Interaction networks are useful as stand-alone models. However, they are most powerful for answering scientific questions when integrated with additional information. Cytoscape allows the user to add arbitrary node, edge and network information to Cytoscape as node/edge/network attributes. This could include, for example, annotation data on a gene or confidence values in a protein-protein interaction. These attributes can then be visualized in a user-defined way by setting up a mapping from data attributes to visual attributes (colors, shapes, and so on). The section on visual styles discusses this in greater detail.
Cytoscape Attribute File Format
Node and edge attribute files are simply formatted: a node attribute file begins with the name of the attribute on the first line (note that it cannot contain spaces). Each following line contains the name of the node, followed by an equals sign and the value of that attribute. Numbers and text strings are the most common attribute types. All values for a given attribute must have the same type. For example:
FunctionalCategory YAL001C = metabolism YAR002W = apoptosis YBL007C = ribosome
An edge attribute file has much the same structure, except that the name of the edge is the source node name, followed by the interaction type in parentheses, followed by the target node name. Directionality counts, so switching the source and target will refer to a different (or perhaps non-existent) edge. The following is an example edge attributes file:
InteractionStrength YAL001C (pp) YBR043W = 0.82 YMR022W (pd) YDL112C = 0.441 YDL112C (pd) YMR022W = 0.9013
Since Cytoscape treats edge attributes as directional, the second and third edge attribute values refer to two different edges (source and target are reversed, though the nodes involved are the same).
Each attribute is stored in a separate file. Node and edge attribute files use the same format. Node and edge attribute file names often use the suffix ".txt".
Node and edge attributes may be loaded at the command line using the –T options or via the File → Import menu.
When expression data is loaded using an expression matrix, it is automatically loaded as node attribute data unless explicitly specified otherwise.
Node and edge attributes are attached to nodes and edges, and so are independent of networks. Attributes for a given node or edge will be applied to all copies of that node or edge in all loaded network files, regardless of whether the attribute file or network file is imported first.
Detailed file format (Advanced users)
??
Import Attribute Table Files
As of Cytoscape 2.4, importing delimited text and MS Excel attribute data tables is supported. Using this functionality, users can now easily import data that isn't formatted into Cytoscape node or edge attribute file formats (as described above).
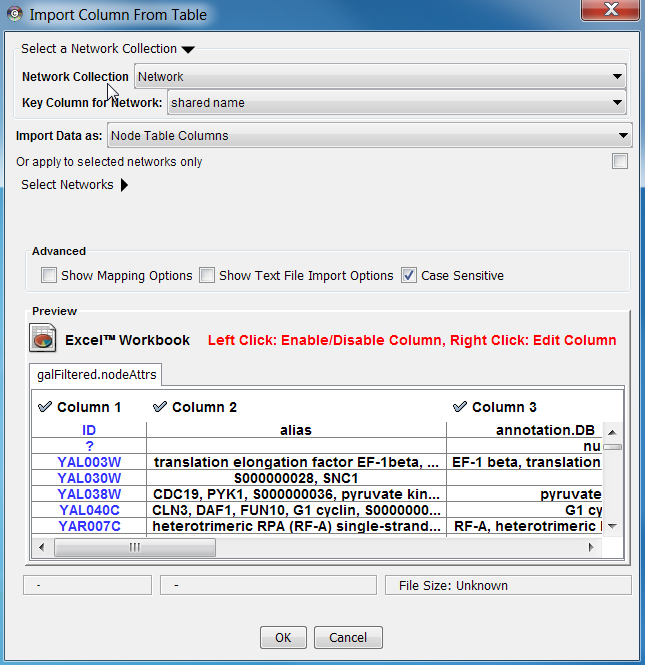
Sample Attribute Table 1
Object Key |
Alias |
SGD ID |
AAC3 |
YBR085W|ANC3 |
S000000289 |
AAT2 |
YLR027C|ASP5 |
S000004017 |
BIK1 |
YCL029C|ARM5|PAC14 |
S000000534 |
The attribute table file should contain a primary key column and at least one attribute column. The maximum number of attribute columns is unlimited. The Alias column is an optional feature, as is using the first row of data as attribute names. Alternatively, you can specify each attribute name from the File → Import → Attribute from Table (text/MS Excel)... user interface.