|
← Revision 4 as of 2012-05-22 23:18:57
Size: 7932
Comment:
|
← Revision 5 as of 2013-01-09 19:58:05 →
Size: 7731
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 5: | Line 5: |
| As of Cytoscape 2.8, attribute values may be formulas. A typical example is '''=ABS($otherAttrib + LOG(10.2))'''. Formulas are modelled after Excel™ but only support references to other attributes at the same node, edge or network. Since Cytoscape attribute names may contain embedded spaces, optional braces around the attribute name (required if the name is not simply a letter followed by one or more letters or digits) is allowed e.g. '''${a name with spaces}'''. Backslashes, opening braces and dollar signs in attribute names have to be escaped with a leading backslash. For example the attribute name '''ex$am{p\le''' would have to be written as '''${ex\$am\{p\\le}'''. '''ID''' is being treated as a pseudo-attribute. String constants are written with double-quotes '''"'''. In order to embed a double-quote or a backslash in a string they have to be escaped with a leading backslash, therefore the string '''"\''' must be written as '''"\"\\"'''. Formula results must be compatible with the type of the attribute that they have been assigned to. The rules are rather lax though, for example anything can be interpreted as a string and all numeric values will be accepted for a boolean (or logical) attribute where non-zero will be interpreted as '''true''' and zero as '''false'''. For integer attributes floating point values will be converted using the rules of the Excel™ '''INT''' function. Parentheses can be used for grouping and to change evaluation order. The operator precedence rules follow those of standard arithmetic. |
Attribute values may be formulas. A typical example is '''=ABS($otherAttrib + LOG(10.2))'''. Formulas are modelled after Excel™ but only support references to other attributes at the same node, edge or network. Since Cytoscape attribute names may contain embedded spaces, optional braces around the attribute name (required if the name is not simply a letter followed by one or more letters or digits) is allowed e.g. '''${a name with spaces}'''. Backslashes, opening braces and dollar signs in attribute names have to be escaped with a leading backslash. For example the attribute name '''ex$am{p\le''' would have to be written as '''${ex\$am\{p\\le}'''. Finally, attribute names are case sensitive. String constants are written with double-quotes '''"'''. In order to embed a double-quote or a backslash in a string they have to be escaped with a leading backslash, therefore the string '''"\''' must be written as '''"\"\\"'''. Formula results must be compatible with the type of the attribute that they have been assigned to. The rules are rather lax though, for example anything can be interpreted as a string and all numeric values will be accepted for a boolean (or logical) attribute where non-zero will be interpreted as '''true''' and zero as '''false'''. For integer attributes floating point values will be converted using the rules of the Excel™ '''INT''' function. Parentheses can be used for grouping and to change evaluation order. The operator precedence rules follow those of standard arithmetic. |
| Line 15: | Line 17: |
| {{{#!wiki comment | |
| Line 22: | Line 25: |
| }}} | |
| Line 44: | Line 48: |
| * Sinh -- Returns the hyperbolic sign of its argument. | |
| Line 46: | Line 49: |
| * Sinh -- Returns the hyperbolic sine of its argument. | |
| Line 48: | Line 52: |
| * Tanh -- returns the hyperbolic tangent of its argument in radians. | |
| Line 71: | Line 76: |
| * BList -- creates a list of boolean (a.k.a. logical or truth) values | |
| Line 73: | Line 77: |
| * FList -- creates a list of floating point (a.k.a. decimal) numbers | |
| Line 75: | Line 78: |
| * IList -- creates a list of integers (a.k.a. whole numbers) | |
| Line 77: | Line 79: |
| * SList -- creates a list of strings (a.k.a. text objects) | |
| Line 102: | Line 103: |
| The possibly biggest problem is the referencing of other attributes that have null values. This is not allowed and leads to errors. In order to mitigate this problem we support the following optional syntax for attribute references: '''${attribName:defaultValue}'''. The interpretation is that if '''attribName''' is null, then the default value will be used, otherwise the value of the referenced value will be used instead. N.B., the referenced attribute must still be a defined attribute and not an arbitrary name! The other potential problem is when there are circular attribute reference dependencies. Circular dependencies will be detected at formula evaluation time and lead to a runtime error. | The possibly biggest problem is the referencing of other attributes that have null values. This is not allowed and leads to errors. In order to mitigate this problem we support the following optional syntax for attribute references: '''${attribName:defaultValue}'''. The interpretation is that if '''attribName''' is null, then the default value will be used, otherwise the value of the referenced value will be used instead. The referenced attribute must still be a defined attribute and not an arbitrary name! The other potential problem is when there are circular attribute reference dependencies. Circular dependencies will be detected at formula evaluation time and lead to a runtime error. |
| Line 106: | Line 107: |
| When working with formulas it can be very helpful to open the Cytoscape Error Console. Formula evaluation errors will be logged there. | When working with formulas it can be very helpful to open the Developer's Log Console. Formula evaluation errors will be logged there. |
Attribute Formulas
Introduction
Attribute values may be formulas. A typical example is =ABS($otherAttrib + LOG(10.2)). Formulas are modelled after Excel™ but only support references to other attributes at the same node, edge or network. Since Cytoscape attribute names may contain embedded spaces, optional braces around the attribute name (required if the name is not simply a letter followed by one or more letters or digits) is allowed e.g. ${a name with spaces}. Backslashes, opening braces and dollar signs in attribute names have to be escaped with a leading backslash. For example the attribute name ex$am{p\le would have to be written as ${ex\$am\{p\\le}. Finally, attribute names are case sensitive.
String constants are written with double-quotes ". In order to embed a double-quote or a backslash in a string they have to be escaped with a leading backslash, therefore the string "\ must be written as "\"\\". Formula results must be compatible with the type of the attribute that they have been assigned to. The rules are rather lax though, for example anything can be interpreted as a string and all numeric values will be accepted for a boolean (or logical) attribute where non-zero will be interpreted as true and zero as false. For integer attributes floating point values will be converted using the rules of the Excel™ INT function. Parentheses can be used for grouping and to change evaluation order. The operator precedence rules follow those of standard arithmetic.
Operators
Currently supported operators are the four basic arithmetic operators and the ^ exponentiation operator. +, -, *, and \ are left-associative and ^ is right-associative. The string concatenation operator is &. Supported boolean or logical operators are the comparison operators <, >, <=, >=, =, and <> (not equal).
Supported Functions
Currently we support the following functions:
Numeric Functions
- Abs -- Returns the absolute value of a number.
- ACos -- Returns the arccosine of a number.
- ASin -- Returns the arcsine of a number.
- ATan2 -- Returns the arctangent of two numbers x and y.
- Average -- Returns the average of a group of numbers.
- Cos -- Returns the cosine of an angle given in radians.
- Cosh -- Returns the hyperbolic sine of its argument.
- Count -- Returns the number of numeric values in a list.
- Degrees -- Returns its argument converted from radians to degrees.
- Exp -- Returns e raised to a specified number.
- Ln -- Returns the natural logarithm of a number.
- Log -- Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base.
- Max -- Returns the maximum of a group of numbers.
- Median -- Returns the median of a list of numbers.
- Min -- Returns the minimum of a group of numbers.
- Mod -- Calculates the modulus of a number.
- Pi -- Returns an approximation of the value of π.
- Radians -- Returns its argument converted from degrees to radians.
- Round -- Rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places.
- Sin -- Returns the sine of an angle given in radians.
- Sinh -- Returns the hyperbolic sine of its argument.
- Sqrt -- Calculates the square root of a number.
- Tan -- returns the tangent of its argument in radians.
- Tanh -- returns the hyperbolic tangent of its argument in radians.
- Trunc -- Truncates a number.
String Functions
- Concatenate -- Concatenates two or more pieces of text.
- Left -- Returns a prefix of s string.
- Len -- Returns the length of a string.
- Lower -- Converts a string to lowercase.
- Mid -- Selects a substring of some text.
- Right -- Returns a suffix of a string.
- Substitute -- Replaces some text with other text.
Text -- Format a number using the Java DecimalFormat class' conventions.
- Upper -- Converts a string to uppercase.
- Value -- Converts a string to a number.
Logical/Boolean Functions
- And -- Returns the logical conjunction of any number of boolean values.
- Not -- Returns the logical negation of a boolean value.
- Or -- Returns the logical disjunction of any number of boolean values.
List Functions
- First -- Returns the first entry in a list.
- Last -- Returns the last entry in a list.
- Nth -- Returns the n-th entry in a list.
Statistical Functions
- Largest -- the kth largest value in a list.
GeoMean -- the geometric mean of a set of numbers.
HarMean -- the harmonic mean of a set of numbers.
- Mode -- the mode of a set of numbers.
NormDist -- Returns the pdf or CDF of the normal distribution.
- Permut -- Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects.
StDev - sample standard deviation.
- Var -- sample variance.
Miscellaneous Functions
- Combin - Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects.
- If -- Returns one of two alternatives based on a boolean value.
ListToString -- Returns a string representation of a list.
- Now -- Returns a string representation of the current date and time.
- Today -- returns a string representation of the current date.
Pitfalls
The possibly biggest problem is the referencing of other attributes that have null values. This is not allowed and leads to errors. In order to mitigate this problem we support the following optional syntax for attribute references: ${attribName:defaultValue}. The interpretation is that if attribName is null, then the default value will be used, otherwise the value of the referenced value will be used instead. The referenced attribute must still be a defined attribute and not an arbitrary name! The other potential problem is when there are circular attribute reference dependencies. Circular dependencies will be detected at formula evaluation time and lead to a runtime error.
Useful Tips
When working with formulas it can be very helpful to open the Developer's Log Console. Formula evaluation errors will be logged there.
The Formula Builder
In order to ease the creation of formulas as well as to facilitate discovery of built-in functions we provide a formula builder in our attribute browser. After selecting a non-list attribute cell, you can invoke it by clicking on  . This should bring up the Formula Builder which looks like this:
. This should bring up the Formula Builder which looks like this:
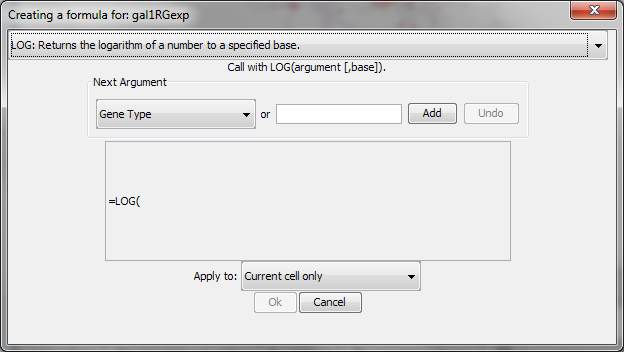
The Formula Builder is a useful tool for discovery of the list of built-in functions, which has the return type matching the data type of the column. Arguments can either be selected from a list of named attributes or constant values can be entered in a text entry field. A major shortcoming at this time is that the Formula Builder won't let you compose functions with function calls as arguments. If you need the most general functionality, please type the expression directly into a cell.
A Note for App Writers
It is relatively easy to add your own built-in formula functions. A simple function can probably be implemented in 15 to 20 minutes. It can then be registered via the parser and becomes immediately available to the user. It will of course also show up in the drop-down list in the formula builder.