==== {{attachment:Locked.png}} |
What is a Visual Style?
One of Cytoscape's strengths in network visualization is the ability to allow users to encode any table data (name, type, degree, weight, expression data, etc.) as a Visual Property (such as color, size of node, transparency, or font type). A set of these encoded or mapped table data sets is called a Visual Style and can be created or edited using the Cytoscape VizMapper. With the VizMapper, the visual appearance of your network is easily customized. For example, you can:
- Specify a default color and shape for all nodes.
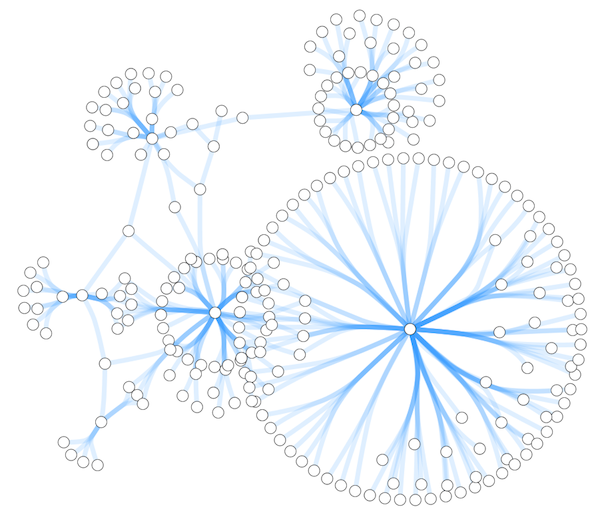
- Set node sizes based on the degree of connectivity of the nodes. You can visually see the hub of a network...
- ...or, set the font size of the node labels instead.
- Visualize gene expression data along a color gradient.
- Encode specific physical entities as different node shapes.
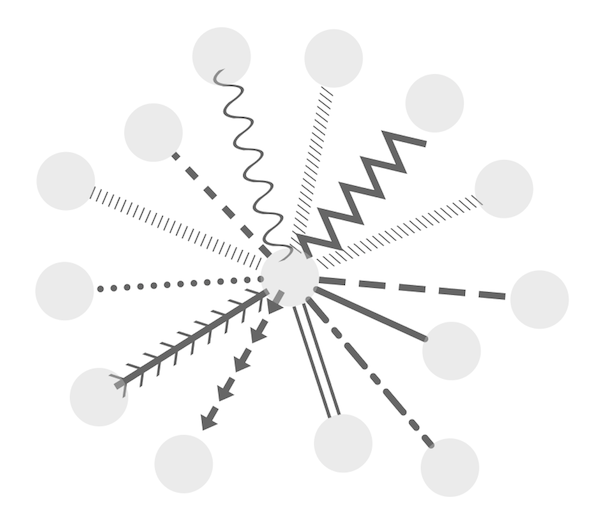
- Use specific line types to indicate different types of interactions.
- Control edge transparency (opacity) using edge weights.
- Control multiple edge visual properties using edge score.
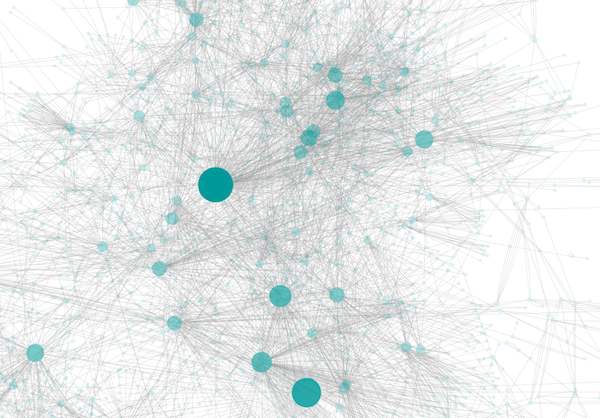
- Browse extremely-dense networks by controlling the opacity of nodes.
- Show highly-connected region by edge bundling and opacity.
- Add photo/image/graphics on top of nodes.
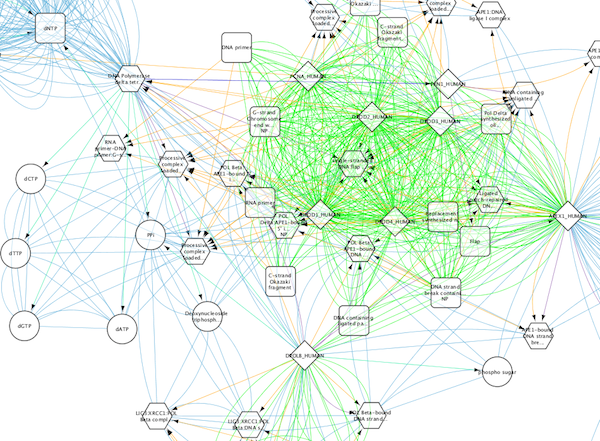
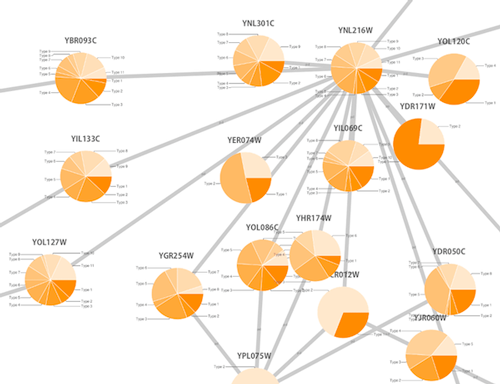
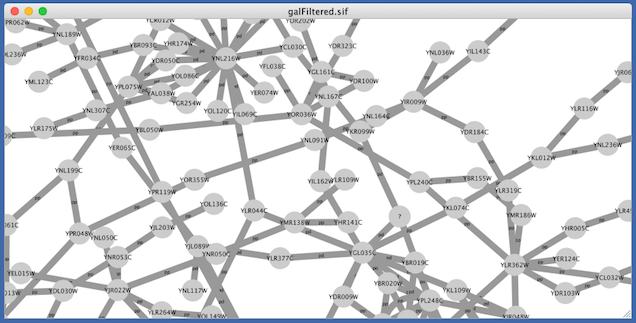
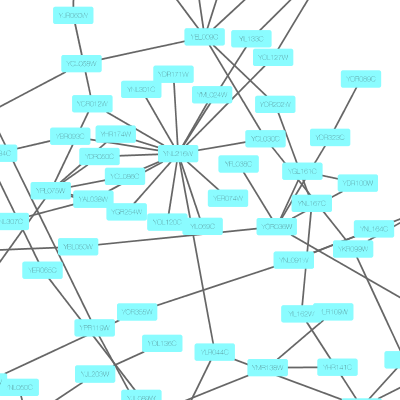
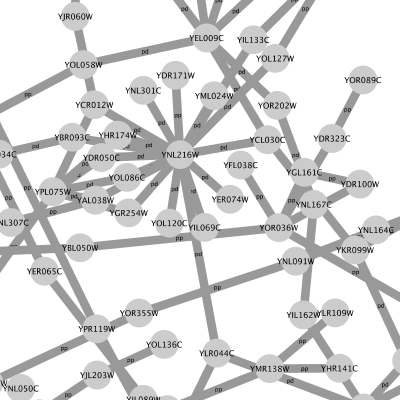
Cytoscape 3 has several sample Visual Styles. You can try those to examine how Visual Styles change the appearence of a network. The following is a list of network views based upon sample styles applied to the galFiltered.sif network :
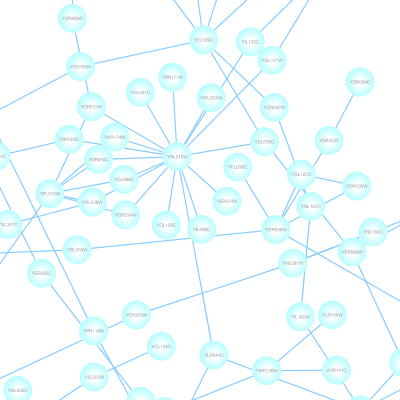
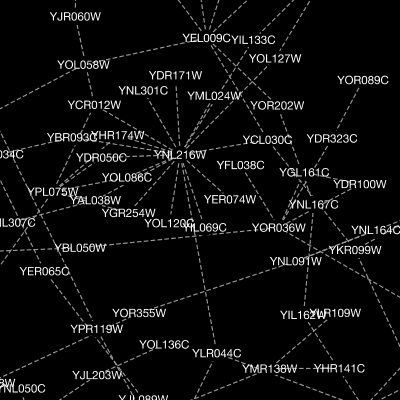
VizMapper is located in a tab on the Control Panel at the left-hand side of the screen.
Introduction to the VizMapper User Interface
There are two main control panels in the VizMapper:
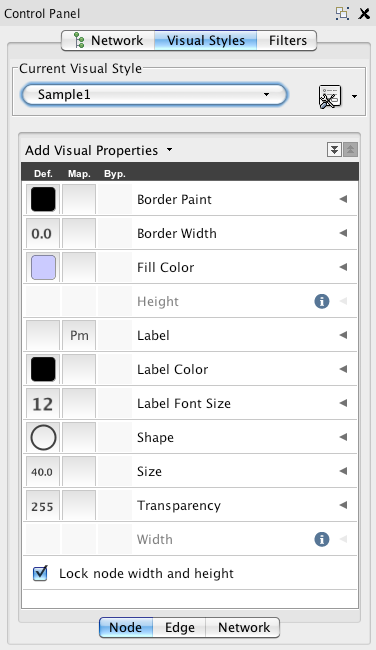
- Main Panel
This panel allows you to create/delete/view/switch between different visual styles using the Current Visual Style options. The panel displays the mapping details for a given visual style and is used to edit these details as well.
Introduction to Visual Styles
The Cytoscape distribution includes several predefined visual styles to get you started. To examine these styles, try out the following example:
Step 1. Load some sample data
Load a sample session file: From the main menu, select File → Open, and select the file sampleData/galFiltered.cys.
The session file includes a network, some annotations, and sample visual styles. By default, the Sample for galFiltered style is selected. Gene expression values for each node are colored along a color gradient between red and green (where red represents a low expression ratio and green represents a high expression ratio, using thresholds set for the gal4RGexp experiment bundled with Cytoscape in the sampleData/galExpData.csv file). Also, node size is mapped to the degree of the node (number of edges connected to the node) and you can see the hubs of the network as larger nodes. See the sample screenshot below:

Step 2. Switch between different Visual Styles
You can change visual styles by making a selection from the Current Visual Style dropdown list (found at the top of the VizMapper Main Panel).
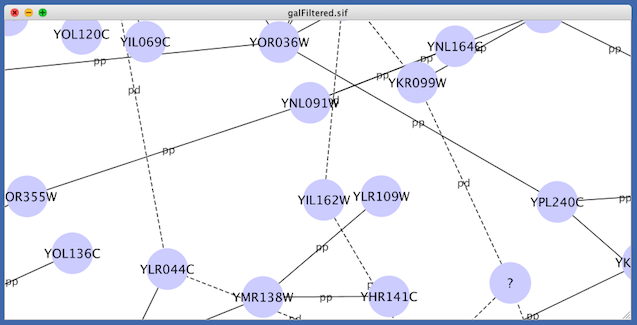
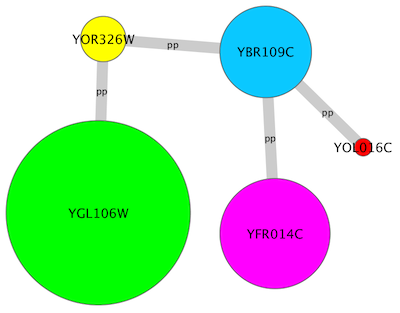
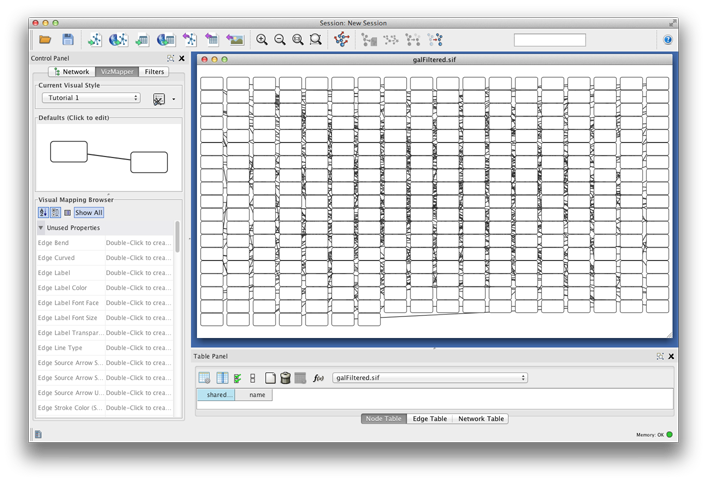
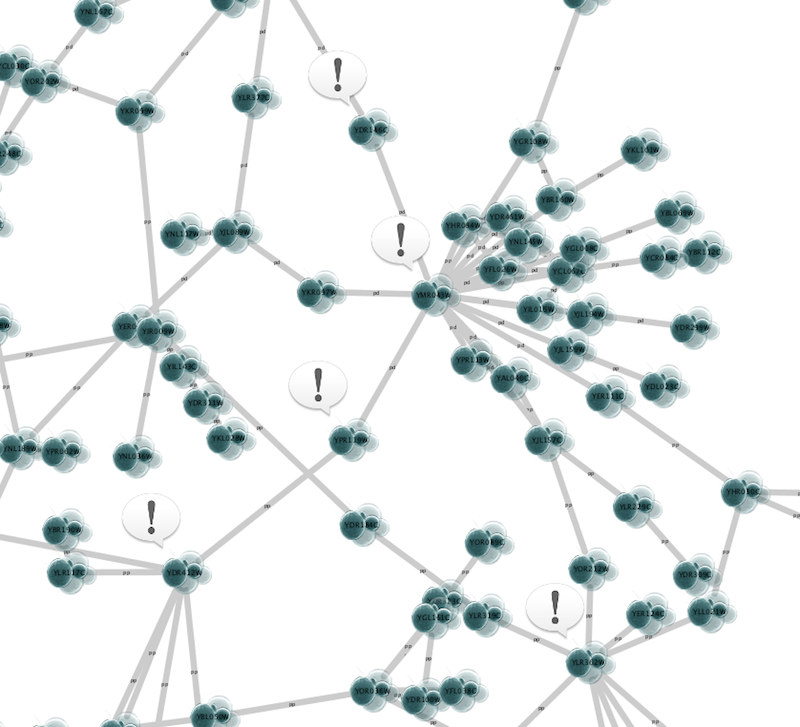
For example, if you select Sample1, a new visual style will be applied to your network, and you will see a white background and round blue nodes. If you zoom in closer, you can see that protein-DNA interactions (specified with the label "pd") are drawn with dashed edges, whereas protein-protein interactions (specified with the label "pp") are drawn with solid edges (see sample screenshot below).
Finally, if you select Solid, you can see the graphics below:
This Visual Style does not have mappings except node/edge labels, but you can modify the network graphics by editing the Default Value for any visual property.
Additional sample styles are available in the sampleStyles.xml file in the sampleData directory. You can import the sample file from File → Import → Vizmap File...
Visual Attributes, Graph Attributes and Visual Mappers
The Cytoscape VizMapper uses three core concepts:
A visual attribute is any visual setting that can be applied to your network. For example, you can change all nodes from circles to squares by changing the node shape visual attribute.
A network attribute is any data attribute associated with a node or an edge. For example, each edge in a network may be associated with a label, such as “pd” (protein-DNA interactions), or “pp” (protein-protein interactions).
A visual mapper maps network attributes to visual attributes. For example, a visual mapper can map all protein-DNA interactions to the color blue, and all protein-protein interactions to the color red.
Cytoscape allows a wide variety of visual attributes to be controlled. These are summarized in the tables below.
Visual Attributes Associated with Nodes |
Description |
Node Shape |
The shape of the node. |
Node Fill Color |
The color of the node. |
Node Selection |
The color of the node when selected. |
Node Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the node. Zero means totally transparent, and 255 is most opaque. |
Node Border Paint |
The color of the border of the node. |
Node Border Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the border of the node. Allows for transparency. |
Node Border Line Type |
The type of line used for the border of the node. |
Node Border Width |
The width of the node border. |
Node Label Font Face |
The font used for the node label. |
Node Label Font Size |
The size of the font used for the node label. |
Node Label |
The text used for the node label. |
Node Label Color |
The color of the node label. |
Node Label Transparency |
The transparency of the color of the node label. Allows for transparency. |
Node Label Position |
The position of the node label relative to the node. |
Node Label Width |
The maximum width of the node label. If the node label is wider than the specified width, Cytoscape will automatically wrap the label on space characters. Cytoscape will not hyphenate words, meaning that if a single word (i.e. no spaces) is longer than maximum width, the word will be displayed beyond the maximum width. |
Node Tooltip |
The text of the tooltip that appears when a mouse hovers over the node. |
Node Size |
The size of the node. Width and height will be equal. This visual property is mutually exclusive of Node Height and Node Width. |
Node Height |
The height of the node. Height will be independent of width. This visual property is mutually exclusive of Node Size. |
Node Width |
The width of the node. Width will be independent of height. This visual property is mutually exclusive of Node Size. |
Node X Location |
X location of the node. Default value of this will be ignored. The value will be used only when mapping function is defined. |
Node Y Location |
Y location of the node. Default value of this will be ignored. The value will be used only when mapping function is defined. |
Node Visible |
Node is visible or not. By default, this value is set to true. |
Nested Network Image Visible |
A boolean value that indicates whether a nested network should be visualized (assuming a nested network is present for the specified node). |
Visual Attributes Associated with Edges |
Description |
Edge Stroke Color (Unselected) |
The color of the edge. |
Edge Stroke Color (Selected) |
The color of the edge when selected. |
Edge Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the edge. Allows for transparency. |
Edge Line Type |
The type of stoke used to render the line (solid, dashed, etc.) |
Edge Width |
The width of the line. |
Edge Label |
The text used for the edge label. |
Edge Label Color |
The color of the edge label. |
Edge Label Transparency |
The opacity of the color of the edge label. Allows for transparency. |
Edge Label Font Face |
The font used for the edge label. |
Edge Label Font Size |
The size of the font used for the edge label. |
Edge Tooltip |
The text of the tooltip that appears when a mouse hovers over the edge. |
Edge Source Arrow Unselected Paint |
The color of the arrow on the source node end of the edge. |
Edge Source Arrow Selected Paint |
The selected color of the arrow on the source node end of the edge. |
Edge Source Arrow Shape |
The shape of the arrow on the source node end of the edge. |
Edge Target Arrow Unselected Paint |
The color of the arrow on the target node end of the edge. |
Edge Target Arrow Selected Paint |
The selected color of the arrow on the target node end of the edge. |
Edge Target Arrow Shape |
The shape of the arrow on the target node end of the edge. |
Edge Bend |
The edge bend. Defines how the edge is rendered. Users can add multiple handles to define how to bend the edge line. |
Edge Curved |
If Egde Bend is defined, edges will be rendered as straight or curved lines. If this value is set to true, edges will be drawn as curved lines. |
Edge Visible |
Edge is visible or not. By default, this value is set to true. |
Network Visual Properties |
Description |
Network Background Paint |
The background color of the network view. |
Network Title |
The title of the network view. |
Network Height |
The height of the network view. |
Network Width |
The width of the network view. |
Network Scale Factor |
The zoom level of the network view. |
Network Center X Location |
The X location of network view center. |
Network Center Y Location |
The Y location of network view center. |
Network Edge Selection |
Edges are selectable or not. If this is false, users cannot select edges. |
Network Node Selection |
Nodes are selectable or not. If this is false, users cannot select nodes. |
Available Shapes and Line Styles |
Sample |
Node Shapes |
|
Edge Line Types |
|
Arrow Shapes |
|
For each visual attribute, you can specify a default value or define a dynamic visual mapping. Cytoscape currently supports three different types of visual mappers:
Passthrough Mapper
- The values of network attributes are passed directly through to visual attributes. A passthrough mapper is typically used to specify node/edge labels. For example, a passthrough mapper can label all nodes with their common gene names.
Discrete Mapper
- Discrete data attributes are mapped to discrete visual attributes. For example, a discrete mapper can map different types of molecules to different node shapes, such as rectangles for gene products and ellipses for metabolites
Continuous Mapper
- Continuous data are mapped to visual attributes. Depending on the visual attribute, there are three kinds of continuous mappers:
Continuous-to-Continuous Mapper: for example, you can map a continuous numerical value to a node size.
Color Gradient Mapper: This is a special case of continuous-to-continuous mapping. Continuous numerical values are mapped to a color gradient.
Continuous-to-Discrete Mapper: for example, all values below 0 are mapped to square nodes, and all values above 0 are mapped to circular nodes.
- However, note that there is no way to smoothly morph between circular nodes and square nodes.
- Continuous data are mapped to visual attributes. Depending on the visual attribute, there are three kinds of continuous mappers:
The table below shows visual mapper support for each visual property.
Legend
Symbol |
Description |
- |
Mapping is not supported for the specified visual property. |
+ |
Mapping is fully supported for the specified visual property. |
o |
Mapping is partially supported for the specified visual property. Support for “continuous to continuous” mapping is not supported. |
Node Visual Mappings
Node Visual Properties |
Passthrough Mapper |
Discrete Mapper |
Continuous Mapper |
|
Color |
Node Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
Node Transparency |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Node Border Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Node Border Transparency |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Node Label Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Node Label Transparency |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Numeric |
Node Size/Width/Height |
o |
+ |
+ |
Node Font Size |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Node Line Width |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Node Label Width |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Other |
Node Border Line Type |
o |
+ |
o |
Node Shape |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Node Label |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Node Tooltip |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Node Font Family |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Node Label Position |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Node Show Nested Network |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Edge Visual Mappings
Edge Properties |
Passthrough Mapper |
Discrete Mapper |
Continuous Mapper |
|
Color |
Edge Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
Edge Transparency |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Edge Target Arrow Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Edge Source Arrow Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Edge Label Color |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
Edge Label Transparency |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
Numeric |
Edge Line Width |
- |
+ |
+ |
Edge Font Size |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
Edge Label Width |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
Other |
Edge Line Type |
o |
+ |
o |
Edge Source Arrow Shape |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Edge Target Arrow Shape |
o |
+ |
o |
|
Edge Label |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Edge Tooltip |
+ |
+ |
o |
|
Edge Font Family |
- |
+ |
o |
|
Text Passthrough Mapper (New feature for version 2.8)
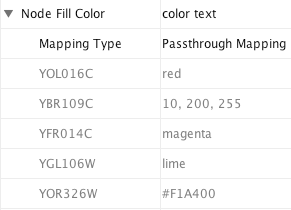
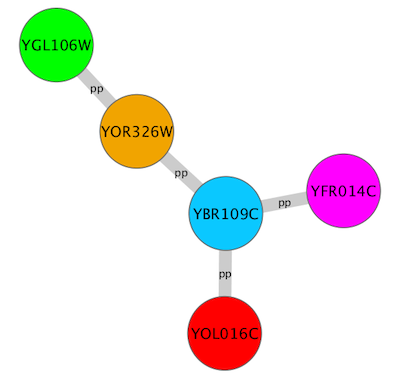
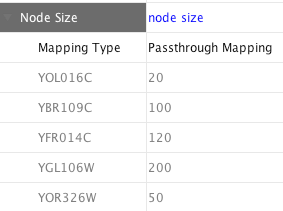
In Cytoscape 2.8.0 and later versions, the Passthrough Mapper can recognize some text representations of values. This means, if you have an integer attribute named Node Size Values, you can directly map those values as the Node Size by setting Node Size Values as controlling attribute name for Node Size Passthrough mapping. The following value types are supported:
Color: Standard color names supported by all browsers or RGB representation in hex
- Numerical Values: Automatically mapped to the specified Visual Property.
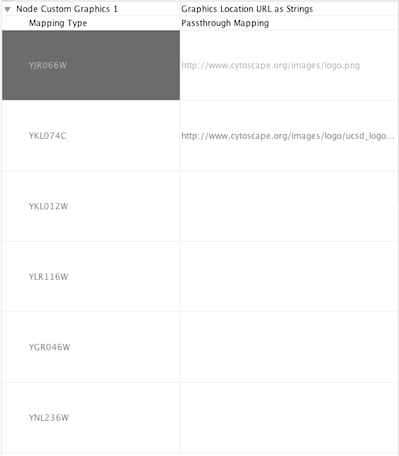
- Custom Graphics: URL String. If the URL is valid and an actual image data exists there, Cytoscape automatically downloads the image and maps it to the node.
Examples
- Color Passthrough Mapping
- Node Size Passthrough Mapping
- Custom Graphics Passthrough Mapping
Custom Graphics Manager
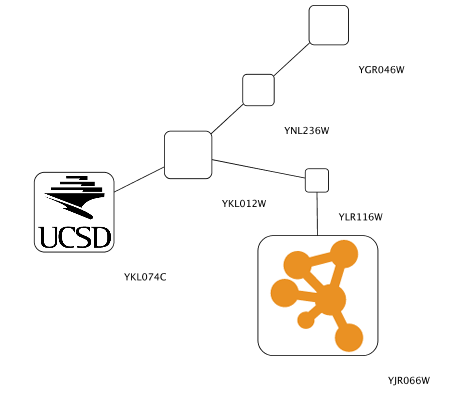
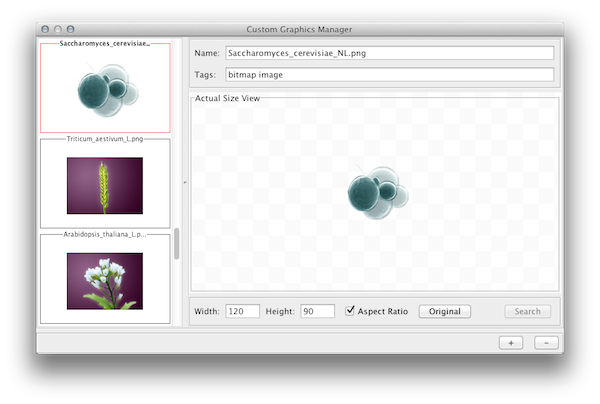
For Cytoscape 2.8.0 and later versions, Cytoscape supports Custom Graphics for nodes. You can add all kinds of bitmap images, such as jpg, png, or gif, on the top of network nodes. From the user's point of view, this is simply an addition to the Visual Properties, and you can use same VizMap user interface to map Custom Graphics to nodes. However, before mapping images, you need to prepare Custom Graphics in the Custom Graphics Manager. It is a simple GUI component to add/remove images to or from a Cytoscape session.
Taxonomy Icon set used in this section is created by Database Center for Life Science (DBCLS) and is distributed under Creative Commons License (CC BY 2.1.)
Adding New Images to Cytoscape
The Custom Graphics Manager supports drag and drop for image files and URLs. If you want to add images from a web browser or local file system, you can drag images from them and drop those images onto the list of images on the left.
If you want to add all images in a folder, press the + button on the bottom of the Custom Graphics Manager window.
Note: When you drag and drop images from web browser, make sure that you are actually dragging the URL for the image. In some cases, images are linked to an HTML page or scripts, and in such cases, this drag and drop feature may not work.
Removing Images
To remove images from the current session's Custom Graphics library, simply select graphics from the list and press the - button.
Resizing Images
You can resize images by typing width/height in the text box. If Keep Aspect Ratio box is checked, the width-height ratio is always synchronized. Any time, you can resize the image to the original size by pressing Original button.
Using Custom Graphics in the VizMapper
Custom Graphics is a new type of Visual Property and you can use them from the standard VizMapper user interface. There are nine Custom Graphics Visual Properties (Node Custom Graphics 1 - 9) and they will be displayed in the standard VizMapper Default View Editor or Mapping Editors.
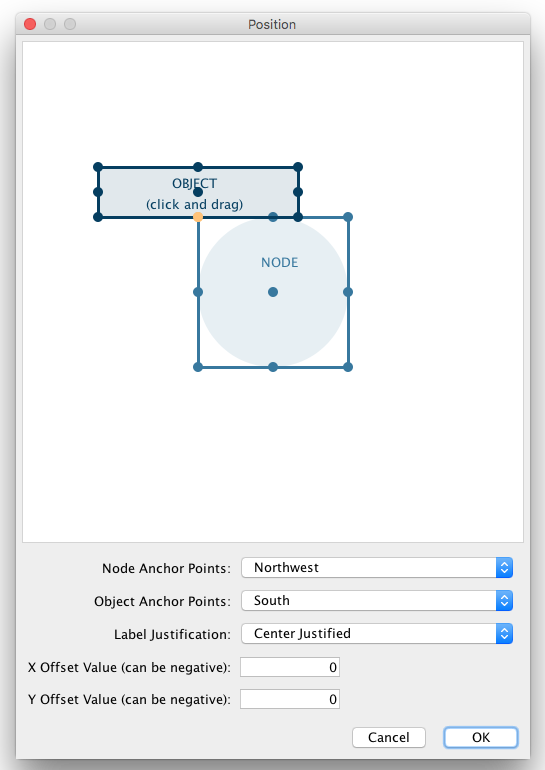
Custom Graphics Positions
Each Custom Graphics Visual Property is associated with a position. You can edit their positions by using same UI as Label Position.
Z-Ordering
This number that appears with the Custom Graphics Visual Property represents an ordering of layers. Basic node color and shape are always rendered first, then Node Custom Graphics 1, 2, ..., through 9.
Synchronize Custom Graphics to Node Size
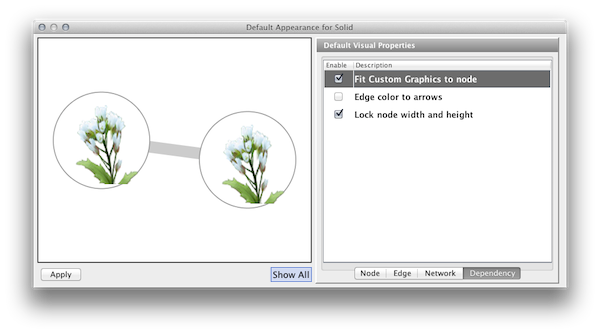
By default, Custom Graphics objects are automatically resized to be consistent with the Node Size Visual Property. To control Custom Graphics size separately, uncheck the Fit Custom Graphics to node dependency. You can find this check box in the Default Editor's Dependencies panel.
Custom Graphics Selector
To select a Custom Graphics, just click one of them and press Apply. To remove a value from mappings/defaults, select the Remove Graphics option from the Custom Graphics list.
Saving and Loading Custom Graphics
In general, saving and loading Custom Graphics is automatic. When you quit Cytoscape, all of the Custom Graphics in the manager will be saved automatically. There are two types of saving:
- To session file
When you save the current session to a file, the Custom Graphics used in Visual Styles will be saved to that file. For example, if you have a Visual Style with a discrete mapping for Custom Graphics, all Custom Graphics used in the style will be saved to the session file. Other graphics will not be saved in your session file. This is because your image library can be huge when you add thousands of images to the Custom Graphics Manager and it takes very long time to save and load the session file.
Automatic saving to CytoscapeConfiguration/images3 directory
When you select File → Quit, all of Custom Graphics in the Manager will be saved automatically to your Cytoscape setting directory. Usually, it's YOUR_HOME_DIRECTORY/CytoscapeConfiguration/images3.
In any case, Custom Graphics will be saved automatically to your system or session and will be restored when you restart Cytoscape or load a session.
Visual Styles Tutorials
The following tutorials demonstrate some of the basic VizMapper features. Each tutorial is independent of the others.
Tutorial 1: Create a Basic Visual Style and Set Default Values
The goal of this tutorial is to learn how to create a new Visual Style and set some default values.
Step 1. Load a sample network. From the main menu, select File → Import → Network → File..., and select sampleData/galFiltered.sif.
Step 2. Create some node/edge statistics by Network Analyzer. Network Analyzer calculates some basic statistics for nodes and edges. From the main menu, select Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network, and click OK. Once the result is displayed, simply close the window. All statistics are stored as a regular table data.
Step 3. Open the VizMapper. Select the VizMapper tab in the Control Panel at the left of the screen. You will now see the VizMapper main panel, as shown below.
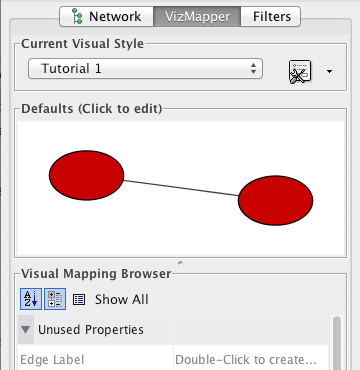
Step 4. Create a new visual style. Click the Options ![]() button, and select Create New Visual Style. Then enter a name for your new visual style when prompted. You will see an empty visual style in the VizMapper Main Panel, as shown below.
button, and select Create New Visual Style. Then enter a name for your new visual style when prompted. You will see an empty visual style in the VizMapper Main Panel, as shown below.
Since no mappings are set up yet, all visual attributes are listed in the Unused Properties category. From this panel, you can create node/edge mappings for all visual properties.
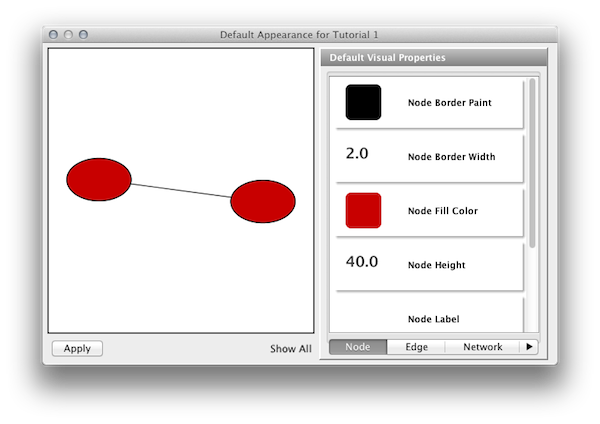
Step 5. Edit default values. Open the Default Appearance Editor by clicking on the Defaults graphics window (shown below) in the VizMapper Main Panel.
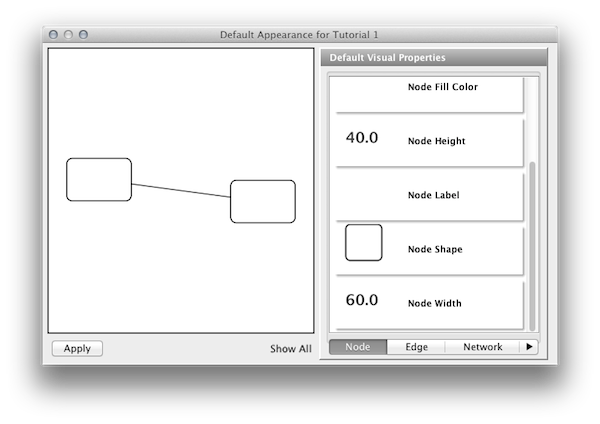
Step 6. Change the default node color and shape. To set the default node shape to triangles, click Node Shape in the Default Visual Properties list. A list of available node shapes will be shown. Click on the Triangle icon and then click the Apply button. The Default Appearance Editor will be automatically updated. You can edit other default values by clicking on visual attribute names on the list. In the example shown below, the node shape is set to Round Rectangle, while the Node Fill Color is set to white.
Step 7. Apply your settings. When you finish editing, click the Apply button at the bottom of the editor. Your new Visual Style will be applied to the current network, as shown below.
Tutorial 2: Creating a New Visual Style with a Discrete Mapper
Now you have a network with new Visual Style. The following section demonstrates how to create a new visual style using a discrete mapper. The goal is to draw protein-DNA interactions as dashed lines, and protein-protein interactions as solid lines.
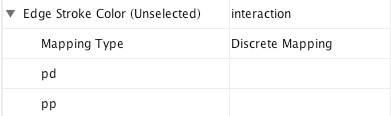
Step 1. Choose a visual attribute. Double click the Edge Stroke Color (Unselected) entry listed in Unused Properties. It will now appear at the top of the list, under the Edge Visual Property category (as shown below).
Step 2. Choose an edge column. Click on the cell to the right of the Edge Stroke Color entry and select "interaction" from the dropdown list that appears.
Step 3. Choose a mapping type. Set the "Discrete Mapping" option as the Mapping Type. All available attribute values for "interaction" will be displayed, as shown below.
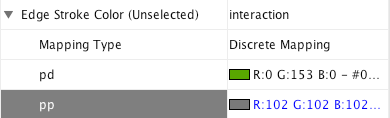
Step 4. Set the mapping relationship. Click the empty cell next to "pd" (protein-DNA interactions). On the right side of the cell, ... and X buttons will appear. Click on the ... button. A popup window will appear; select green or similar, and the change will immediately appear on the network window.
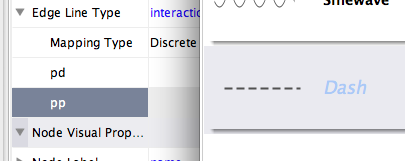
Repeat step 4 for "pp" (protein-protein interactions), but select a darker color as edge stroke color. Then repeat steps 3 through 4 for the Edge Line Type attribute. You can select the correct line style ("Dash" or "Solid") from the list.
Now your network should show "pd" interactions as dashed green lines and "pp" interactions as solid lines. A sample screenshot is provided below.
Tutorial 3: Creating a New Visual Style with a Continuous Mapper
At this point, you have a network with some edge visual mappings. Next, let's create mappings for nodes. The following section demonstrates how to create a new visual style using a continuous mapper. The goal is to superimpose node statistics (in this example, node degree) onto a network and display it along a color gradient.
Step 1. Choose a visual attribute. Double click the 'Node Fill Color' entry listed in Unused Properties. Node Fill Color will now appear at the top of the list, under the Node Visual Property category.
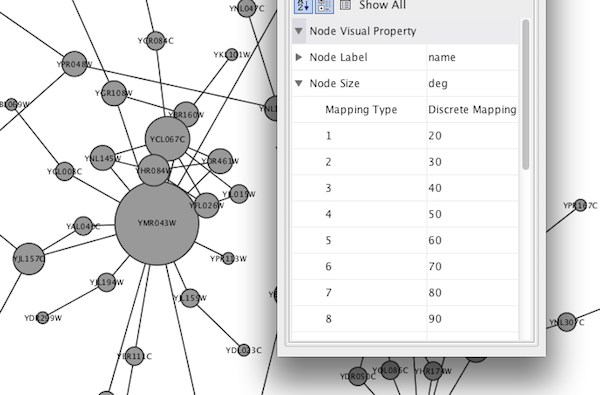
Step 2. Choose a node table column. Click on the cell to the right of the Node Fill Color entry and select "Degree" from the dropdown list that appears.
Step 3. Choose a mapping type. Set the "Continuous Mapping" option as the Mapping Type. This automatically creates a default mapping
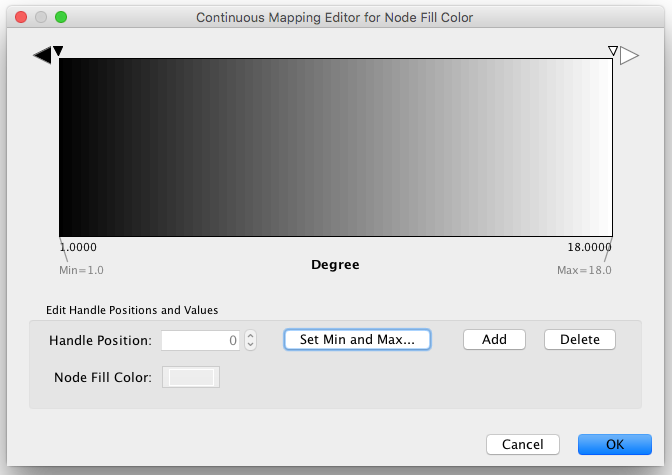
Step 4. Define the points where colors will change. Double-click on the black-and-white gradient rectangle next to Graphical View to open the Color Gradient Mapper. Click and drag one to left, and move the second point to right.
Step 5. Define the colors between points. Double-click on the leftmost triangle (facing left) and a color palette will appear. Choose a shade of yellow and click OK. Double-click on the triangle at left and set the color white. For the triangle at the right, set its color to green.
The color gradients will immediately appear in the network window. All nodes with degree 1 will be set to white, and all values between 1 and 18 will be painted with a white/green color gradient. A sample screenshot is below.
Step 6. Repeat for other Visual Properties. You can create some more mappings for other numeric table data. For example, edge data table column "EdgeBetweenness" is a number, so you can use it for continuous mapping. The following is an example visualization by mapping Edge Width to "EdgeBetweenness".
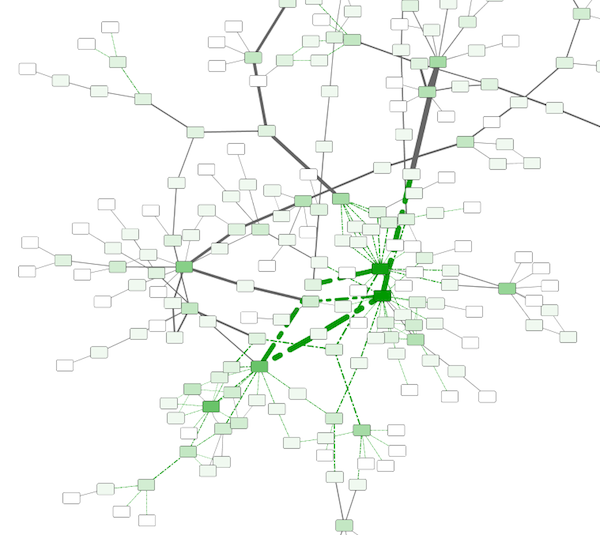
Tutorial 4: How to Use Utilities for Discrete Mappers
The following tutorial demonstrates utilities for editing discrete mappings. The goal of this section is learning how to set and adjust values for discrete mappings automatically.
Switch the Visual Style to Minimal. Now your network looks like the following:
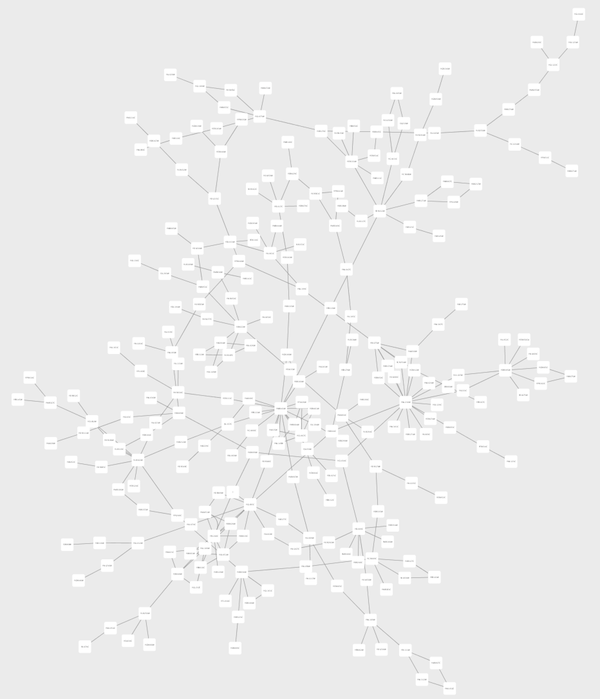
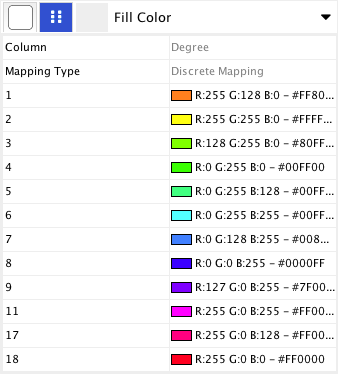
Cretate a Discrete Node Color Mapping. Select "AverageShortestPathLength" (generated by Network Analyzer) as controlling attribute.
Click the Node Fill Color cell, then right-click it to show the popup menu. Select Mapping Value Generators → Rainbow. It generates different colors for different table values as shown below:
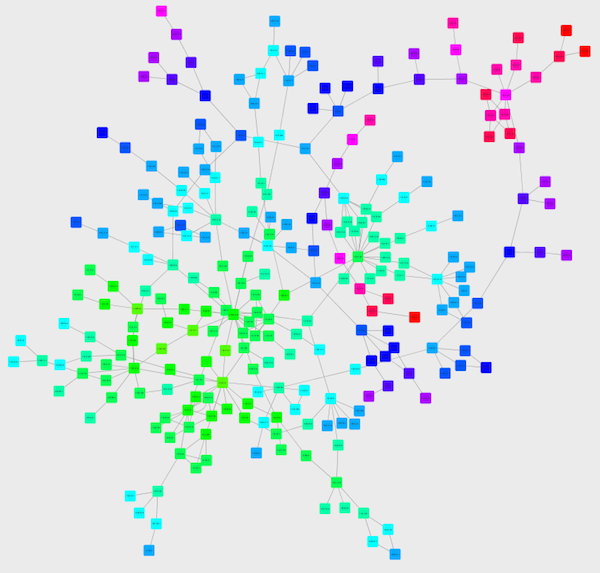
Create a Discrete Node Label Font Size Mapping. Select "AverageShortestPathLength" as controlling attribute.
Click the Node Label Font Size cell, then right-click it to show the popup menu. Select Mapping Value Generators → Number Series. Type 3 for the first value and click OK. Enter 3 for increment.
Apply Layout → yFiles Layouts → Organic. The final view is shown below:
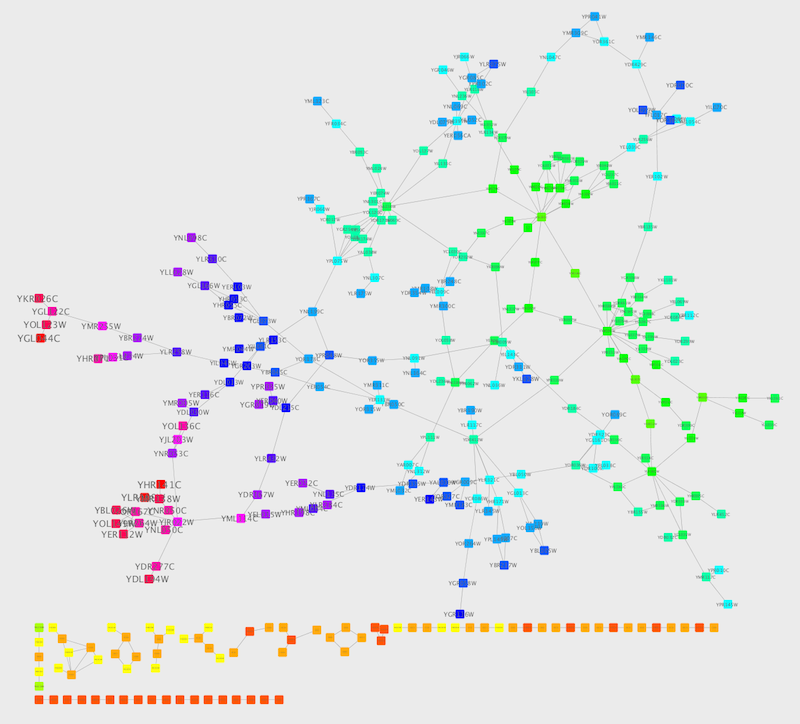
This mapping generator utility is useful for categorical data. The following example is created by adding node color discrete mapping from species column to color.
Tutorial 5: Using Custom Graphics in Visual Styles
This tutorial is a quick introduction to Custom Graphics feature. You can assign up to nine images per node as a part of Visual Style.
Prepare images. These can be any type of bitmap graphics. In this tutorial, we are going to use the Crystal Project's PNG icons. You can download it from here.
Start Cytoscape and select View → Open Custom Graphics Manager. Cytoscape 3 has some preset images and in this example, we use these presets. You can close the Custom Graphics Manager window for now.
Load a network and run the Network Analyzer (Tools → Network Analyzer → Network Analysis → Analyze Network). This creates several new table columns (statistics for nodes and edges).
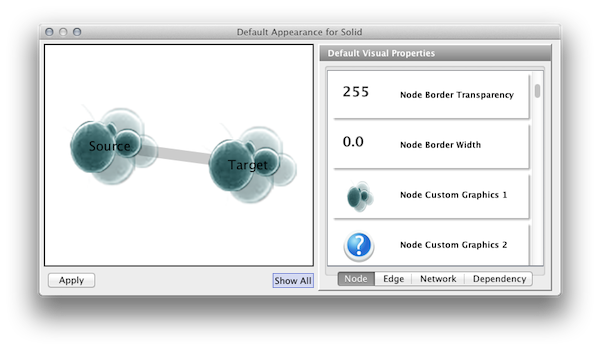
Click the VizMapper tab in the Control Panel, and select the Solid style.
Click the Defaults section to open the Default Appearance Editor.
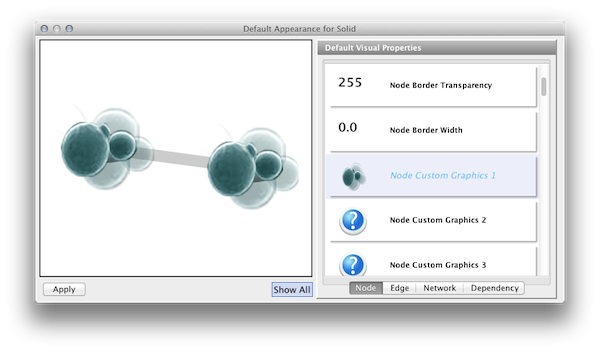
Click Node Custom Graphics 1 and select any of the custom graphics from the list. Click Node Transparency and set the value to zero.
Press Apply. Now your network looks like the following:
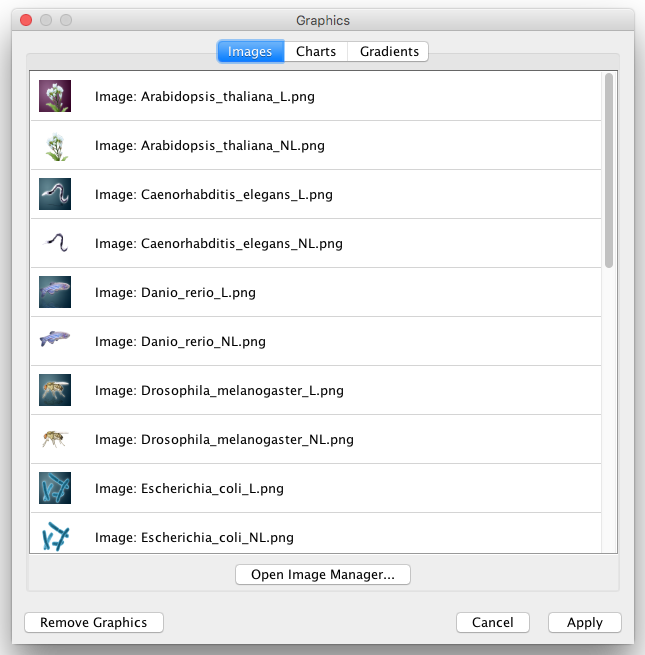
Open the Custom Graphics Manager again. Drag and Drop this
 icon to the image list. It automatically adds it to the manager.
icon to the image list. It automatically adds it to the manager. 
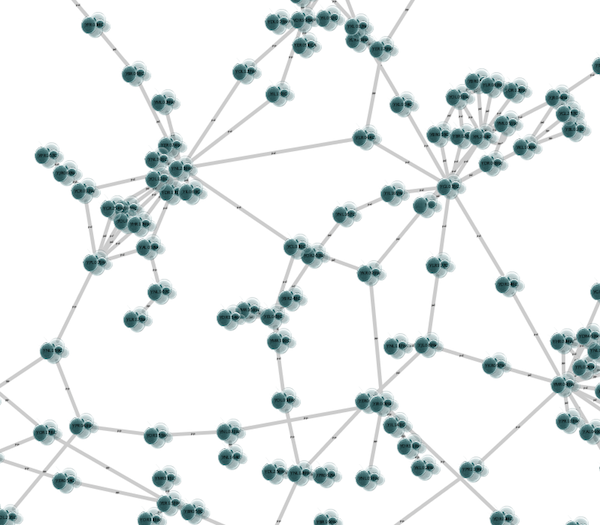
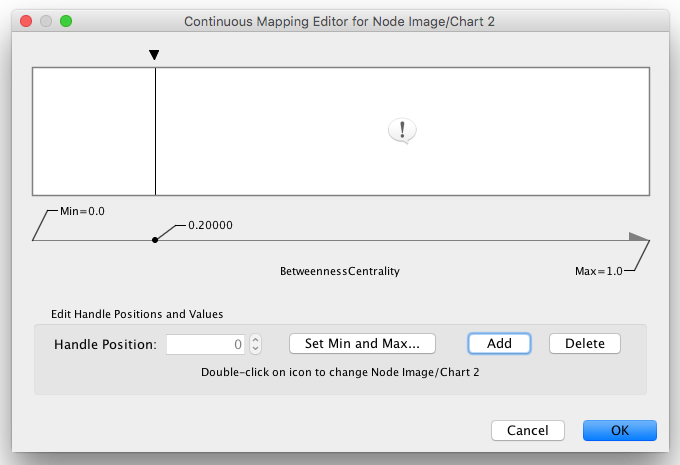
1. Create a Continuous Mapping for Node Custom Graphics 2. Select "BetweennessCentrality" as controlling column and move the handle to 0.2. Double click the region over 0.2 and set the new icon you have just added in the last step.
1. Press Apply and now open the Default Appearance Editor again. Click Node Custom Graphics Position 2 and move the position of the graphics to upper left.
1. Press Apply. Now the important nodes in the network (nodes with high betweenness centrality) is annotated with the icon.
Advanced Topics
Editing Discrete Mappings
Several utility functions are available for Discrete Mappings. You can use those functions by right clicking anywhere on the Visual Mapping Browser (shown below.)
Automatic Value Generators
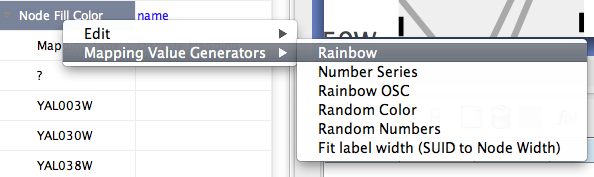
Mapping Value Generators - Functions in this menu category are value generators for discrete mappings. Users can set values for discrete mappings automatically by these functions.
Rainbow and Rainbow OSC - These functions try to assign as diverse a set of colors as possible for each data value.
Random Numbers and Random Colors - Randomize numbers and colors. If you use this function for numerical values (node size, opacity, etc.) you need to specify a range. For example, if you want to set values from 1 to 100, you need to type 1-100 in the dialog.
Number Series - Set a series of numbers to the specified mapping.
Fit label width - This function is only for node width and height. When the node size is unlocked AND Node Width/Height discrete mappings are available, you can fit the size of each node to its label automatically by selecting this function. See the example below:
Edit Selected Values at Once
You can set multiple values at once. First, you need to select rows in which you want to change values then select Edit all selected rows... under Edit right-click menu. A dialog pops up and you can enter the new value for the selected rows.
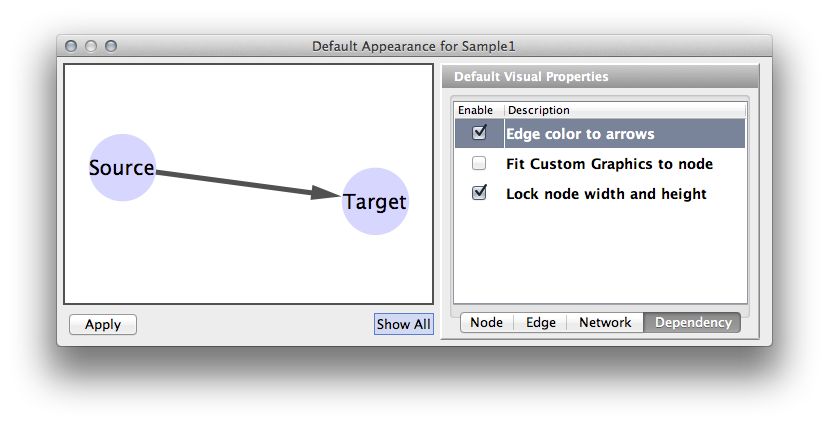
Visual Property Dependencies
The fourth tab in the Default Editor is the list of available Visual Property Dependencies. A Visual Property Dependency can be established between different visual properties. Currently there are three dependencies: Lock Node with and height, Edge color to arrows, and Fit Custom Graphics to node.
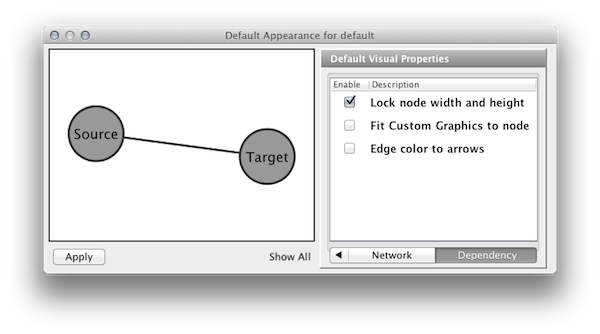
Lock Node with and height - If this menu item is checked, Node Width and Node Height mappings are ignored and Node Size overrides them. If you want to use Fit node size to label function, you need to unlock this.
Edge color to arrows - If this menu item is checked then Edge Source Arrow Color and Edge Target Arrow Color are overridden and Edge Color is used in both cases.
Fit Custom Graphics to node - If a Custom Graphics is assigned to a node and this option is enabled, Custom Graphics will be resized to fit in the node.
Working with Continuous Mapping Editors
There are three kinds of Continuous Mapping Editors. Each of them are associated with a specific visual attributes:
Editor Type |
Supported Data Type |
Visual Attributes |
Color Gradient Editor |
Color |
node/edge/border/label colors |
Continuous-Continuous Editor |
Numbers |
size/width/opacity |
Continuous-Discrete Editor |
All others |
font/shape/text |
Range Setting Panel
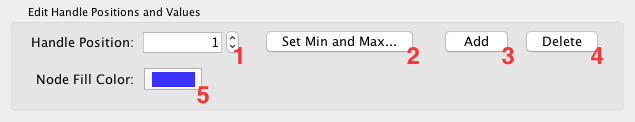
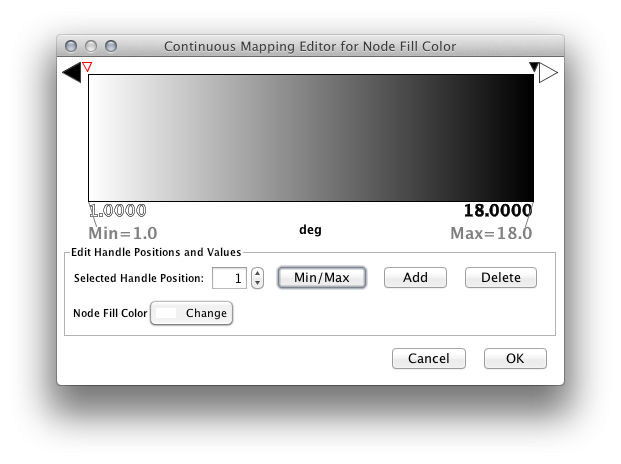
Each editor has a common section named Range Setting.
Handle Value Box - This box displays the current value for the selected slider handle. Also you can directly type the value in this box to move the slider to an exact location.
Min/Max Button - Set the overall range of this editor. First time you open the editor, the Min and Max values are set by the range of attribute you selected, i.e., minimum and maximum value of the attribute will be set to the range of this editor. You can change this range anytime you want by pressing this button.
Add Handle Button - Add a new handle to the editor.
Delete Handle Button - Delete the selected handle from the slider widget.
Handle Value Editor Button - Edit value assigned to the selected handle.
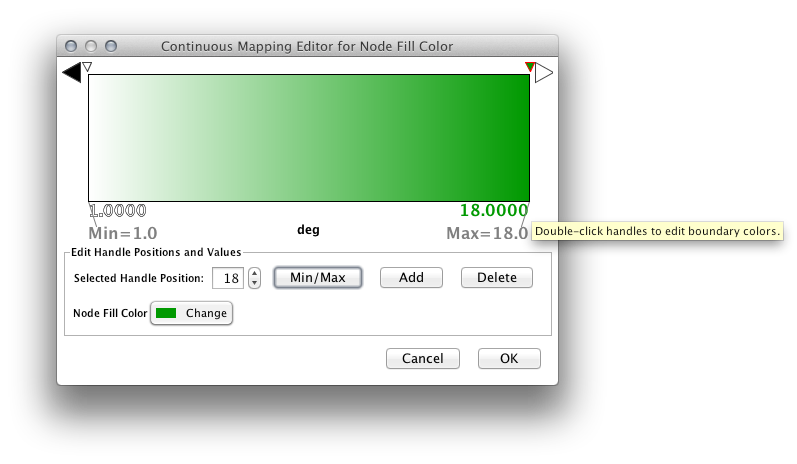
Gradient Editor
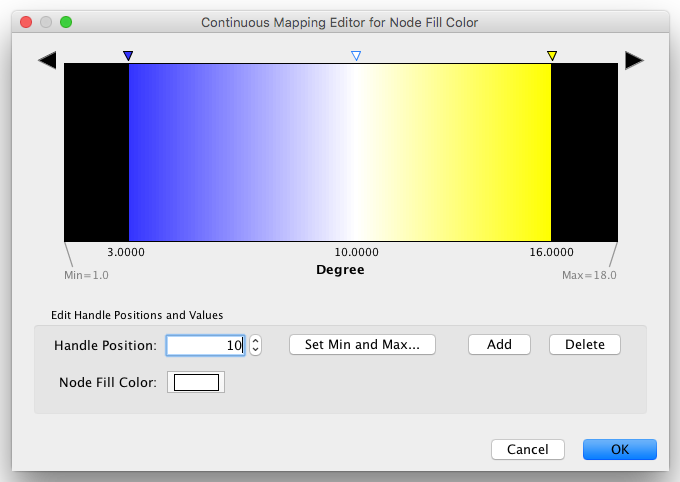
The Gradient Editor is an editor for creating continuous mappings for colors. To change the color of each region, just double click the handles (small triangles on the top). A Color gradient will be created only when the editor has two or more handles (see the example below).
1 handle (no gradient) |
2 handles |
|
|
Continuous-Continuous Editor
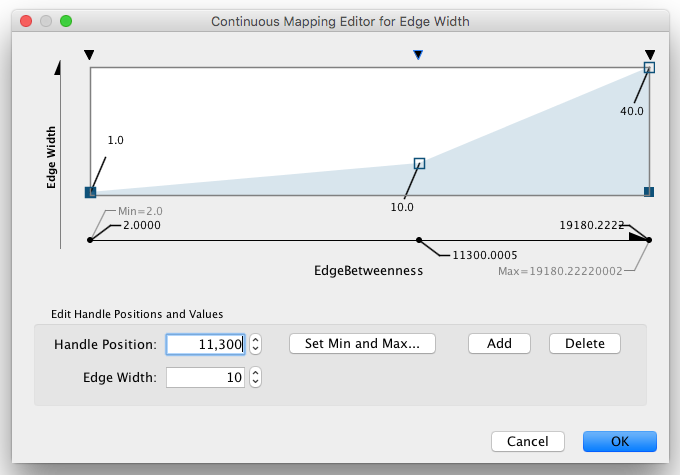
The Continuous-Continuous Editor is for creating mappings between numerical attributes and numerical visual properties (size/opacity). To change the value assigned on Y-axis (the visual property shown in the example above is node size), drag the red squares or double click on the squares to directly type an exact value.
Continuous-Discrete Editor
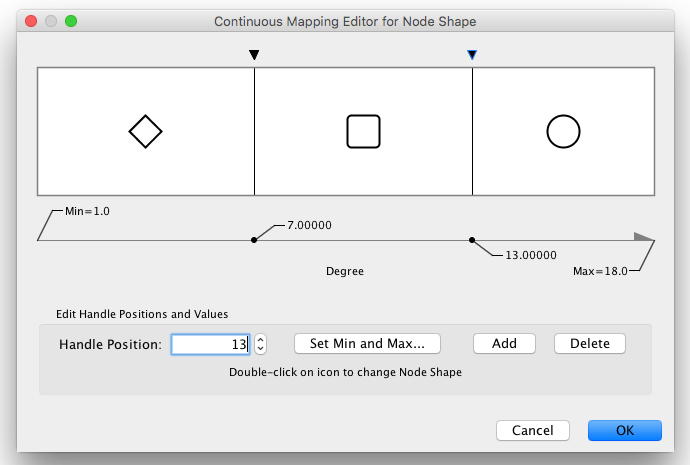
The Continuous-Discrete Editor is used to create mappings from numerical attribute values to discrete visual properties, such as font, shape, or line style. To edit a value for a specific region, double click on the icon on the track.
Managing Visual Styles
All Cytoscape Visual Style settings are initially loaded from a default file that cannot be altered by users. When users make changes to the visual properties, a session_vizmap.xml file is saved in the session file. This means that if you save your session, you will not lose your visual properties. No other vizmap files are saved during normal operation.
Saving Visual Styles
Visual styles are automatically saved with the session they were created in. Before Cytoscape exits, you will be prompted to make sure you save the session before quitting. It is also possible to save your visual styles in a file separate from the session file. To do this, navigate to the File → Export → Vizmap... menu option and save the properties as an XML file. This feature can be used to share visual styles with other users.
Importing Visual Styles
To import existing visual styles, navigate to the File → Import → Vizmap File... menu option and select a vizmap.props (Cytoscape 2 format) or vizmap.xml (Cytoscape 3 format) file. Imported properties will supplement existing properties or override existing properties if the properties have the same name. You can also specify a visual properties file using the -V command line option (cytoscape.sh -V myVizmap.props). Visual properties loaded from the command line will override any default properties.
Bypassing Visual Styles
Cytoscape has a feature that allows users to override visualizations created by the VizMapper for individual nodes and edges. This feature is available by right-clicking on a node or edge and then clicking on Edit → Bypass Visual Style.
Each visual property of the node or edge is displayed. When a property is overridden, a lock icon ![]() appears next to the property and Clear / Edit Bypass menu options appear. By clicking the Clear option, the bypass will be removed and the attribute will be displayed as defined by the VizMapper. At the bottom of the menu a Reset All option appears. When clicked, this will remove all bypasses for the specified node or edge. In the example above, you can see the selected node size, color, and shape have been overridden. This is apparent in the appearance of the node itself and by the check marks in the popup menu.
appears next to the property and Clear / Edit Bypass menu options appear. By clicking the Clear option, the bypass will be removed and the attribute will be displayed as defined by the VizMapper. At the bottom of the menu a Reset All option appears. When clicked, this will remove all bypasses for the specified node or edge. In the example above, you can see the selected node size, color, and shape have been overridden. This is apparent in the appearance of the node itself and by the check marks in the popup menu.
It is important to realize that the Visual Mapping Bypass only works for individual nodes and edges and not for all nodes or edges of a specific type. Using the bypass function is not particularly resource intensive, you can use it as much as you like. However, if you find yourself repeating the same bypasses, then you should consider using the VizMapper instead.
The bypass values will persist between sessions only as long as you save your session. If you don't save your session, you will lose whatever bypass values you set.
Visual Property Dependencies
In some cases, you want to use the same value for multiple Visual Properties. For example, if you want to use the same value for Node Width and Node Height, you have to use the Visual Property Dependency feature in VizMapper. Currently, Cytoscape supports the following Visual Property Dependencies:
Edge color to arrows - Assign same color for edge and arrows.
Fit Custom Graphics to node - Adjust the size of Custom Graphics based on Node Size.
Lock node width and height - Assign the same value to node width and height.
Example: Unlocked
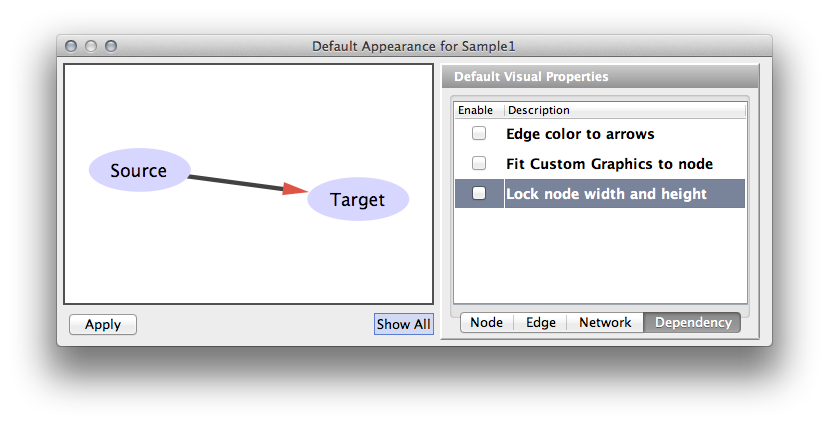
Example: Locked